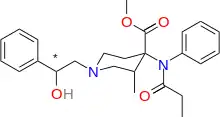
Ohmecarfentanil
Ohmecarfentanil (RTI-4614-38), also known as Ohlofentanil, is a mu opioid receptor agonist from the class of fentanyl analogues which was found to be 30,000 times more potent than morphine in the rhesus monkey single dose suppression test.[1] This makes ohmecarfentanil, along with some closely related analogues, among the most potent opioid agonists known at this time, even surpassing lofentanil and ohmefentanyl.
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H32N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 424.541 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
See also
References
- Carroll FI, Lewin AH, Mascarella SW, Seltzman HH, Reddy PA (April 2021). "Designer drugs: a medicinal chemistry perspective (II)". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1489 (1): 48–77. Bibcode:2021NYASA1489...48C. doi:10.1111/nyas.14349. PMID 32396701. S2CID 218617085.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.