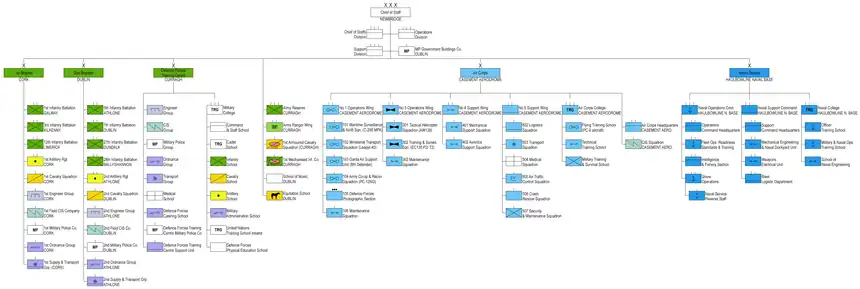
Structure of the Irish Defence Forces
This article represents the structure of the Irish Defence Forces as of May 2020:
Chief of staff
Chief of staff is a three-star general rank, and the holder of this post has authority and responsibility in respect to all staff duties relating to the management of the Irish Defence Forces.
- Chief of staff, in Newbridge[1]
- Chief of Staff's Division, headed by the assistant chief of staff, based in Newbridge
- Office of the Chief of Staff
- Office of the Assistant Chief of Staff
- Strategic Planning Branch
- Public Relations Branch
- The Military Judge
- Operations Division, headed by the deputy chief of staff operations, based in Newbridge and Dublin
- Office of the Deputy Chief of Staff Operations
- J2 Intelligence Branch
- J3 & J5 Planning & Operations Branch
- Combat Support Branch
- J6 CIS Branch
- Defence Forces Headquarters CIS Company
- J7 Training Branch
- Support Division, headed by the Deputy Chief of Staff Support, based in Newbridge and Dublin
- Office of the Deputy Chief of Staff Support
- J1 Human Resources Management Branch
- J4 Logistics
- CAOGA
- Conciliation & Arbitration (Mil)
- Transport Branch
- Legal Services Branch
- Engineers Branch
- Ordnance Branch
- Medical Branch
- Military Police Branch
- Military Chaplaincy Service
- Military Police Government Buildings Company, in Dublin
- Chief of Staff's Division, headed by the assistant chief of staff, based in Newbridge
Army
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
The Army is the land warfare branch of the Irish Defence Forces and consists of two brigades, a training centre, providing training to all the defense forces, and other units, including musical units.
 Army Headquarters, in Dublin
Army Headquarters, in Dublin
- Army Ranger Wing, in Curragh
- 1st Mechanised Infantry Company, in Curragh
- 1st Armoured Cavalry Squadron, in Curragh
- Defence Forces School of Music, in Dublin[2]
- Army No 1 Band, in Dublin
- Band of the 1st Brigade, in Cork
- Band of the 2nd Brigade, in Dublin
- Equitation School, in Dublin[3]
1st Brigade
_(2).jpg.webp)
The 1st Brigade is headquartered at Collins Barracks in Cork. The brigade is responsible for the counties of Carlow, Clare, Cork, Galway, Kerry, Kilkenny, Laois, Limerick, Offaly, Tipperary, Waterford, and Wexford.[4]
 1st Brigade, in Cork
1st Brigade, in Cork
- 1st Infantry Battalion, in Galway
- 3rd Infantry Battalion, in Kilkenny
- 12th Infantry Battalion, in Limerick
- 1st Artillery Regiment, in Cork, with L118/119 105mm light guns and 120mm mortars[5]
- 1st Cavalry Squadron, in Cork
- 1st Engineer Group, in Cork
- 1st Supply and Transport Group, in Cork
- 1st Ordnance Group, in Cork
- 1st Field CIS Company, in Cork
- 1st Military Police Company, in Cork
2nd Brigade
.jpg.webp)
The 2nd Brigade is headquartered at the Cathal Brugha Barracks in Dublin. The brigade is responsible for the counties of Cavan, Donegal, Dublin, Kildare, Leitrim, Longford, Louth, Mayo, Meath, Monaghan, Roscommon, Sligo, Westmeath, and Wicklow.[6]
.svg.png.webp) 2nd Brigade, in Dublin
2nd Brigade, in Dublin
- 6th Infantry Battalion, in Athlone
- 7th Infantry Battalion, in Dublin
- 27th Infantry Battalion, in Dundalk
- 28th Infantry Battalion, in Ballyshannon
- 2nd Artillery Regiment, in Athlone, with L118/119 105mm light guns and 120mm mortars[5]
- 2nd Cavalry Squadron, in Dublin
- 2nd Engineer Group, in Athlone
- 2nd Supply and Transport Group, in Athlone
- 2nd Ordnance Group, in Athlone
- 2nd Field CIS Company, in Dublin
- 2nd Military Police Company, in Dublin
Defence Forces Training Centre
.jpg.webp)
