Parallelogon
In geometry, a parallelogon is a polygon with parallel opposite sides (hence the name) that can tile a plane by translation (rotation is not permitted).[1][2]

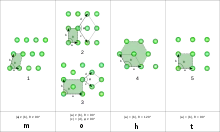
Parallelogons have an even number of sides and opposite sides that are equal in length. A less obvious corollary is that parallelogons can only have either four or six sides;[1] Parallelogons have 180-degree rotational symmetry around the center.
A four-sided parallelogon is called a parallelogram.
The faces of a parallelohedron (the three dimensional analogue) are called parallelogons.[2]
Two polygonal types
Quadrilateral and hexagonal parallelogons each have varied geometric symmetric forms. They all have central inversion symmetry, order 2. Every convex parallelogon is a zonogon, but hexagonal parallelogons enable the possibility of nonconvex polygons.
| Sides | Examples | Name | Symmetry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Parallelogram | Z2, order 2 | ||
| Rectangle & rhombus | Dih2, order 4 | |||
| Square | Dih4, order 8 | |||
| 6 | 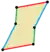 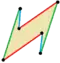 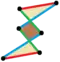 | Elongated parallelogram | Z2, order 2 | |
| Elongated rhombus | Dih2, order 4 | |||
| Regular hexagon | Dih6, order 12 | |||
Geometric variations
A parallelogram can tile the plane as a distorted square tiling while a hexagonal parallelogon can tile the plane as a distorted regular hexagonal tiling.
| 1 length | 2 lengths | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Skew | Right | Skew |
 Square p4m (*442) |
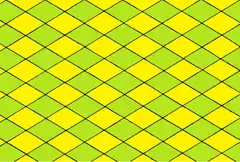 Rhombus cmm (2*22) |
 Rectangle pmm (*2222) |
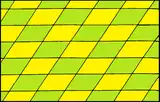 Parallelogram p2 (2222) |
| 1 length | 2 lengths | 3 lengths | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
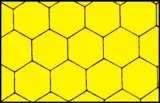 |
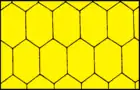 |
 |
 |
 |
| Regular hexagon p6m (*632) |
Elongated rhombus cmm (2*22) |
Elongated parallelogram p2 (2222) | ||
References
- Aleksandr Danilovich Alexandrov (2005) [1950]. Convex Polyhedra. Translated by N.S. Dairbekov; S.S. Kutateladze; A.B. Sosinsky. Springer. p. 351. ISBN 3-540-23158-7. ISSN 1439-7382.
- Grünbaum, Branko (2010-12-01). "The Bilinski Dodecahedron and Assorted Parallelohedra, Zonohedra, Monohedra, Isozonohedra, and Otherhedra". The Mathematical Intelligencer. 32 (4): 5–15. doi:10.1007/s00283-010-9138-7. hdl:1773/15593. ISSN 1866-7414. S2CID 120403108. PDF
- The facts on file: Geometry handbook, Catherine A. Gorini, 2003, ISBN 0-8160-4875-4, p.117
- Grünbaum, Branko; Shephard, G. C. (1987). Tilings and Patterns. New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-1193-1. list of 107 isohedral tilings, p.473-481