Nebraska's 2nd congressional district
Nebraska's 2nd congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of Nebraska that encompasses the core of the Omaha–Council Bluffs metropolitan area. It includes all of Douglas County, which includes the state's largest city Omaha; it also includes Saunders County and areas of Western Sarpy County. It has been represented in the United States House of Representatives since 2017 by Don Bacon, a member of the Republican Party. It was one of 18 districts that would have voted for Joe Biden in the 2020 presidential election had they existed in their current configuration while being won or held by a Republican in 2022. With a Cook Partisan Voting Index rating of EVEN, it is the least Republican district in Nebraska, a state with an all-Republican congressional delegation.[2]
| Nebraska's 2nd congressional district | |||
|---|---|---|---|
.png.webp) Nebraska's 2nd congressional district since January 3, 2023 | |||
| Representative |
| ||
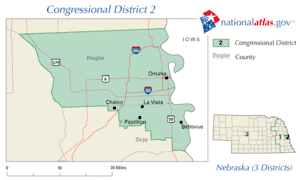
| Distribution |
| ||
| Population (2022) | 658,116 | ||
| Median household income | $77,535[1] | ||
| Ethnicity | |||
| Cook PVI | EVEN[2] | ||
History
While the rest of the state's electorate tends to be solidly Republican, the 2nd district is much more closely divided between the Republican and Democratic parties.[3] In the 2010s, the district has become known as a swing district; it was one of two districts with a margin of less than 5% in all elections held after the 2010 census. Since 2000, it has backed the electoral winner of the presidential election with the exception of 2012.
Since 1992, Nebraska is one of only two states in the United States that distributes their electoral votes for president by both congressional district and statewide popular vote (the other being Maine). In the 2008 United States presidential election, Democratic presidential candidate Barack Obama targeted the district as a strategy of breaking a potential electoral-vote tie.[4] He won the district's electoral vote by a margin of 3,325 votes over Republican John McCain, who won the state's other four electoral votes.[5] Obama's victory in the 2nd district meant that Nebraska's electoral delegation was split for the first time ever, and the first Nebraskan electoral vote for a Democrat since 1964.[5] However, he subsequently failed to win the district in 2012 against Mitt Romney.[6] In 2014, longtime Representative Lee Terry, a Republican, was ousted by Democratic challenger Brad Ashford, one of only two Republican incumbents that cycle to lose their seat.[7]
In 2016, Republican Donald Trump won only a plurality of the 2nd district over Democrat Hillary Clinton; he won only 2% over Clinton, a sharp reduction of Romney's seven-point advantage over Obama. In 2020, Trump notably targeted the district in a fashion similar to Obama as Democrat Joe Biden polled at an advantage in the district.[8] Trump's campaigning in the district drew criticism after rally attendees were left stranded in freezing temperatures due to transportation issues.[9] Biden ultimately won in the district over Trump by six points, nearly matching Romney's margin over Obama.[10] Precious McKesson cast the electoral vote, making her the first woman of color in the state to cast an Electoral college ballot.[11][12]
Demographics
According to the APM Research Lab's Voter Profile Tools[13] (featuring the U.S. Census Bureau's 2019 American Community Survey), the district contained about 473,000 potential voters (citizens, age 18+). Of these, 80% are White, 9% Black, and 6% Latino. Immigrants make up 5% of the district's potential voters.The median income among households (with one or more potential voters) in the district is about $73,400, while 8% of households live below the poverty line. As for the educational attainment of potential voters in the district, 40% hold a bachelor's or higher degree.
Redistricting controversies
During redistricting in 2011, state lawmakers removed the city of Bellevue — an area with a large minority population — and Offutt Air Force Base from the district, and moved it to Omaha's Republican-heavy suburbs in western Sarpy County. The move was criticized by Democrats as a gerrymander meant to dilute the urban vote due its support of Obama in 2008.[14]
Following its support of Joe Biden in the 2020 election, State Senator Lou Ann Linehan proposed a new map that would again dilute the Democratic vote by splitting the city of Omaha into two separate districts, and adding heavily Republican-leaning Sarpy and Saunders Counties.[15][16] State Senator Justin Wayne proposed an alternative map that would restore the map to its pre-2011 movement by adding Bellevue back to the district and remove areas that lean Republican. Linehan's congressional redistricting plan passed the committee 5-4 on a party-line vote, but failed a cloture vote following a filibuster; both maps received bipartisan criticism for splitting Douglas and/or Sarpy counties.[16] The legislature ultimately passed a map that kept Douglas County intact, while retaining rural parts in Western Sarpy County and adding the rural Saunders County. The resulting maps have again been criticized as gerrymanders, and both Linehan's and the final maps have again been characterized as diluting urban voters.[17]
Election results from statewide races
| Year | Office | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1992 | President | George H.W. Bush 48% – Bill Clinton 32% |
| 1996 | President | Bob Dole 53% – Bill Clinton 38% |
| 2000 | President | George W. Bush 57% – Al Gore 39% |
| 2004 | President | George W. Bush 60% – John Kerry 38% |
| 2008 | President | Barack Obama 50% – John McCain 49% |
| 2012 | President | Mitt Romney 53% – Barack Obama 46% |
| 2016 | President | Donald Trump 48% – Hillary Clinton 46% |
| 2020 | President | Joe Biden 52% – Donald Trump 46% |
| 2022 | Governor | Jim Pillen 48.2% – Carol Blood 48.1% |