The Defence Forces Training Centre (DFTC) based at the Curragh Camp is provides professional training to the Irish Army:
 Defence Forces Training Centre, in Curragh
Defence Forces Training Centre, in Curragh
- Military College[7]
- Command and Staff School
- Cadet School
- Infantry School[8]
- Officer Training Wing
- Non Commissioned Officer Training Wing
- Infantry Weapons Wing
- Artillery School
- Cavalry School
- United Nations Training School Ireland
- Military Administration School
- Defence Forces Physical Education School
- CIS Group
- Communications and Information Services School[9]
- Engineer Group
- Military Engineering School[9]
- Ordnance Group
- Ordnance School[9]
- Military Police Group
- Military Police School[9]
- Transport Group
- Transport and Vehicle Maintenance School[9]
- Medical School[9]
- Defence Forces Catering School[9]
- Central Medical Unit Detachment
- Defence Forces Training Centre Military Police Company
- Defence Forces Training Centre Support Unit
- Military College[7]
Army Reserve
The Army Reserve is a part-time, voluntary organisation established on 1 October 2005, whose members round out regular army units. The Army Reserve is present at the following locations:[10]
- 1st Brigade, in Cork[11]
- C Company, 1st Infantry Battalion, in Clifden
- D Company, 1st Infantry Battalion, in Galway[12]
- E Company, 1st Infantry Battalion, in Ennis
- C Company, 3rd Infantry Battalion, in Kilkenny[12]
- D Company, 12th Infantry Battalion, in Mallow
- E Company, 12th Infantry Battalion, in Tralee
- F Company, 12th Infantry Battalion, in Skibbereen
- C Company, 12th Infantry Battalion, in Limerick[12]
- D Company, 3rd Infantry Battalion, in Templemore
- E Company, 3rd Infantry Battalion, in Wexford
- F Company, 3rd Infantry Battalion, in Waterford
- 4th and 5th Artillery Battery, 1st Artillery Regiment, 2x Cavalry Squadron Troops, 1x CIS Radio Platoon, 2x Transport Platoons, 1x Military Police Platoon, in Cork[12]
- 2nd Brigade, in Dublin[11]
- C Company, 6th Infantry Battalion, in Mullingar
- D Company, 6th Infantry Battalion, in Castlebar
- E Company, 6th Infantry Battalion, in Boyle
- D Company, 7th Infantry Battalion, 2x Cavalry Squadron Troops, 1x CIS Radio Platoon, 2x Transport Platoons, 1x Military Police Platoon, in Dublin[12]
- E Company, 7th Infantry Battalion, in Bray
- C Company, 27th Infantry Battalion, in Cavan
- D Company, 27th Infantry Battalion, in Dundalk
- E Company, 27th Infantry Battalion, in Navan
- C Company, 28th Infantry Battalion, in Letterkenny
- D Company, 28th Infantry Battalion, in Sligo
- E Company, 28th Infantry Battalion, in Donegal
- 4th and 5th Artillery Battery, 2nd Artillery Regiment, 1x Field Engineer Platoon, in Athlone[12]
- Defence Forces Training Centre, in Curragh[11]
- various units, in Curragh
Infantry battalion organization
.jpg.webp)
The infantry battalions of the Irish Army are organized as follows:
- Infantry Battalion[13]
- Headquarters Company
- Administrative Platoon
- Communications Platoon
- Transport Platoon
- Logistic Platoon
- 3x to 6x Infantry companies
- 3x Infantry platoons
- Weapons Platoon, with M1 60mm mortars, FN MAG machine guns, and 84mm recoilless rifles[14]
- Support Company[15]
- Reconnaissance Platoon, includes a Sniper section
- Heavy Machine Gun Platoon, with M2 Browning heavy machine guns
- Anti-armour Platoon, with Javelin anti-tank missiles
- Mortar Platoon, with LLR 81mm mortars
- Headquarters Company
Air Corps
The Air Corps is the air branch of the Irish Defence Forces. Headed by a brigadier general it comprises a staff headquarters, two operational wings, two support wings, one independent squadron and the Air Corps College.
