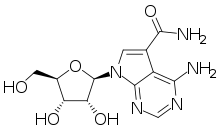
Sangivamycin
Sangivamycin is a natural product originally isolated from Streptomyces rimosus, which is a nucleoside analogue. It acts as an inhibitor of protein kinase C. It has antibiotic, antiviral and anti-cancer properties and has been investigated for various medical applications, though never approved for clinical use itself. However, a number of related derivatives continue to be researched.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.068 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 309.28 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Oyagen, a biotechnology company, has been developing sangivamycin or OYA1, which showed efficacy against Ebola infections,[8] as a broad spectrum antiviral for COVID-19.[9][10] Tonix Pharmaceuticals licensed OYA1 from Oyagen in April 2021 to develop it for the treatment of COVID-19 and it is now called TNX-3500. [11][12][13]
See also
- CMX521 (methylated analogue)
- GS-441524
- NITD008
- Pyrazofurin
References
- Tolman RL, Robins RK, Townsend LB (January 1968). "Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotics. Total synthesis and structure of toyocamycin, unamycin B, vengicide, antibiotic E-212, and Sangivamycin (BA-90912)". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 90 (2): 524–6. doi:10.1021/ja01004a076. PMID 5634627.
- De Clercq E, Bernaerts R, Bergstrom DE, Robins MJ, Montgomery JA, Holy A (March 1986). "Antirhinovirus activity of purine nucleoside analogs". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 29 (3): 482–7. doi:10.1128/aac.29.3.482. PMC 180418. PMID 3013084.
- Loomis CR, Bell RM (February 1988). "Sangivamycin, a nucleoside analogue, is a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (4): 1682–92. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)77930-7. PMID 3338987.
- Kučić N, Mahmutefendić H, Lučin P (August 2005). "Inhibition of protein kinases C prevents murine cytomegalovirus replication". The Journal of General Virology. 86 (Pt 8): 2153–2161. doi:10.1099/vir.0.80733-0. PMID 16033962.
- Lee SA, Jung M (May 2007). "The nucleoside analog sangivamycin induces apoptotic cell death in breast carcinoma MCF7/adriamycin-resistant cells via protein kinase Cdelta and JNK activation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (20): 15271–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701362200. PMID 17371872.
- Bastea LI, Hollant LM, Döppler HR, Reid EM, Storz P (November 2019). "Sangivamycin and its derivatives inhibit Haspin-Histone H3-survivin signaling and induce pancreatic cancer cell death". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 16588. Bibcode:2019NatSR...916588B. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53223-0. PMC 6851150. PMID 31719634.
- Smith HC, et al. Methods of treating and inhibiting ebola virus infection. Patent application CA3040540, Oyagen Inc, 17 May 2018
- Bennett RP, Finch CL, Postnikova EN, Stewart RA, Cai Y, Yu S, et al. (December 2020). "A Novel Ebola Virus VP40 Matrix Protein-Based Screening for Identification of Novel Candidate Medical Countermeasures". Viruses. 13 (1): 52. doi:10.3390/v13010052. PMC 7824103. PMID 33396288.
- Philippidis A (2020-05-18). "OyaGen - OYA1". GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- Philippidis A (2020-03-18). "Catching Up to Coronavirus: Top 60 Treatments in Development". GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- "Tonix hopes for COVID-19 drug tonic as it pens OyaGen antiviral pact". FierceBiotech. 19 April 2021. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- "BioWorld Science". science.bioworld.com. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- "Tonix Seeks to Advance OyaGen's COVID-19 Treatment Under New Global Licensing Deal". BioSpace. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.