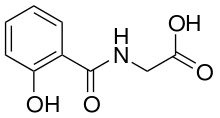
Salicyluric acid
Salicyluric acid is the glycine conjugate of salicylic acid and is the primary form in which salicylates are excreted from the body,[1] via the kidneys. The pathway is very similar to the pathway of benzoic acid excretion as hippuric acid.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.965 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H9NO4 |
| Molar mass | 195.174 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 164–165 °C (327–329 °F) |
| |
| |
References
- Schrör K (2016). "Biotransformations of Salicylic Acid". Acetylsalicylic acid (Second ed.). Weinheim. p. 70. ISBN 978-3-527-68502-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.