Disodium hydrogen phosphite
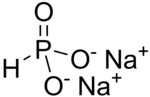
Disodium hydrogen phosphite is the name for inorganic compounds with the formula Na2HPO3•(H2O)x. The commonly encountered salt is the pentahydrate.[1] A derivative of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2), it contains the anion HPO32−. Its common name suggests that it contains an acidic hydrogen atom, as in sodium hydrogen carbonate. However, this name is misleading as the hydrogen atom is not acidic, being bonded to phosphorus rather than oxygen. The salt has reducing properties. It is white or colorless solid, and is little studied.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
sodium phosphonate pentahydrate | |
| Other names
Sodium phosphate dibasic pentahydrate, sodium phosphite | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.848 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HNa2O3P | |
| Molar mass | 125.958 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Brodalla, Dieter; Goeters, Christiane; Kniép, Ruediger; Mootz, Dietrich; Wunderlich, Hartmut (1978). "Zur Kenntnis der Hydrate des Na2PHO3, Phasenbeziehungen und kristallographische Untersuchungen (Hydrates of sodium phosphite, phase relations and crystallographic studies)". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 439: 265–74. doi:10.1002/zaac.19784390132.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.