Nodoid
In differential geometry, a nodoid is a surface of revolution with constant nonzero mean curvature obtained by rolling a hyperbola along a fixed line, tracing the focus, and revolving the resulting nodary curve around the line.[1]
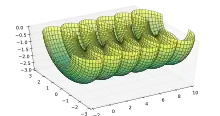
Half of a nodoid surface.
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.