Saudi Arabian National Guard
The Saudi Arabian National Guard or SANG (Arabic: الحَرَس الوَطنيّ, romanized: al-Ḥaras al-Waṭanī), also known as the "White Army", is one of the three major branches of the military forces of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.[5]
| Saudi Arabian National Guard | |
|---|---|
| الحَرَس الوَطنيّ al-Ḥaras al-Waṭanī | |
| Founded | 1910 [lower-alpha 1] |
| Country | Saudi Arabia |
| Allegiance | CTHM |
| Branch | Army, Air force |
| Type | National guard |
| Role | Counter-insurgency |
| Size | 153,000 [lower-alpha 2] |
| Part of | Ministry of National Guard |
| Regional HQ | Riyadh (central) Western Province Eastern Province |
| Nickname(s) | "The White Army", "SANG" |
| Anniversaries | 23 September ;91 years ago |
| Website | www.sang.gov.sa |
| Commanders | |
| Supreme commander | |
| Commander-in-Chief | |
| Notable commanders |
|
The national guard is under the administrative control of the Ministry of National Guard, instead of the Ministry of Defence. It differs from the regular Saudi Arabian Army in being forged out of tribal elements loyal to the House of Saud and tasked with protecting the royal family from internal dangers such as a coup d'état.[6]
Organisation and roles

The Saudi Arabian National Guard has a standing force of 125,000 troops and a tribal militia of some 28,000 Fouj (tribal levies).[3] It serves both as a defence force against external attack and as an Internal security force. Its duties include protecting the House of Saud, guarding against military coups, guarding strategic facilities and resources, and providing security for the cities of Mecca and Medina.
It reports directly to the king through the Minister of the National Guard and, unlike the army, navy and air force, is not under the control of the Ministry of Defense. The Guard's command structure and communication network are entirely separate from those of the Ministries of Defense and the Interior.
Its personnel are drawn from tribes loyal to the king and the royal family, whose high-ranking members are always appointed its commander. It has been described as an institution that "ties the tribes to the House of Saud" (by Sandra Mackey).[7] It also draws recruits from official Wahhabi religious establishment. [8] It differs from the army in that its officers command units (e.g. battalions) "largely made up of their own tribal cousins, which makes the leaders and their followers less susceptible to subversive ideas and outside ideologies."[8]
According to journalist John R. Bradley, its leaders and their followers are 'supposed to have a vested interest in maintaining the status quo."[8] The force was extensively reorganised and retrained by the Vinnell Corporation (using over a thousand US Vietnam War veterans) in the 1980s. The United States' support for the SANG has been delivered both through private contractors and the U.S. army's Office of the Program Manager, Saudi Arabian National Guard Modernization Program.
History


The SANG was founded as the successor to the Ikhwan, the tribal army of King Abdulaziz. The Ikhwan had helped King Abdulaziz conquer the Arabian Peninsula and take it from the Hashimites in World War I. However, the Ikhwan committed many excesses and atrocities not just on The Hejazi army but on other Arabs as well. The various tribal groups of the Ikhwan also had a tendency to go off and do their own things and thus needed to be brought under a more centralised control. The SANG acquired its moniker of the "White Army" during this period due to its wearing of traditional Arab dress instead of Western-style military uniforms. In 1954, the office of Jihad and Mujahidin was transformed into the modern National Guard.[9] It was called White Army until 1963 when a British military mission reorganized it.[10]
Training of the National Guard became the responsibility of the US Vinnell corporation in 1975. About 1,000 United States Vietnam veterans were initially recruited to serve in the long-term training program designed to convert the guard into a mobile and hard-hitting counterinsurgency force that could also reinforce the regular army if necessary. These contractors were supervised by a United States military group with the designation Office of the Program Manager—Saudi Arabian National Guard (OPM-SANG).
Extensive military infrastructure facilities have been built to ensure the comfort and well-being of national guard units. Their major cantonments were in Al-Ahsa Oasis near Al-Hufuf and the major oil installations of the Eastern Province and at Al-Qasim in the Nejd, in an area where many of the tribal elements were recruited and most training was conducted. A large new housing project for guard personnel, with associated schools, shops, and mosques, has been constructed near Riyadh, also the site of the guard's military academy, the King Khalid Military College. Other National Guard military cities were located at At-Ta'if, Dammam, and Jeddah, while a new headquarters complex was built in Riyadh in the early 1980s.
