S416
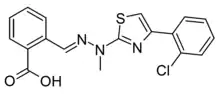
S416 (GTPL-11164) is a drug which acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). This enzyme is involved in the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleosides in the body, which are required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. This is an important rate-limiting step in the replication of viruses, and so DHODH inhibitors may have applications as broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. In tests in vitro, S416 was found to have antiviral activity against a range of pathogenic RNA viruses including influenza, Zika virus, Ebola virus and SARS-CoV-2.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H14ClN3O2S |
| Molar mass | 371.84 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Xiong R, Zhang L, Li S, Sun Y, Ding M, Wang Y, et al. (October 2020). "Novel and potent inhibitors targeting DHODH are broad-spectrum antivirals against RNA viruses including newly-emerged coronavirus SARS-CoV-2". Protein & Cell. 11 (10): 723–739. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00768-w. PMC 7402641. PMID 32754890.
- Tian D, Liu Y, Liang C, Xin L, Xie X, Zhang D, et al. (May 2021). "An update review of emerging small-molecule therapeutic options for COVID-19". Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 137: 111313. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111313. PMC 7857046. PMID 33556871.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.