Prostitution by region
This is an overview of prostitution by region.
Africa
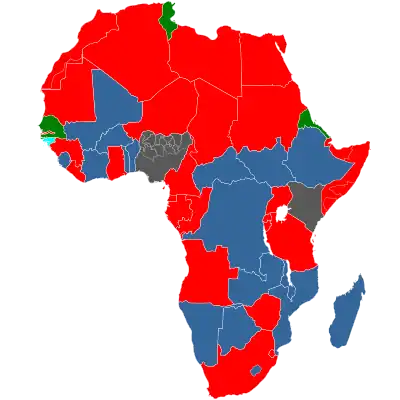
Prostitution is illegal in the majority of African countries. HIV/AIDS infection rates are particularly high among African sex workers.[1]
Nevertheless, it is common, driven by the widespread poverty in many sub-Saharan African countries,[2] and is one of the drivers for the prevalence of HIV/AIDS in Africa.[3] Social breakdown and poverty caused by civil war in several African countries has caused further increases in the rate of prostitution in those countries. For these reasons, some African countries have also become destinations for sex tourism.
Long-distance truck drivers have been identified as a group with the high-risk behaviour of sleeping with prostitutes and a tendency to spread the infection along trade routes in the region. Infection rates of up to 33% were observed in this group in the late 1980s in Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania.
| Prostitution in African areas |
|---|
Sovereign states
States with limited recognition Dependencies and other territories
|
Americas
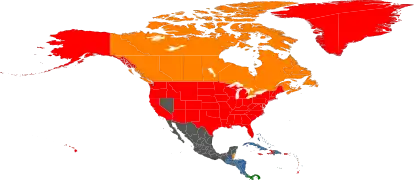
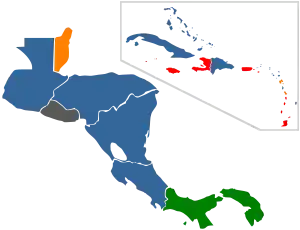
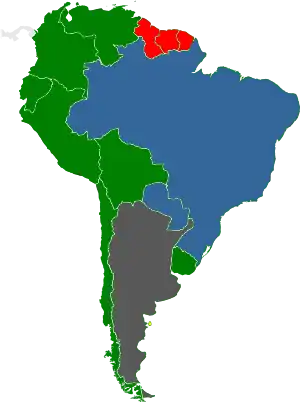
Legality of prostitution in the Americas varies by country. Most countries only legalized prostitution, with the act of exchanging money for sexual services legal. The level of enforcement varies by country.
| Prostitution in North American areas |
|---|
| Sovereign states
Dependencies and other territories |
| Prostitution in Central American areas |
Sovereign states
|
| Prostitution in Caribbean areas |
| Sovereign states
Dependencies and other territories |
| Prostitution in South American areas |
| Sovereign states
Dependencies and other territories |
Asia
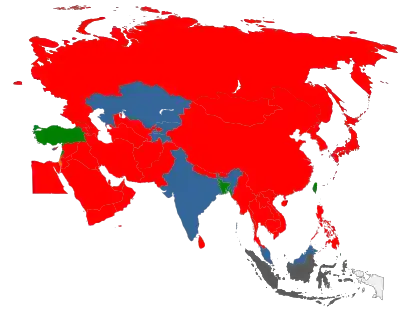
In Asia, the main characteristic of the region is the very big discrepancy between the laws which exist on the books and what occurs in practice. For example, in Thailand prostitution is illegal,[4] but in practice it is tolerated and partly regulated, and the country is a destination for sex tourism. Such situations are common in many Asian countries.
In Japan, prostitution is legal[5] with the exception of heterosexual, vaginal intercourse. Advertisements that detail what each individual prostitute will do (oral sex, anal sex, etc.) are a common sight in the country, although many prostitutes disregard the law.
In India, prostitution is legal only if carried out in the private residence of a prostitute or others.[6]
Child prostitution is a serious problem in this region. Past surveys indicate that 30 to 35 percent of all prostitutes in the Mekong sub-region of Southeast Asia are between 12 and 17 years of age.[7]
| Prostitution in Asian areas |
|---|
Sovereign states
States with limited recognition
Dependencies and other territories |
Europe
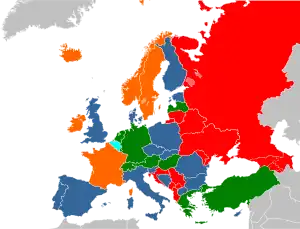
Compared to other continents, Europe has very diverse laws when it comes to prostitution. The most common legal system in the European Union is that which allows prostitution itself (the exchange of sex for money) but prohibits associated activities (brothels, pimping, etc.). Prostitution remains illegal in most of the ex-communist countries of Eastern Europe.