During the 1950s and early 1960s, the regular army and the national guard were both small and of roughly equal strength. The guard suffered when the army's expansion was given priority, but in the 1970s the decline was reversed when the guard was converted to a light mechanized force with the help of United States advisers. Initially consisting of four combined arms battalions, the active-duty component had by 1992 been enlarged to two mechanized brigades, each with four infantry battalions, an artillery battalion, and engineering and signals companies. The guard's mobility over desert terrain was assured by 1,100 Commando V-150 armoured cars. Firepower came from 105 mm and 155 mm towed howitzers, 106 mm recoilless rifles, 90mm guns and BGM-71 TOW platforms. In the 1990s, the V-150s were replaced in the mechanized battalions with over LAV-25 Family of Vehicles bought from DDGM/GD in Canada.
The second component of the national guard, made up of tribal battalions under the command of local sheikhs, was organised into four infantry brigades (called the Fowj). These men, often the sons of local chiefs or of veterans of the original Ikhwan forces, reported for duty about once a month for the purpose of receiving stipends. They were provided with Heckler & Koch G3 rifles, although many had individually acquired AK-47s and other automatic weapons. They also have radios and are equipped with Toyota pickup trucks or Land Rovers. Many units are stationed along the borders of the Kingdom and have the mission to patrol the border areas. Although neither particularly well trained nor well equipped, they could be counted on to be loyal to the House of Saud if called for service. Their enrollment in the guard was largely a means to bolster the subsidies paid to local shaykhs and to retain the support of their tribes.
The national guard's King Abdulaziz Mechanized Brigade was swiftly deployed to the border area after Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990 and was actively engaged in the war, notably in the fighting to retake the town of Ra's al Khafji. After the war ended, it was reported that an enlargement of the national guard to eleven or twelve active brigades was contemplated. In addition, the ageing Commandos were to be replaced by more than 1,000 eight-wheeled LAV-25s and LAV variants manufactured by General Motors in Canada. The LAVs were to be mounted with a variety of armaments, such as 25 mm autocannon, larger-calibre 90 mm guns, 120mm mortars and TOW missile launchers.
Command
The Saudi Arabian National Guard's communications and chain of command maintained a separate network from regular Saudi Arabian military channels with a senior member of the royal family as its head. This structure was established by King Saud in 1956.[11] Prior to 1956 the Guard was led by tribal sheikhs.[11] Following the 1956 reorganization the first royal, Khalid bin Saud who was King Saud's son, was assigned to command the Guard in July 1957.[11] In 1959 Saad bin Saud, another son of King Saud, became the commander.[11]

King Abdullah commanded SANG for four decades, from 1962 until 17 November 2010 when he appointed his son, Prince Mutaib bin Abdullah, as the new commander.[12] In addition, three of his sons hold high positions within the organization. SANG's Deputy Commander was Prince Badr until 2010, who was a senior member of the Al Saud. Prince Mutaib was later arrested because of corruption and was imprisoned for a few months.[13] Its general headquarters, located in Riyadh, directly controlled the three regional sectors and the training facilities and the King Abdulaziz Independent Mechanized Brigade of four battalions.
The three regional (eastern, central, and western) sectors each command one or more mechanized or motorized brigades, several independent Security and Military Police and logistical battalions, but also the irregular fowj battalions.
