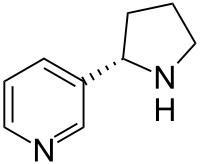
Nornicotine
Nornicotine is an alkaloid found in various plants including Nicotiana, the tobacco plant. It is chemically similar to nicotine, but does not contain a methyl group.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[(2S)-2-Pyrrolidinyl]pyridine | |
| Other names
Demethylnicotine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.165.066 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 148.209 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is a precursor to the carcinogen N-nitrosonornicotine that is produced during the curing and processing of tobacco.[1] Nornicotine can react in human saliva to form N-nitrosonornicotine,[2] a known type 1 carcinogen.[3]
Synthesis
There are several routes for the synthesis of nornicotine. One route is the demethylation of nicotine, which can be accomplished by reaction with silver oxide.[4]
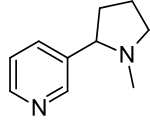
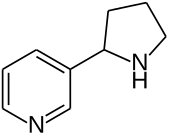
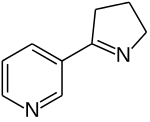
Another route is the partial reduction of 3-myosmine, which can be accomplished by standard catalytic hydrogenation conditions using palladium as a catalyst[5] or with sodium borohydride.[6] This reaction gives the racemic product.

Pharmacology
Nornicotine possess high affinity for alpha-6 and alpha-7 subunits of nAChRs.[7] It also inhibits DAT in striatum via nAChR and releases dopamine in rats.[8][9][10]
References
- Siminszky, B. (2005). "Conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in Nicotiana tabacum is mediated by CYP82E4, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (41): 14919–24. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506581102. PMC 1253577. PMID 16192354.
- Knezevich A, Muzic J, Hatsukami DK, Hecht SS, Stepanov I (February 2013). "Nornicotine nitrosation in saliva and its relation to endogenous synthesis of N'-nitrosonornicotine in humans". Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 15 (2): 591–5. doi:10.1093/ntr/nts172. PMC 3611998. PMID 22923602.
- "List of Classifications – IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans". monographs.iarc.fr. Retrieved 2020-07-22.
- Spaeth (1936). "Über dasd-Nor-nicotin". Chem. Ber. 69 (2): 250–251. doi:10.1002/cber.19360690207.
- Haines (1945). "Chemical Reactivity of Myosmine". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 67 (8): 1258–1260. doi:10.1021/ja01224a011.
- Dickerson, TJ; Janda, KD (2002). "Aqueous aldol catalysis by a nicotine metabolite". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124 (13): 3220–1. doi:10.1021/ja017774f. PMID 11916401..
- Papke RL, Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA (April 2007). "The pharmacological activity of icotine and nornicotine on nAChRs subtypes: relevance to nicotine dependence and drug discovery". Journal of Neurochemistry. 101 (1): 160–7. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04355.x. PMID 17241116.
- Middleton LS, Crooks PA, Wedlund PJ, Cass WA, Dwoskin LP (March 2007). "Nornicotine inhibition of dopamine transporter function in striatum via nicotinic receptor activation". Synapse (New York, N.Y.). 61 (3): 157–65. doi:10.1002/syn.20351. PMID 17146768. S2CID 35071082.
- Dwoskin LP, Teng LH, Crooks PA (September 2001). "Nornicotine, a nicotine metabolite and tobacco alkaloid: desensitization of nicotinic receptor-stimulated dopamine release from rat striatum". European Journal of Pharmacology. 428 (1): 69–79. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01283-3. PMID 11779039.
- Dwoskin LP, Buxton ST, Jewell AL, Crooks PA (June 1993). "S(-)-nornicotine increases dopamine release in a calcium-dependent manner from superfused rat striatal slices". Journal of Neurochemistry. 60 (6): 2167–74. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03502.x. PMID 8492124. S2CID 25622404.