Proser1
PROSER1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PROSER1 gene.[2]
| Proser1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | 2810046L04Rik9330161F11proline and serine rich 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | HomoloGene: 13463 GeneCards: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nomenclature
PROSER1 has several aliases: C13orf23, KIAA2032, and proline and serine-rich protein 1.[3] [4]
Gene
Location
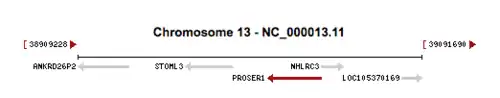
PROSER1 is located on the negative (reverse) strand of chromosome 13 at position 13q13.3. It spans from 39,009,865 base pairs from the pter to 39,038,095 bp from the pter, with a size of 28,231 bases.[5] PROSER1 has a total of 13 exons in its primary unspliced transcript mRNA of 5,185 bp. There are 2 isoforms of PROSER1, both within the 5,000 bp range.[6]
Gene neighborhood
Genes STOML3 and NHLRC3 neighbor PROSER1 on chromosome 13.[7]
Tissue distribution
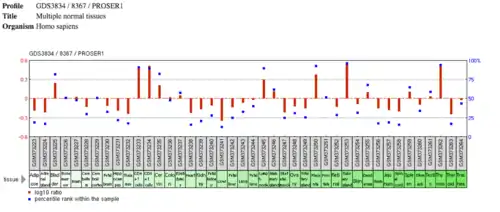
Expressed Sequence Tag mapping of PROSER1 expression shows that it has particularly high expression in lymph, embryonic tissue, thymus, and uterus sites. It has moderate expression in testis, larynx, nerve, blood, and adipose tissue sites.[8] According to the Human Protein Atlas, PROSER1 has general cytoplasmic expression and is expressed in all RNA tissue categories.[9]
Homology
Paralogs
PROSER1 has no paralogs.[10]
Orthologs
PROSER1 is highly conserved among mammals. It is less highly conserved, though has been found, in fish, birds, and some invertebrates. It is not expressed in bacteria, plants, or fungi.[11] Show below is table of orthologs compiled from NCBI.
| Latin name | Common name | Date of divergence (from H. sapiens) | Accession number | Protein sequence length | Sequence identity | Sequence similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | - | NP_079414.3 | 944 amino acids | - | - |
| Gorilla gorilla | Gorilla | 8.9 million years ago | XP_004054459 | 994 aa | 99% | 99% |
| Colobus angolensis palliatus | Angola colobus | 29.1 MYA | XP_011798372 | 947 aa | 97% | 97% |
| Nannospalax galili | Spalax | 90.9 MYA | XP_008847583 | 916 aa | 80% | 85% |
| Cricetulus griseus | Chinese Hamster | 90.9 MYA | XP_007626898 | 912 aa | 79% | 84% |
| Panthera tigris altaica | Siberian Tiger | 97.5 MYA | XP_007097793 | 665 aa | 85% | 89% |
| Acinonyx jubatus | Cheetah | 97.5 MYA | XP_014926409 | 770 aa | 79% | 83% |
| Tursiops truncatus | Common Bottlenose Dolphin | 97.5 MYA | XP_004332367 | 1064 aa | 77% | 83% |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | 179.2 MYA | XP_007666895 | 888 aa | 69% | 74% |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Sea Turtle | 320.5 MYA | XP_007070970 | 936 aa | 75% | 83% |
| Pygoscelis adeliae | Adelie Penguin | 320.5 MYA | XP_009318201 | 938 aa | 75% | 83% |
| Calidris (philomachus) pugnax | Ruff | 320.5 MYA | XP_014821534 | 899 aa | 74% | 83% |
| Chrysemys picta bellii | Painted Turtle | 320.5 MYA | XP_008175998 | 825 aa | 73% | 82% |
| Aquila chrysaetos Canadensis | Golden Deagle | 320.5 MYA | XP_011579121 | 916 aa | 73% | 81% |
| Alligator sinensis | Chinese Alligator | 320.5 MYA | XP_014376376 | 940 aa | 72% | 81% |
| Gekko japonicus | Japanese Gecko | 320.5 MYA | XP_015281837 | 1053 aa | 65% | 75% |
| Python bivittatus | Burmese Python | 320.5 MYA | XP_007438154 | 924 aa | 65% | 75% |
| Anolis carolinensis | Carolina Anole | 320.5 MYA | XP_008124125 | 920 aa | 64% | 75% |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Western Clawed Frog | 355.7 MYA | XP_012813331 | 944 aa | 51% | 63% |
| Lepisosteus oculatus | Spotted Gar | 429.6 MYA | XP_015197497 | 885 aa | 47% | 58% |
| Callorhinchus milii | Australian Ghost Shark | 482.9 MYA | XP_007889503 | 965 aa | 64% | 75% |
Protein
General properties
The translated PROSER1 protein is 944 amino acids long. Its predicted molecular weight is 95.7 kdal.[12] PROSER1 has an isoelectric point of 9.[13] It is predicted to be localized to the nucleus.[14]
Composition
The sequence is rich in proline and serine and not particularly low in any other amino acids.
Domains
PROSER1 contains one domain of unknown function, DUF 4476, part of pfam14771. The DUF spans from amino acids 26 to 121. The molecular weight of DUF 4476 is 11.1 kdal.
Secondary structure
PROSER1 is composed primarily of alpha helices, beta sheets, and coils. The protein is largely coiled. The DUF is composed mainly of alpha helices and coils. It has slightly fewer beta sheets compared to the protein as a whole.[15]
References
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "GeneCards". Human Gene Database.
- "BioCompare". BioCompare.
- "Ensembl". Ensembl.
- "GeneCards". Human Gene Database.
- "NCBI Gene". NCBI.
- "NCBI Gene". NCBI.
- "Uniprot". Uniprot.
- "Tissue Atlas". The Human Protein Atlas.
- "Ensembl". Ensembl.
- "Ensembl". Ensembl.
- "Uniprot". Uniprot.
- "Expasy". Expasy.
- "PSORT II Prediction". PSORT II.
- "SDSC Biology Workbench". SDSC.