Rosiridin
Rosiridin is a chemical compound that has been isolated from Rhodiola sachalinensis.[1] Rosiridin can inhibit monoamine oxidases A and B, possibly meaning that the compound could help in the treatment of depression and senile dementia.[2][3]
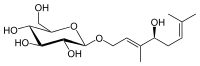 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2E,4S)-4-Hydroxy-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H28O7 | |
| Molar mass | 332.393 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Yoshikawa, Masayuki; Nakamura, Seikou; Li, Xuezheng; Matsuda, Hisashi (2008). "Reinvestigation of absolute stereostructure of (−)-rosiridol: Structures of monoterpene glycosides, rosiridin, rosiridosides A, B, and C, from Rhodiola sachalinesnsis". Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 56 (5): 695–700. doi:10.1248/cpb.56.695. PMID 18451561.
- Panossian, Alexander; Wikman, Georg (2010). "Effects of adaptogens on the central nervous system and the molecular mechanisms associated with their stress-protective activity". Pharmaceuticals. 3 (1): 188–224. doi:10.3390/ph3010188. PMC 3991026. PMID 27713248.
- van Diermen, Daphne; Marston, Andrew; Bravo, Juan; Reist, Marianne; Carrupt, Pierre-Alain; Hostettmann, Kurt (2009-03-18). "Monoamine oxidase inhibition by Rhodiola rosea L. roots". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 122 (2): 397–401. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2009.01.007. ISSN 0378-8741.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.