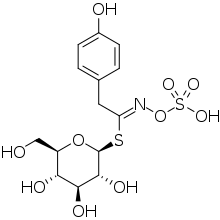
Sinalbin
Sinalbin is a glucosinolate found in the seeds of white mustard, Sinapis alba, and in many wild plant species. In contrast to mustard from black mustard (Brassica nigra) seeds which contain sinigrin, mustard from white mustard seeds has only a weakly pungent taste.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]
2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-N-sulfooxyethanimidothioate | |
| Other names
Glucosinalbin; 4-Hydroxybenzyl glucosinolate; Glucosinalbate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.606 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H19NO10S2 | |
| Molar mass | 425.42 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Sinalbin is metabolised to form the mustard oil 4-hydroxybenzyl isothiocyanate by the enzyme myrosinase. The less sharp taste of white mustard is because 4-hydroxybenzyl isothiocyanate is unstable and degrades to 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol and a thiocyanate ion, which are not pungent. The half-life of the isothiocyanate depends on the pH of the solution – the longest time is 321 minutes at pH 3, and the shortest is 6 minutes at pH 6.5.[2] Glucobrassicin is a structurally related glucosinolate that likewise yields a non-pungent isothiocyanate due to reaction with water.
References
- (in French) RICHARD H. Arômes alimentaires Document de cours Archived 2007-02-14 at the Wayback Machine
- Borek, Vladimir; Morra, Matthew J. (2005-09-24). "Ionic Thiocyanate (SCN−) Production from 4-Hydroxybenzyl Glucosinolate Contained in Sinapis alba Seed Meal". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (22): 8650–8654. doi:10.1021/jf051570r. PMID 16248567.