Sharon plain
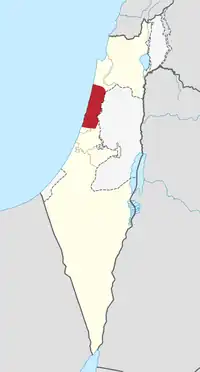
The Sharon plain (Hebrew: השרון, romanized: HaSharon; Arabic: سهل شارون, romanized: Sahel Sharon) is the central section of the Israeli coastal plain. The plain lies between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Samarian Hills, 15 km (9.3 mi) to the east. It stretches from Nahal Taninim, a stream marking the southern end of Mount Carmel in the north, to the Yarkon River in the south, at the northern limit of Tel Aviv, over a total of about 90 km (56 mi). The level of the Sharon plain is connected to the level of the Mediterranean Sea by the Sharon Escarpment.
Parts of the Plain are included in the Central, Haifa and Tel Aviv Districts of Israel.
History
Early
The Sharon valley is mentioned in an ancient Egyptian stele of Amenhotep II,[1] and as the Sharon field containing both Jaffa and Dor on the Sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II.
The Plain of Sharon is mentioned in the Bible (1 Chronicles 5:16, 27:29; Book of Isaiah 33:9, 35:2, 65:10), including the famous reference to the enigmatic "Rose of Sharon" (Song of Songs 2:1).
Excavations were performed before road construction in the north part of Sharon plain. Near En Esur, an early Bronze Age planned metropolis, including a temple, stretching over 65 ha for 6,000 inhabitants, was discovered. Under the 5000-year-old city, an even older settlement from 7000 YBP has been found, according to a report from the antiquities office of Israel on 6 October 2019.[2]
Modern
Before the 20th century, the region was covered by the Forest of Sharon, an open woodland dominated by Mount Tabor Oak (Quercus ithaburensis), which extended from Kfar Yona in the north to Ra’ananna in the south. The local Arab inhabitants traditionally used the area for pasture, firewood and intermittent cultivation. The intensification of settlement and agriculture in the coastal plain during the 19th century led to deforestation and subsequent environmental degradation known from Hebrew sources.[3]
Prior to 1948, the region was subordinate to Jaffa Subdistrict and Tulkarm Subdistrict.
Historically, while some parts of the Sharon plain were very fertile, much of it was swampy and malarial, a condition exacerbated by massive Ottoman deforestation. Zionist immigrants arrived in the early 20th century, drained much of the swampy land, and populated the region with many settlements.[4]
By 1945, Jaffa Subdistrict had a population of 373,800, consisting of 71% Jewish and 29% Palestinian Muslim and Christian. Tulkarm Subdistrict had a population 86,120, consisting of 17% Jewish and 83% Palestinian Muslim and Christian. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the Arab population of the region left or was expelled almost entirely.
In 2008, it was the most densely populated region of Israel.[5]
Cities and regional councils
| Cities | Regional Councils |
|---|---|
|
See also
- Sarona, a Templar settlement in the Plain of Sharon.
References
- Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte (1943). Vol 42: Annales du Service des Antiquités de l'Égypte (1943). France) Bibliothèque d'égyptologie du Collège de France (Paris. Le Caire, Imprimerie de l'Institut Français d'Archéologie Orientale.
- "Archäologen finden in Israel 5.000 Jahre alte Großstadt". ORF (in German). 2019-10-06. Retrieved 2019-10-06.
- Marom, Roy (2022-12-01). "יער השרון (אל-ע'אבה) בתקופה העות'מאנית: בתקופה מהמחקר חדשות תובנות הגיאוגרפי-היסטורי The Oak Forest of the Sharon (al-Ghaba) in the Ottoman Period: New Insights from Historical- Geographical Studies". Muse. 5: 90–107.
- "Sharon Plain". Bartleby.com. Archived from the original on 2008-07-06. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
- "Sharon Plain of Israel". Encarta. Archived from the original on 2007-09-16. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
