Stannocene
Stannocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Sn(C5H5)2. It is a metallocene that can be produced efficiently from cyclopentadienyl sodium and tin(II) chloride.[3] Unlike in ferrocene the two cyclopentadienyl rings are not parallel.[4]
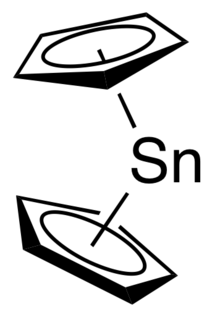 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10Sn | |
| Molar mass | 248.900 g·mol−1 |
| Structure[2] | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Pbcm, No.57 | |
a = 5.835 Å, b = 25.385 Å, c = 12.785 Å | |
Formula units (Z) |
8 formula per cell |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Stannocene
- Atwood, Jerry L.; Hunter, William E; Cowley, Alan H.; Jones, Richard A.; Stewart, Constantine A. "X-Ray Crystal Structures of Bis(cyclopentadienyl)tin and Bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)lead". J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.
- Janiak, Christpher (2010), "Stannocene as cyclopentadienyl transfer agent in transmetallation reactions with lanthanide metals for the synthesis of tris(cyclopentadienyl)lanthanides", Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie, 636 (13–14): 2387–2390, doi:10.1002/zaac.201000239
- Smith, P. J. (2012). Chemistry of Tin. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9789401149389.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.