Ramsey car-transfer apparatus
In railroad industry, the Ramsey car-transfer apparatus (Ramsey transfer) was a device to replace bogies on railroad cars to permit transfer of a train between railroad lines with different gauge.
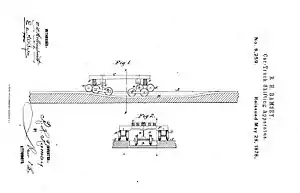
The Ramsey transfer existed in a number of variations covered by several different patents. It was typically used to transfer cars between 6 ft (1,829 mm) broad gauge, 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge and narrow gauge (usually 3 ft / 914 mm in width) track.
Invention
It was invented and patented in 1876 by Robert Henry Ramsey as a simple and rapid device for removing trucks at repairing shops, and for transferring car-bodies between rail roads of different gauges.[1]
Operation
.jpg.webp)
Two parallel tracks of 18 in (457 mm) were set approximately 9 feet (2.74 m) apart. Between these two tracks, the standard and narrow gauge tracks descended into a pit, one from each end of the pit, overlapping in the center and having a common center line. Beams resting on trucks riding on the 18-inch (457 mm) gauge tracks were inserted under the car to have its trucks changed. The car was then pushed over pit, resting on the beams. This allowed the old trucks to slip off the center pins. The old trucks were pulled out of the pit and new trucks were pushed in from the opposite side. As the car passed over the opposite side of the pit, the new trucks were guided to fit on the center pins. The car now continued on its way, its load undisturbed.
Speed
It was claimed that the entire procedure could be performed in less than eight minutes. However in 1851, this would have referred to wagons without continuous brakes. More time would have been taken to deal with post 1880 wagons with continuous brakes.
Users
.jpg.webp)
The Ligonier Valley Railroad was the first to use the method in 1878 in Latrobe, Pennsylvania.[2] It was also used in the same year by the Rochester and State Line Railroad at its Salamanca junction with the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad, a 6 ft (1,829 mm) gauge line.
It was also adopted by the Lehigh Valley Railroad; Wilmington, Columbia and Augusta Railroad; W. C. Virginia Midland & Gt. S. Railroad; Atlantic and Great Western Railroad; Pittsylvania [sic] R. R.; Pittsburg Southern Railroad; Dayton, Covington & Toledo Railroad; Dayton & Southeastern R. R.; Memphis & Little Rock R. R. and many others.[1] The East Broad Top Railroad, a coal rail road in Pennsylvania used it in its Mount Union Yard up to the closure in 1956.[1]
Patents
- U.S. Patent 178,079, 30 May 1876, Car Truck Shifting Apparatus
- U.S. Patent RE8,259, 28 May 1878, Reissue of 178,079
- U.S. Patent 204,087, 21 May 1878, Car Transfer Apparatus
- U.S. Patent 304,562, 2 September 1884, Car and Freight Transfer Apparatus
- U.S. Patent 304,563, 2 September 1884, Car and Freight Transfer Apparatus
See also
References
- Mid-Continent Railway Museum: Ramsey's Car Truck Shifting Apparatus.
- "Ligonier Valley Rail Road History". www.lvrra.org. Archived from the original on 2005-03-23.