List of members representing the district
Election history
2006
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lee Terry (Incumbent) | 99,475 | 54.7% | −6.4% | |
| Democratic | Jim Esch | 82,504 | 45.3% | +9.1% | |
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 181,979 | ||||
2008
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lee Terry (Incumbent) | 142,473 | 51.9% | −2.8% | |
| Democratic | Jim Esch | 131,901 | 48.1% | +2.8% | |
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 274,374 | ||||
2010
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lee Terry (Incumbent) | 93,840 | 60.8% | +8.9% | |
| Democratic | Tom White | 60,486 | 39.2% | −8.9% | |
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 154,326 | ||||
2012
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lee Terry (Incumbent) | 133,964 | 50.8% | −10.0% | |
| Democratic | John Ewing | 129,767 | 49.2% | +10.0% | |
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 263,731 | ||||
2014
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Brad Ashford | 83,872 | 49.0% | −0.2% | |
| Republican | Lee Terry (Incumbent) | 78,157 | 45.7% | −5.1% | |
| Libertarian | Steven Laird | 9,021 | 5.3% | +5.3% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 171,050 | ||||
2016
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Don Bacon | 141,066 | 48.9% | +3.2% | |
| Democratic | Brad Ashford (Incumbent) | 137,602 | 47.7% | −1.3% | |
| Libertarian | Steven Laird | 9,640 | 3.3% | −2.0% | |
| Republican gain from Democratic | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 288,308 | ||||
2018
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Don Bacon (Incumbent) | 126,715 | 51.0% | +2.1% | |
| Democratic | Kara Eastman | 121,770 | 49.0% | +1.3% | |
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
| Turnout | 248,485 | ||||
2020
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Don Bacon (Incumbent) | 171,071 | 50.8% | -0.2% | |
| Democratic | Kara Eastman | 155,706 | 46.2% | -2.8% | |
| Libertarian | Tyler Schaeffer | 10,185 | 3% | +3% | |
| Turnout | 336,962 | ||||
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
2022
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Don Bacon (incumbent) | 112,663 | 51.33% | |
| Democratic | Tony Vargas | 106,807 | 48.67% | |
| Total votes | 219,470 | 100.0% | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
References
- Center for New Media & Promotion (CNMP), US Census Bureau. "My Congressional District". www.census.gov.
- "2022 Cook PVI: District Map and List". Cook Political Report. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- Sanderford, Aaron (November 15, 2022). "In Nebraska's Sea of Red, few felt splash from 'Republican wave'". Nebraska Examiner. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
Nebraska's most competitive congressional race in the Omaha area is starting to settle into a pattern that nearly matches the district's 4 percentage point GOP registration advantage. An analysis of 2nd District election results and voting patterns show U.S. Rep. Don Bacon did not secure more votes this year than in 2020 or 2018.
- Curry, Tom (November 2, 2008). "Is Obama-Terry the winning ticket in Omaha?". NBC News. Retrieved November 20, 2008.
If the national electoral vote tally is close, then the one electoral vote in Omaha would loom large. But with Obama apparently ahead in competitive states such as Virginia, the presidency may not hinge on Omaha's vote.
- Staff reporter (November 14, 2008). "Obama wins 1 of Nebraska's electoral votes". NBC News. Retrieved October 17, 2009.
- Walton, Don (November 7, 2012). "Romney wins 2nd District electoral vote". Lincoln Journal Star. Retrieved December 12, 2022.
Republican nominee Mitt Romney appeared to have won the battle for Nebraska's only competitive presidential electoral vote Tuesday night. [...] Romney held comfortable leads in both the 1st District, which includes Lincoln, and the vast 3rd District, as well as statewide.
- Robertson, Ryan; Peterson, Lindsey (November 5, 2014). "Lee Terry concedes 2nd Dist. to Brad Ashford". Nebraska Public Media. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
- "The Latest: Trump heaping attention on 1 Nebraska district". Associated Press. October 27, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
- Zeleny, Jeff (October 28, 2020). "Hundreds stranded in the cold waiting for buses in chaotic post-Trump rally scene". CNN. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- "Joe Biden wins one electoral vote from Nebraska's District 2". KETV. November 4, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
- Sanderford, Aaron (November 29, 2020). "The Elector: Precious McKesson will cast Nebraska's 2nd District electoral vote for Biden". Omaha World-Herald. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- Behrmann, Savannah (December 15, 2020). "First woman of color elector in Nebraska casts Electoral College vote for Joe Biden". USA Today. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- "Representing US: 2020 Voter Profiles". APM Research Lab. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- Schulte, Grant (May 27, 2011). "Nebraska Redistricting Maps Approved". AP. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- "Nebraska redistricting panel hits impasse, turns to public".
- "First-round debate begins on congressional redistricting plan". September 17, 2021.
- Kipper, Jon (January 28, 2022). "Nebraska's redistricting maps finalized for now, but Unicameral's methods still questioned". KMTV. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
- Evnen, Robert B. (November 8, 2022). 2022 General Canvass Book (PDF). Nebraska Secretary of State. p. 10. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Congressional Biographical Directory of the United States 1774–present
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)







.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)







.tif.png.webp)
.jpg.webp)