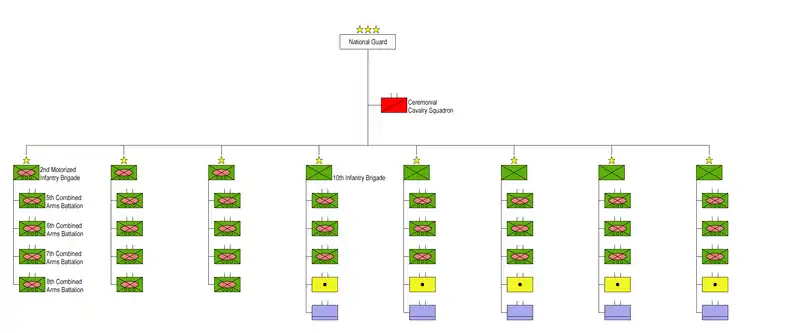
Structure
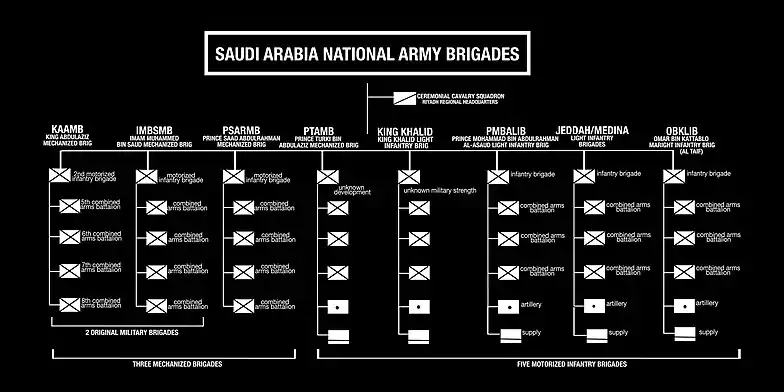
The SANG was restructured with the help of the Vinnell Corporation into a light mechanized force equipped with over a thousand Cadillac Gage Commando armored fighting vehicles (replaced with LAV-25s in the 1990s). Its mobile force consisted of three mechanized brigades and five motorized infantry brigades. The militia portion consists of around 24 battalions of fowj, tribal warriors on "retainer".
Brigades
The twenty one SANG brigades include:
- King Abdulaziz Mechanized Brigade (KAAMB), the second of the original mechanized brigades formed in the late 1970s with Cadillac-Gage V-150 vehicles. These were replaced in the 1990s by the more-capable LAV series of tactical vehicles. This was also the brigade that fought at the Battle of Khafji. Its reported garrison in early 1991 was Al Hofuf.[14]
- King Faisal Light Infantry Brigade (KFB) based in Medina
- King Khalid Light Infantry Brigade's strength is unknown
- Prince Mohammad bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud Light Infantry Brigade
- Imam Muhammad bin Saud Mechanized Brigade (IMBSMB) the first of two mechanized brigades created in the late 1970s with Cadillac-Gage V-150 vehicles. These were replaced in the 1990s by the more-capable LAV series of tactical vehicles.
- Prince Saad bin Abdul Rahman Mechanized Brigade (PSARMB)was formed in the late 1990s and equipped with LAV series of tactical vehicles
- Prince Turki bin Abdulaziz Mechanized Brigade (PTAMB) was formed by 2006 and equipped with LAV series of tactical vehicles
- King Saud Light Infantry Brigade (KSB) based in Jeddah
- Omar bin Khattab light infantry brigade based in al-Taif
The two original motorized brigades, IMBSMB and KAAMB, had V-150 Commando armored cars, M‑102 howitzers (IMBS) and 155 mm M‑198 howitzers, plus TOW anti-tank guided missile systems in the anti-tank platoons of the line motorized companies; two in each company in the IMBS and six in the KAAB. The two brigades each had a headquarters company, four-line motorized battalions, a field artillery battalion, a support battalion, and air defense, signals, and engineers companies.[15]
Regions
Central
Riyadh Regional Headquarters controlled:
- Imam Muhammad bin Saud Mechanized Brigade (IMBS), which controls four battalions (1st–4th) as well as the 1st SANG Artillery Battalion, and is based in Riyadh
- Prince Saad Abdulrahman Mechanized Brigade (PSAR), which controls four combined-armed battalions, and is based in Riyadh
- Turki Mechanized Brigade was reported to be in formation in 2002. As of 2006, it remains uncertain as to how developed this unit is.