 Air Corps Headquarters, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel[16]
Air Corps Headquarters, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel[16]
- Office of General Officer Commanding
- Operations Section
- Support Section
- Military Airworthiness Authority
- Flight Safety Section
- Military Police Section
- CIS Squadron[17] (former 501 CIS Squadron, No 5 Support Wing)
- Squadron Headquarters
- Airfield Services Flight
- Communications Flight
- Technical Services Flight
- Information Technology Flight
No 1 Operations Wing

No 1 Operations Wing operates the fixed-wing assets of the Air Corps.[18] The wing is divided into four flying and two non-flying squadrons:
- No 1 Operations Wing, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel
- 101 Maritime Surveillance and Airlift Squadron, with 2x CN-235 MPA maritime patrol aircraft (to be replaced by 2x C-295 MPA[19])
- 102 Ministerial Transport Squadron, with 1x Learjet 45 plane
- 103 Garda Air Support Unit, with 1x Defender plane
- 104 Army Co-op and Reconnaissance Squadron, with 4x PC-12NG planes
- 105 Defence Forces Photographic Section
- 106 Maintenance Squadron
No 3 Operations Wing
.jpg.webp)
No 3 Operations Wing is operates all Air Corps helicopters,[20] and is divided into three squadrons. It provides pilots for the Emergency Aeromedical Service, the air ambulance service which is jointly operated by the Air Corps and the HSE National Ambulance Service.
- No 3 Operations Wing, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel
- 301 Tactical Helicopter Squadron, with 6x AW139 helicopters
- 302 Training and Surveillance Squadron, with 2x EC135 P2 helicopters, and 2x EC135 T2 helicopters for the Garda Air Support Unit (Detachment at Finner Camp)
- 303 Maintenance Squadron
No 4 Support Wing
No 4 Support Wing carries out second line maintenance and manages the procurement of spares and aviation fuel.[21] This formation has two squadrons.
- No 4 Support Wing, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel
- 401 Mechanical Support Squadron
- 402 Avionics Support Squadron
No 5 Support Wing
No 5 Support Wing is responsible for the logistic support for the Air Corps and the management and security of Casement Aerodrome.[22]
- No 5 Support Wing, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel
- 502 Logistics Squadron
- 503 Transport Squadron
- 504 Medical Squadron
- 505 Air Traffic Control Squadron
- 506 Crash Rescue Squadron
- 507 Security and Maintenance Squadron
Air Corps College

The Air Corps College is the principal training unit of the Irish Air Corps, where all entrants into the service undertake their training. The College is divided into three distinct schools:[23]
- Air Corps College, at Casement Aerodrome in Baldonnel
- Flying Training School, pilot and officer training, with PC-9 trainer aircraft
- Technical Training School, aircraft technicians training
- Military Training and Survival School, basic military, Non-commissioned Officer, and SERE training
Naval Service
The Naval Service is the sea branch of the Irish Defence Forces. Headed by a brigadier general it comprises a staff headquarters, two commands, and the Naval College.
