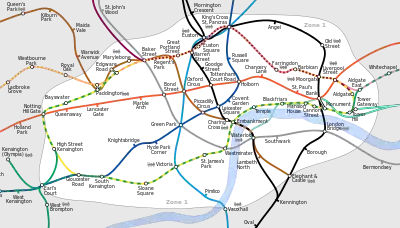
Portal:London transport
|
|
|
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals













%252C_Showbus_2012_rally.jpg.webp)




_building.JPG.webp)



.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)



_(geograph_4758436).jpg.webp)
_engraving.jpg.webp)



_2011_New_Bus_for_London%252C_Victoria%252C_route_38%252C_27_February_2012.jpg.webp)












_Railway_Poster%252C_1905.png.webp)

.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)