Pforzen buckle
The Pforzen buckle is a silver belt buckle found in Pforzen, Ostallgäu (Schwaben) in 1992. The Alemannic grave in which it was found (no. 239) dates to the end of the 6th century and was presumably that of a warrior, as it also contained a spear, spatha, seax and shield. The buckle is of the Alemannic Weingarten type (Babucke 1999).
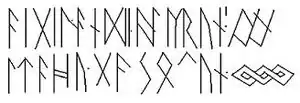
Inscription
The buckle bears a runic inscription on its front, incised after its manufacture:
- aigil andi aïlrun [ornament or bind-rune]
- ltahu (or elahu) gasokun [ornamental braid]
Linguistic analysis of the inscription reveals that it was composed in an early High German dialect and is the oldest preserved line of alliterative verse in German. However, scholars have yet to reach a consensus as to its translation.
Interpretations
Wagner (1995) reads the final ornament in line 1 as a bind rune consisting of ![]()
![]()
![]() (angi) and connects this directly with the beginning of line 2, producing angiltahu. He translates the inscription as "Aigil and Ailrun scolded Angiltah". However, this interpretation has been criticized (Düwel 2001) on the grounds that (1) the scribe had no apparent reason to resort to a complex bind-rune for part of the inscription and (2) a ‘scolding’ does not seem to be worthy of an inscription on an object interred with the remains of a warrior.
(angi) and connects this directly with the beginning of line 2, producing angiltahu. He translates the inscription as "Aigil and Ailrun scolded Angiltah". However, this interpretation has been criticized (Düwel 2001) on the grounds that (1) the scribe had no apparent reason to resort to a complex bind-rune for part of the inscription and (2) a ‘scolding’ does not seem to be worthy of an inscription on an object interred with the remains of a warrior.
Düwel (2001) reads the end of line 1 as a simple ornament and the beginning of line 2 as a bind-rune formed of ![]()
![]() (el), producing the transliteration elahu, which would represent an acc. pl. of elah(h)o "elk, stag". The whole is then read as Áigil andi Áilrun élahu[n] gasókun. The verb gasókun is understood as an early form of Old High German gasahhan "forsake, deny, repent", and translated as “Aigil and Ailrun damned the stags (i.e. the stag masquerades)”. This is seen as a reference to the heathen tradition of dressing up in the skins of stags as part of New Year celebrations. Thus the inscription is to be understood as the record of the declaration of a couple (Aigil and Ailrun) to forsake participation in the celebration, possibly as a sign of their acceptance of Christianity.
(el), producing the transliteration elahu, which would represent an acc. pl. of elah(h)o "elk, stag". The whole is then read as Áigil andi Áilrun élahu[n] gasókun. The verb gasókun is understood as an early form of Old High German gasahhan "forsake, deny, repent", and translated as “Aigil and Ailrun damned the stags (i.e. the stag masquerades)”. This is seen as a reference to the heathen tradition of dressing up in the skins of stags as part of New Year celebrations. Thus the inscription is to be understood as the record of the declaration of a couple (Aigil and Ailrun) to forsake participation in the celebration, possibly as a sign of their acceptance of Christianity.
Nedoma (2004) also sees the end of line 1 as ornament, yet reads the beginning of line 2 as a bind-rune composed of ![]()
![]() (íl), and the whole as Áigil andi Áilrun | Íltahu gasōkun. This would translate as "Aigil and Ailrun fought at the Ilz river". This is seen as a reference to Egil, the heroic archer of Norse mythology, who is depicted on the lid of the Auzon Runic or Franks Casket together with his wife (presumably Ailrun) engaged in battle. The casket is thought to date to approximately the same time as the Pforzen buckle.
(íl), and the whole as Áigil andi Áilrun | Íltahu gasōkun. This would translate as "Aigil and Ailrun fought at the Ilz river". This is seen as a reference to Egil, the heroic archer of Norse mythology, who is depicted on the lid of the Auzon Runic or Franks Casket together with his wife (presumably Ailrun) engaged in battle. The casket is thought to date to approximately the same time as the Pforzen buckle.
Looijenga (2003) argues that the inscription shows evidence of scribal error. Assuming that the verse alliterates, she interprets the ![]() at the beginning of line 2 as indicative of an original [a]l. Her amended reading runs Aigil andi Ailrūn | (a)l tahu gasokun, which she translates as "Aigil and Ailrun vigorously fought/condemned all". She also suggests that the text could be a quotation from a lost version of the Wieland story.
at the beginning of line 2 as indicative of an original [a]l. Her amended reading runs Aigil andi Ailrūn | (a)l tahu gasokun, which she translates as "Aigil and Ailrun vigorously fought/condemned all". She also suggests that the text could be a quotation from a lost version of the Wieland story.
Simmons (2010) likewise takes the first element as representing al- "all, entire", but takes the second element as the dative (singular or plural) of an ablaut variant of the Old English word teoh "army, war-band", with the compound meaning "the entire war-band". Simmons notes that gasokun "fought" (preterite 3rd plural indicative) requires a dative object, which is furnished in al-tahu. He translates the buckle inscription, "Aigil and Alrun fought the entire war-band." Simmons confirms that the writing on the Pforzen buckle refers to the same Germanic character depicted on the Franks Casket (Aegil), and argues that this translation of the buckle line best accords with the figuration on the casket lid, each representing the same legend of "two against all comers".
Mees (2017) accepts that Aigil and Ailrun are a heroic pair and compares the buckle to contemporary Burgundian plate-buckles that feature references to the Biblical story of Daniel in the lions' den. Mees rejects Nedoma's reading of ltahu as a river name and compares the form instead to the Old Saxon name Aldako. Mees sees the inscription as a historiola, much like the texts found on the Burgundian Daniel buckles evidently are.
See also
References
- Volker Babucke, Die Runenschnalle von Pforzen (Allgäu) — Aspekte der Deutung. l. Zur Herkunft und Datierung in: Pforzen und Bergakker: Neue Untersuchungen zu Runen inschriften, ed. Alfred Bammesberger (1999), 15–24.
- Klaus Düwel, Runenkunde, Weimar (2001), 19–20. (ISBN 3-476-13072-X)
- Tineke Looijenga, Texts & Contexts of the Oldest Runic Inscriptions", Brill (2003), 253–255. (ISBN 90-04-12396-2)
- Bernard Mees, Egill and Ǫlrún in Early High German in: Futhark 8, 2017. 151–56. (http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1333698/FULLTEXT01.pdf)
- Robert Nedoma, Noch einmal zur Runeninschrift auf der Gürtelschnalle von Pforzen in: Alemannien und der Norden, ed. Naumann (2004), 340–370.
- Austin Simmons, The Cipherment of the Franks Casket. (https://web.archive.org/web/20120303013402/http://homeros.godsong.org/FRANKS_CASKET.pdf)
- Norbert Wagner, Zu den Runeninschriften von Pforzen und Nordendorf in: Historische Sprachforschung 108, 1995. 104–112.