- King Khalid Light Infantry Brigade's strength is unknown
- Ceremonial Cavalry Squadron
- King Khalid Military College
- Military Police battalion
- 1st Special Security Brigade based in Riyadh
- 1st Rapid Deployment Special Brigade
- Irregular (Fowj) tribal regiments
Eastern
Eastern Regional Headquarters, which is located in Dammam, controlled:
- King Abdulaziz Mechanized Brigade (KAAB), was in information in 2002, but its strength and organization is still unknown. Stanton, writing in 1996, identified this brigade as the King Abdul Aziz Brigade, stationed in Hofuf south of Dammam. It comprised the 5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th Combined Arms Battalions and the 2nd Artillery Battalion (155mm M-198 towed howitzers).[15]
- Prince Mohammad bin Abdulrahman al-Saud Light Infantry Brigade
- Military Police battalion
- 3rd Special Security Brigade based in Dammam
- 3rd Rapid Deployment Special Brigade
- Irregular (Fowj) tribal regiments
Western
Western Regional Headquarters, which is located in Jeddah, controlled:
- King Saud Light Infantry Brigade (KSB) based in Jeddah
- King Faisal Light Infantry Brigade (KFB) based in Medina
- Khalifa Omar bin Khattab Light Infantry Brigade (KOKB) based in Taif
- Military Police battalion
- 2nd Special Security Brigade based in Jeddah
- 2nd Rapid Deployment Special Brigade
- Irregular (Fowj) tribal regiments
Other units
National Guard Aviation
- Dirab Air Base - Center of Excellence and Aviation Training Brigade[16]
- Khasm Alan Air Base - 1st Aviation Brigade[17]
- Al Hofuf Air Base - 2nd Aviation Brigade[18]
- Prince Abdullah Air Base - 3rd Aviation Brigade[19]
Independent battalions
- In addition to the battalions under the control of the three regional headquarters, SANG has four independent light infantry battalions, which appear to be dedicated to protecting facilities and installations[20]
Tribal militia
The second component of the national guard is the Fowj (Arabic:فَيْج (also fayj) "legman, courier; company"),[21] made up of Bedouin tribal (militia) battalions under the command of local sheikhs. These men, often the sons of local chiefs or of veterans of the original Ikhwan forces, reported for duty about once a month for the purpose of receiving stipends. They were provided with obsolete rifles, although many had individually acquired AK-47 assault rifles. Although neither particularly well trained nor well equipped, they could be counted on to be loyal to the House of Saud if called for service. Their enrollment in the guard is largely a means to bolster the subsidies paid to local sheikhs and to retain the support of their tribes.[22] The Fowj is currently organized into 27 battalions with approximately 27,000 men.[23]
Uniforms
Uniforms worn by personnel of Saudi Arabia's national guard are closely patterned on the British and United States models that influenced them during their early development. The most common uniform colors are khaki or olive drab. Officers had semidress uniforms for various functions and dress uniforms for formal occasions. All personnel wear berets, and officers also have peaked caps.[24]
.jpg.webp)
When in modern uniforms personnel wear a red beret. British three color British Desert pattern DPM[25] used throughout the Middle East, American Desert Camouflage Uniform (DCU), used in Iraq and other desert regions throughout the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) regions. Some units still wear the American Desert Battle Dress Uniform of which a Saudi grey variant is worn by SANG security guards. These are being replaced by several new digital or pixelated camouflage designs with an embedded Saudi Arabian National Guard crest.[26] National guardsmen often wear the traditional red-checkered keffiyeh Arab headdress. Tribal units often wear the thawb with crossed bandoliers.[24]
Equipment

The SANG is, by tradition, issued equipment not used by the regular military; it does not possess any tanks but has several thousand wheeled armored fighting vehicles and armoured personnel carriers. It possesses its own helicopters and light aircraft and all the remaining types of military hardware including artillery.