 Naval Headquarters, at Haulbowline Naval Base
Naval Headquarters, at Haulbowline Naval Base
Naval Operations Command

.jpg.webp)
Naval Operations Command is the command component of the Irish Naval Service responsible for all day-to-day activities of the service, both at sea and on shore.
- Naval Operations Command, at Haulbowline Naval Base
- Operations Command Headquarters
- Fleet Operational Readiness Standards and Training
- LÉ Eithne (P31), LÉ Orla (P41) (in operational reserve), LÉ Ciara (P42), LÉ Róisín (P51), LÉ Niamh (P52), LÉ Samuel Beckett (P61), LÉ James Joyce (P62), LÉ William Butler Yeats (P63), and LÉ George Bernard Shaw (P64)
- Intelligence and Fishery Section
- Naval Intelligence Cell
- Navigation Cell
- Naval Computer Centre
- Fisheries Monitoring Centre[25]
- Vessel Monitoring System
- Fishery Protection System - Lirguard
- Fishery Information System
- Fishery Geographic System
- Fishery Legislative System
- Electronic Recording and Reporting System
- Shore Operations
- Headquarters Section
- Naval Service Operations Room
- Naval Service Reserve Staff
- Naval Base Communications Centre
- Operations Security Section
- Naval Service Diving Section[26]
- Harbour Master Naval Base
- Boat Transport
Naval Support Command

Naval Support Command oversees the personnel, logistical and technical resources of the Naval Service, allowing the service to meets its operational and training commitments. Ship procurement, maintenance, repair, provisions, ordnance, food, fuel, personnel and transportation are handled by Naval Support Command.
- Naval Support Command, at Haulbowline Naval Base
- Support Command Headquarters
- Personnel Management Section
- Maintenance Management/Planning and Inspectorate
- Mechanical Engineering and Naval Dockyard Unit
- Plant and Machinery Section
- Naval Dockyard
- Base Logistic Department
- Naval Technical Stores
- Central Supply Unit
- Accommodation and Messes Section
- Base Engineering Maintenance Section
- Road Transport Section
- Weapons Electrical Unit
- Communications Technical Section
- Electrical/Electronics Section
- Ordnance Section
- Support Command Headquarters
Naval College
The Naval College provides training to cadets, non-commissioned officers, and recruits of the Naval Service. The Naval College trains and educates personnel for service, providing a mixture of different courses ranging from officer training right through to Naval Engineering. The Naval College is based out of the Naval Service's headquarters at Naval Base Haulbowline but also provides classes and lessons in non-military naval training at the nearby National Maritime College of Ireland in Ringaskiddy.
- Naval College, at Haulbowline Naval Base
- Officer Training School
- Military and Naval Operational Training School
- School of Naval Engineering
Naval Service Reserve
The Naval Service Reserve is the reserve force of the Naval Service. Its personnel supplements the crew of vessels of the Naval Service during operations, and conducts stand-alone operations within their respective ports, such as security duties, sighting reports and intelligence gathering.
Defence Forces structure graphic
Geographic distribution of units
D Co. 1st Inf.
C Co. 3rd Inf.
C Co. 12th Inf.
7th Inf. Bn.
D Co. 27th Inf.
References
- "About the General Staff". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Defence Forces School of Music". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "The Equitation School". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "1st Brigade". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "Artillery Corps". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "2nd Brigade". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "The Military College". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "The Infantry School". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Schools of the DFTC". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Army Reserve Locations". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Reserve Defence Forces Contacts". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Defence Forces Permanent Barracks". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Infantry Corps". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Company Level Weapons". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Battalion Level Weapons". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Air Corps Headquarters". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "CIS Squadron". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "No 1 Operations Wing". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "Irish Air Corps to Acquire Two New Maritime Patrol Aircraft". Flying in Ireland. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "No 3 Operations Wing". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "No 4 Support Wing". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "No 5 Support Wing". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "Air Corps College". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- "Fisheries Monitoring Centre". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Naval Service Diving Section". Irish Defence Forces. Retrieved 18 May 2020.