Piracy is theft
"Piracy is theft" was a slogan used by the UK non-profit organisation Federation Against Software Theft.[1][2] It was first used in the 1980s and has since then been used by other similar organisations such as the Motion Picture Association of America.[3] It has also been used as a statement, and that has been acknowledged as being accurate.
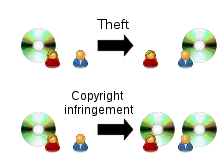
Copyright holders frequently refer to copyright infringement as theft, and such use has been accepted by legislatures and courts.[4] In copyright law, infringement refers to theft of physical objects that take away the owner's possession, but an instance where a person exercises one of the exclusive rights of the copyright holder without authorisation.[5] Courts have distinguished between copyright infringement and theft.[4] For instance, the United States Supreme Court held in Dowling v. United States (1985) that bootleg phonorecords did not constitute stolen property. Instead,
"interference with copyright does not easily equate with theft, conversion, or fraud. The Copyright Act even employs a separate term of art to define one who misappropriates a copyright: '[...] an infringer of the copyright.'"
The court said that in the case of copyright infringement, the province guaranteed to the copyright holder by copyright law – certain exclusive rights – is invaded, but no control, physical or otherwise, is taken over the copyright, nor is the copyright holder wholly deprived of using the copyrighted work or exercising the exclusive rights held.[6]
See also
- Beware of illegal video cassettes
- Don't Copy That Floppy
- Home Recording Rights Coalition
- Home Taping Is Killing Music
- Knock-off Nigel
- Property is theft!
- Public information film (PIF)
- Public service announcement
- Sony Corp. of America v. Universal City Studios, Inc.
- Spin (public relations)
- Steal This Film
- The Pirate Bay
- Who Makes Movies?
- You can click, but you can't hide
- You Wouldn't Steal a Car
References
- http://www.ntk.net/2002/11/29/elspa.gif
- "CLASSIC ANTI-PIRACY ADS". worldofstuart.excellentcontent.com.
- "Technology News, Analysis, Comments and Product Reviews for IT Professionals". ZDNet.
- Patry, William (2009). Moral Panics and the Copyright Wars. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-19-538564-9.
- Clough, Jonathan (2010). Principles of Cybercrime. Cambridge University Press. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-521-72812-6.
- Dowling v. United States (1985), 473 U.S. 207, pp. 217–218.