A$2.2 billion foreign military sale contract delivered 724 LAV‑II 8×8 wheeled armored personnel carriers in ten different varieties in 2001.
In December 2012, the Saudi National Guard ordered 68 French Multi-Purpose Combat Vehicle (MPCV) air-defense vehicles.[27] In September 2014, 24 Boeing AH-6i Little Bird light attack and reconnaissance helicopters were ordered from Boeing with deliveries to begin in 2016.[28]
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small arms | |||||
| FN Five-Seven |  | Standard issue pistol. | |||
| FN P90 |  | ||||
| H&K MP5 |  | ||||
| AK-47 | Used by tribal militias of the National Guard. | ||||
| H&K G36 |  | ||||
| FN FAL | Used for ceremonial purposes. | ||||
| FN F2000 |  | ||||
| FN MINIMI |  | ||||
| FN MAG |  | ||||
| Vektor SS-77 | .jpg.webp) | ||||
| WKW Wilk (Tor) |  | <15 | |||
| Explosives, anti-tank weapons | |||||
| RPG-7 |  | ||||
| FN GL1 |  | Attaches to the rifle. | |||
| Mk19 |  | ||||
| Armored personnel carriers | |||||
| LAV-III |  | 19[29] | 900 LAV 6.0 on order. Some of the 900 combat vehicles will be fitted with a 105 mm anti-tank cannon known as the Cockerill CT-CV 105H and the rest will be fitted with a CPWS 20-25-30 which can be armed from a 20 mm to a 30 mm auto-cannon. | ||
| Al-Fahd | Saudi Arabia | 100 | First indigenously designed APC. | ||
| Piranha II |  | Switzerland | 1,117 | 172 more on order. | |
| LAV-25 |  | Multiple variants | N/A | ||
| LAV II | ten different varieties | 724 | |||
| Cadillac Gage Commando |  |
V-150S | 579+ | between 7 and 10 of the Saudi V-150s were destroyed when they were used against Iraq | |
| EE-11 Urutu | .jpg.webp) | 20 | |||
| Al-Naif | |||||
| Artillery | |||||
| CAESAR |  | France | 156[30] [31] | ||
| Aircraft | |||||
| Boeing AH-64 Apache | .jpg.webp) |
36 | 12 + 24 on order | ||
| Boeing AH-6 | .jpg.webp) | 24[32] | |||
| Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk | .jpg.webp) | UH-60M | 48 | 72 order. 3 batches of 24. Introduced during 2015.[33] | |
| Air Defense | |||||
| MPCV |  | 68[30] | |||
| VL-MICA |  | 5[30] | |||
| M167 VADS |  | 30[30] | |||
Ranks
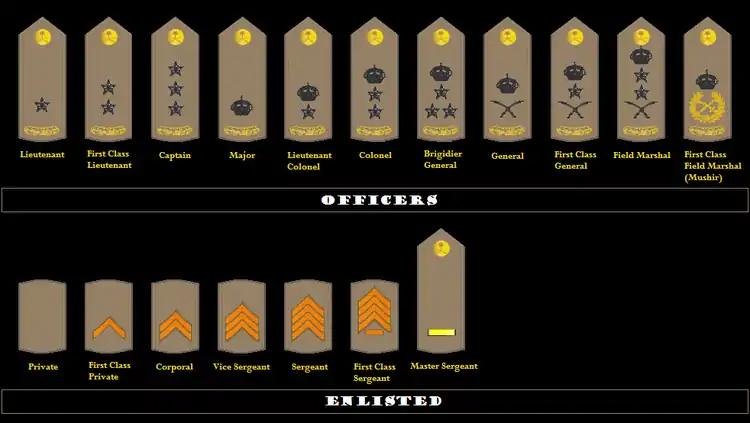 |
Officers
- Lieutenant/Mulazim (Arabic:ملازم)
- 1st Lieutenant/Mulazim Awwal (Arabic:ملازم أول)
- Captain/Naqib (Arabic:نقيب)
- Major/Ra'id (Arabic:رائد)
- Lieutenant Colonel/Muqaddam (Arabic:مقدم)
- Colonel/'Aqid (Arabic:عقيد)
- Brigadier General/'Amid (Arabic:عميد)
- Major General/Liwa (Arabic:لواء)
- Lieutenant General/Fariq (Arabic:فريق)
- General/Fariq Awwal (Arabic:فريق أول)
Enlisted
- Private/Jundi (Arabic:جندي)
- First Private/Jundi Awwal (Arabic:جندي أول)
- Corporal/A'rif (Arabic:عريف)
- Sergeant/Wakil Raqib (Arabic:وكيل رقيب)
- Staff Sergeant/Raqib (Arabic:رقيب)
- Master Sergeant/Raqib Awwal (Arabic:رقيب أول)
- Sergeant Major/Ra'is Ruquba (Arabic:رئيس رقباء)
2013 reorganization
The SANG was transformed into a ministerial body on 27 May 2013.[34] Prince Mutaib bin Abdullah, former commander of the SANG, became the minister of national guard on the same day.[34] On 4 November 2017, Prince Mutaib was replaced by Prince Khalid bin Abdulaziz bin Eyaf Al Saud (until December 2018)[35]
References
- The Ikhwan of Najd and Their Role in the Creation of the Sa'udi Kingdom, 1910–1930. John S. Habib. 1977.
- "List of countries by number of reserve personnel". Armed Forces. Archived from the original on 6 March 2020. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "Mapping the Saudi State, Chapter 5: The Saudi Arabian National Guard" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2019.
- "السعودية.. مزايا لنحو ربع مليون عسكري في الحرس الوطني" (in Arabic). 2019. Archived from the original on 14 February 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- "Saudi Arabian National Guard (SANG)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 January 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- Anthony H. Cordesman (2009). Saudi Arabia: National Security in a Troubled Region. ABC-CLIO. pp. 175–7. ISBN 9780313380761. Archived from the original on 22 March 2015.