In Belgium, sex work has been decriminalized since 1 June 2022.[8] It is the first country in Europe and the second country in the world (after New Zealand) to decriminalize sex work.
In Sweden,[9] Northern Ireland,[10] Norway,[11] Iceland,[12] and France[13] it is illegal to pay for sex (the client commits a crime, but not the prostitute).
In the United Kingdom, it is illegal to pay for sex with a prostitute who has been "subjected to force" and this is a strict liability offense (clients can be prosecuted even if they did not know the prostitute was forced), but prostitution itself is legal.[14][15]
In Germany prostitution is legal, as are brothels.
In Finland, Norway and Switzerland the right to sell sex is restricted based on citizenship. Aliens caught selling sex in Finland or Norway may be deported and of foreign citizens only EU citizens can get a Swiss prostitution license.
The enforcement of the anti-prostitution laws varies by country.
In Eastern Europe, prostitution was outlawed by the former communist regimes, and most of those countries chose to keep it illegal even after the fall of the Communists. It was only legalized by the former communist countries that joined the European Union (except for Lithuania and Croatia, where it remains illegal). It is even regulated in Hungary and Latvia.
Lithuania and Croatia remain the only countries in the European Union where women providing sexual services are punished. Croatia is the only one in which only a sex worker is criminalized, because Lithuania also criminalizes clients. In Sweden, France and Ireland only clients are punished, while in other countries both the sale and purchase of sexual services is legal.
| Prostitution in European areas |
|---|
Sovereign states
States with limited recognition Dependencies and other territories
|
Oceania
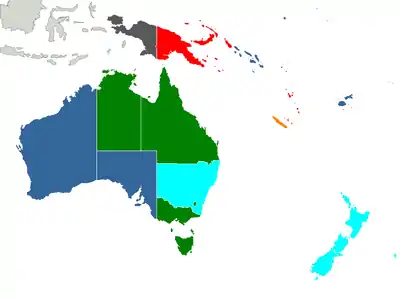
Prostitution in Oceania varies greatly across the region. In American Samoa, prostitution is illegal,[16] whereas in New Zealand most aspects of the trade are decriminalised.[17]
| Prostitution in Oceania areas |
|---|
Sovereign states
Associated states of New Zealand Dependencies and other territories |
See also
References
- "Sex Workers, Prostitution, HIV and AIDS". 2015-07-20.
- Increasing prostitution driven by poverty in drought-stricken – Welthungerhilfe Archived 2007-01-03 at the Wayback Machine. Welthungerhilfe.de. Retrieved on 2012-01-11.
- Sex Workers, Prostitution and AIDS. Avert.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-11.
- 2008 Human Rights Report: Thailand. State.gov (2009-02-25). Retrieved on 2012-01-11.
- Hongo, Jun. "Law bends over backward to allow 'fuzoku'". japantimes.co.jp. Retrieved 2015-08-18.
- "The Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956". wcd.nic.in. Archived from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- Deena Guzder "UNICEF: Protecting Children from Commercial Sexual Exploitation". Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting. August 20, 2009
- "LOI - WET". www.ejustice.just.fgov.be. Retrieved 2022-06-25.
- Yvonne Svanström, “Through the Prism of Prostitution: Conceptions of Women and Sexuality in Sweden at Two Fins-de-Siècle”, Nordic Journal of Women’s Studies, 2005 (13): 48-58
- "Human Trafficking Bill receives Royal Assent". BBC News. 14 January 2015. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- Elden, John Christian; Skirbekk, Sigurd (2014). "Prostitusjon". In Henriksen, Petter (ed.). Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Oslo: Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- "Jafnréttisstofa". Jafnretti.is. 2009-04-21. Archived from the original on 2015-07-09. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- Prostitution : le Parlement adopte définitivement la pénalisation des clients 'Le Monde', accessed 7 April 2016
- Policing and Crime Act 2009. Opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved on 2012-01-11.
- Policing and Crime | UK | Anti-trafficking | Exploitation | Sex Industry | The Naked Anthropologist. Nodo50.org (2010-04-06). Retrieved on 2012-01-11.
- Godwin, John (October 2012). "Sex Work and the Law in Asia and the Pacific" (PDF). UNAIDS.
- Prostitution Reform Act 2003.
.svg.png.webp)