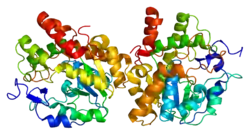
SULT1B1
Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 1B member 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1B1 gene.[5][6][7]
Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and xenobiotic compounds. These cytosolic enzymes are different in their tissue distributions and substrate specificities. The gene structure (number and length of exons) is similar among family members. However, the total genomic length of this gene is greater than that of all of the other SULT1 genes.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173597 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029269 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Meinl W, Glatt H (Nov 2001). "Structure and localization of the human SULT1B1 gene: neighborhood to SULT1E1 and a SULT1D pseudogene". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 288 (4): 855–62. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5829. PMID 11688987.
- Fujita K, Nagata K, Ozawa S, Sasano H, Yamazoe Y (Feb 1998). "Molecular cloning and characterization of rat ST1B1 and human ST1B2 cDNAs, encoding thyroid hormone sulfotransferases". J Biochem. 122 (5): 1052–61. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021846. PMID 9443824.
- "Entrez Gene: SULT1B1 sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1B, member 1".
Further reading
- Weinshilboum RM, Otterness DM, Aksoy IA, et al. (1997). "Sulfation and sulfotransferases 1: Sulfotransferase molecular biology: cDNAs and genes". FASEB J. 11 (1): 3–14. doi:10.1096/fasebj.11.1.9034160. PMID 9034160. S2CID 12532583.
- Glatt H, Engelke CE, Pabel U, et al. (2000). "Sulfotransferases: genetics and role in toxicology". Toxicol. Lett. 112–113 (1–3): 341–8. doi:10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00214-3. PMID 10720750.
- Glatt H (2001). "Sulfotransferases in the bioactivation of xenobiotics". Chem. Biol. Interact. 129 (1–2): 141–70. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(00)00202-7. PMID 11154739.
- Glatt H, Boeing H, Engelke CE, et al. (2001). "Human cytosolic sulphotransferases: genetics, characteristics, toxicological aspects". Mutat. Res. 482 (1–2): 27–40. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(01)00207-X. PMID 11535246.
- Wang J, Falany JL, Falany CN (1998). "Expression and characterization of a novel thyroid hormone-sulfating form of cytosolic sulfotransferase from human liver". Mol. Pharmacol. 53 (2): 274–82. doi:10.1124/mol.53.2.274. PMID 9463486.
- Tsoi C, Falany CN, Morgenstern R, Swedmark S (2001). "Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a canine sulfotransferase that is a human ST1B2 ortholog". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 390 (1): 87–92. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2373. PMID 11368519.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Dombrovski L, Dong A, Bochkarev A, Plotnikov AN (2006). "Crystal structures of human sulfotransferases SULT1B1 and SULT1C1 complexed with the cofactor product adenosine-3'- 5'-diphosphate (PAP)". Proteins. 64 (4): 1091–4. doi:10.1002/prot.21048. PMID 16804942. S2CID 32647194.
- Allali-Hassani A, Pan PW, Dombrovski L, et al. (2007). "Structural and chemical profiling of the human cytosolic sulfotransferases". PLOS Biol. 5 (5): e97. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050097. PMC 1847840. PMID 17425406.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.