- Mackey, The Saudis: Inside the Desert Kingdom, p. 207.
- John R. Bradley (2005). Saudi Arabia Exposed: Inside a Kingdom in Crisis. Palgrave. p. 69. ISBN 9781403964335.
The National Guard, in contrast to the army, has institutionalized and cemented tribal, social, and religious ties in the kingdom because it is made up of young men drawn from the various ranks of the Bedu, tribes, and official Wahhabi religious establishment. Commanders, for instance, often head battalions largely made up of their own tribal cousins, which makes the leaders and their followers less susceptible to subversive ideas and outside ideologies. Since they and their families reap all of the benefits of being part of the state apparatus, they are supposed to have a vested interest in maintaining the status quo. (p.69)
- "History of the Saudi National Guard". Asharq Alawsat. 11 September 2006. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- Stephanie Cronin (2013). "Tribes, Coups and Princes: Building a Modern Army in Saudi Arabia". Middle Eastern Studies. 49 (1): 2–28. doi:10.1080/00263206.2012.743892. S2CID 143713882. Archived from the original on 14 February 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- Bruce R. Nardulli (2002). Dance of Swords: U.S. Military Assistance to Saudi Arabia, 1942-1964 (PhD Thesis thesis). The Ohio State University. Retrieved 13 September 2020.
- "Saudi king transfers National Guard duties to son". The Washington Post. 17 November 2010.
- "Saudi anti-corruption drive: Prince Miteb freed 'after $1bn deal'". BBC News. 29 November 2017. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- Martin Stanton (12 March 2009). Somalia on $5 a Day: A Soldier's Story. Random House Publishing Group. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-307-54699-9. Archived from the original on 14 February 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- Martin N. Stanton (March–April 1996), "The Saudi Arabian National Guard Motorized Brigades" (PDF), Armor magazine, pp. 6–11
- "Saudi Arabian National Guard - Riyadh/Dirab (--)". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- "Saudi Arabian National Guard - Riyadh/Khasm Alan (OEKA)". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- "Saudi Arabian National Guard - Al Hofuf (--)". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- "Saudi Arabian National Guard - Jeddah/Prince Abdullah Air Base (OEJN)". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- Tartter (1993)
- "فوج - Wiktionary". en.wiktionary.org. Archived from the original on 5 February 2023. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- Saudi Arabia: A Country Study, Federal Research Division, Library of Congress
- "About OPM SANG". Archived from the original on 26 June 2018. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 10 January 2009. Retrieved 3 November 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Armies of the Gulf War, Elite 45, Osprey Publishing 1993, Gordon L Rottman, ISBN 185532 277 3
- "Saudi Arabia - Camopedia". camopedia.org. Archived from the original on 13 January 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- Saudi Arabia National Guard ordered 68 MPCV air defense vehicles Archived 30 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine – Army Recognition, 26 December 2012
- Gareth Jennings (11 October 2015). "Saudi AH-6i deliveries to begin mid-2016". Janes Defence Weekly. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 30 March 2017.
- "Canadian arms exports hit 12 billion last year 4 billion sent to Saudi Arabia". Ottawa Citizen. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2022). The military balance. 2022. Abingdon, Oxon. p. 368. ISBN 978-1032279008.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Trade Registers". armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 15 June 2023.
- "Trade Registers". SIPRI Arms Transfers Database. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- AirForces Monthly. Stamford, Lincolnshire, England: Key Publishing Ltd. May 2022. p. 18.
- "King Abdullah transforms National Guard into ministry". Asharq Alawsat. 28 May 2013. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- "Minister of National Guard, Prince Mutaib bin Abdullah removed from his position". Al Arabiya. 4 November 2017. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
Notes
- As the White Army.[1]
- By 2013, it was estimated that more than 125,000 active duty (153,000if the irregular fowj regiments are included)[2][3][4]
Sources
- Mackey, Sandra. The Saudis: Inside the Desert Kingdom. Updated Edition. Norton Paperback. W.W. Norton and Company, New York. 2002 (first edition: 1987). ISBN 0-393-32417-6 pbk.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Jean R. Tartter (1993). Helen Chapin Metz (ed.). Saudi Arabia: A Country Study. Federal Research Division. Saudi Arabian National Guard.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Jean R. Tartter (1993). Helen Chapin Metz (ed.). Saudi Arabia: A Country Study. Federal Research Division. Saudi Arabian National Guard.
.svg.png.webp)