Proroxan
Proroxan (INN; also known as pyrroxane and pirroksan) is a pharmaceutical drug used as an antihypertensive and in the treatment of Ménière’s disease, motion sickness, and allergic dermatitis.[1][2]
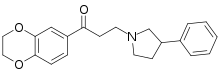 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pyrroxane, Pirroksan |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 337.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Proroxan is a non-selective alpha-blocker (α-adrenoreceptor antagonist).[1]
Proroxan was developed in the 1970s at the Institute of Toxicology of the USSR Ministry of Health[3] and today is primarily used in Russia. Though originally developed as an antihypertensive, its use can lead to a decrease in alcohol and drug consumption. Currently proroxan is used almost exclusively in psychiatry, narcology, and neurology.[3]
References
- "Proroxan hydrochloride". Inxight Drugs. National Institutes of Health.
- "ПРОРОКСАН (PROROXAN) ОПИСАНИЕ". vidal.ru.
- Shabanov PD (2020). "Clinical pharmacology of pyrroxane (proroxane)". Reviews on Clinical Pharmacology and Drug Therapy (in Russian). 18 (4): 335–350. doi:10.17816/RCF184335-350. S2CID 234440112.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.