Oxytocin receptor agonist
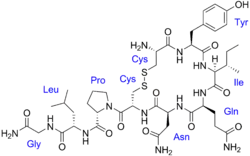
An oxytocin receptor agonist is a compound that acts as an agonist of the oxytocin receptor.[1][2] Examples include peptide oxytocin receptor agonists like oxytocin (Pitocin, Syntocinon), carbetocin (Duratocin, Pabal), and demoxytocin (Sandopart) and small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists like TC OT 39, WAY-267464, and LIT-001.[1][2] Oxytocin receptor agonists are used medically to induce labor, promote lactation, and for other uses.[3] In addition, oxytocin receptor agonists are of theoretical interest for the potential treatment of social disorders, such as autism and social anxiety.[1][2] Small-molecule oxytocin receptor agonists are considered to be more promising for such uses due to better pharmacokinetic profiles, such as blood–brain barrier permeability, elimination half-lives, and potential for oral bioavailability.[1][2]
References
- Nashar PE, Whitfield AA, Mikusek J, Reekie TA (2022). "The Current Status of Drug Discovery for the Oxytocin Receptor". Oxytocin. Methods Mol Biol. Vol. 2384. pp. 153–174. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1759-5_10. ISBN 978-1-0716-1758-8. PMID 34550574. S2CID 239090096.
- Gulliver D, Werry E, Reekie TA, Katte TA, Jorgensen W, Kassiou M (January 2019). "Targeting the Oxytocin System: New Pharmacotherapeutic Approaches". Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40 (1): 22–37. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2018.11.001. PMID 30509888. S2CID 54559394.
- Viero C, Shibuya I, Kitamura N, Verkhratsky A, Fujihara H, Katoh A, Ueta Y, Zingg HH, Chvatal A, Sykova E, Dayanithi G (October 2010). "REVIEW: Oxytocin: Crossing the bridge between basic science and pharmacotherapy". CNS Neurosci Ther. 16 (5): e138–56. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00185.x. PMC 2972642. PMID 20626426.