NCSoft
NCSoft Corporation (Korean: 엔씨소프트, stylized as NC, formerly stylized as NCSOFT) is a South Korean video game developer and publisher headquartered in Pangyo, Seongnam, South Korea, primarily known for the distribution of massively multiplayer online role-playing games such as Lineage and Guild Wars.
 | |
Native name | 엔씨소프트 |
|---|---|
| Type | Public company |
| KRX: 036570 | |
| Industry | Video games |
| Founded | 11 March 1997 |
| Founder | Kim Taek Jin |
| Headquarters | Pangyo, Seongnam, South Korea |
Key people | Kim Taek Jin (CEO) |
| Products | See complete list of products |
| Revenue |
|
| |
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
| Owner |
|
Number of employees | 3100 |
| Website | ncsoft |
| Footnotes / references [2] | |
_from_acrofan.jpg.webp)
History
NCSoft was founded in March 1997 by Kim Taek Jin. In September 1998, NCSoft launched its first game Lineage. In April 2001 the company created a US subsidiary under the name NC Interactive (based in Austin, Texas, and would later become NCSoft West) after acquiring Destination Games, headed by Richard Garriott and Robert Garriott.[4] In 2004, NCSoft launched two MMORPGs, Lineage II and City of Heroes.[5]
The company formed NCSoft Europe in July 2004 as a wholly owned subsidiary with its main office in Brighton, England. They brought City of Heroes to several European countries on February 4, 2005, and have since established European service for WildStar and Blade & Soul as well.
On April 26, 2005, NCSoft published Arenanet's first MMO Guild Wars Prophecies as well as Arenanets follow up campaigns Factions and Nightfall and the expansion Eye of the North. NCSoft also published Guild Wars 2 but stopped being the publisher for Guild Wars 2 in 2015 with the release of Heart of Thorns.
On September 10, 2008, NCSoft announced the formation of NCSoft West, a subsidiary which manages NCSoft's other western organizations, and established its headquarters for that subsidiary in Seattle, Washington.[6] On July 28, 2021, NCSoft announced that it was adding the talents of long-time video game industry veteran Jeffrey Anderson (game designer) to its executive leadership team as the new CEO of NCSoft West, overseeing its games business in the Americas, EMEA, and Oceana regions.[7]
On July 8, 2011, NCSoft started talks with SK Telecom to acquire Ntreev Soft Co., Ltd.[8] The talks were expected to last less than a month, but it took seven for NCSoft to complete the acquisition; purchasing 76% of Ntreev's stock for ₩108 billion (US$96.7 million) on February 15, 2012.[9]
In 2011, NCSoft purchased Hotdog Studio, a mobile game studio based in Seoul that produces phone and smartphone titles such as Dark Shrine.[10]
In June 2012, NCSoft launched Blade & Soul, their first MMORPG since Aion launched in 2006.
In 2012 Nexon acquired a 14.7 percent interest in NCSoft for $688 million.[11] Nexon sold all of its shares of NCSoft in October 2015.
On November 19, 2015, NCSoft West announced the formation of Iron Tiger studios, a developer based in San Mateo, California focused on adapting Korean-made mobile titles for the West, as well as developing their own mobile games.[12]
On August 21, 2020, NCSoft entered the Korean entertainment industry by launching a new subsidiary called "Klap Co., Ltd."[13] Klap and NCSoft launched the entertainment platform UNIVERSE on January 28, 2021.[14]
In March 2022, the Public Investment Fund of Saudi Arabia acquired a 9.26 percent stake in NCSoft, becoming the company's second largest shareholder after Kim Taek Jin.[1]
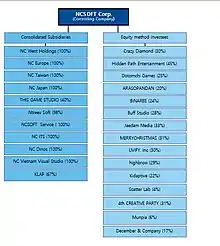
Subsidiaries
Current
- ArenaNet
- Iron Tiger Studios
- Ntreev Soft
- NC Dinos
Controversies
Stolen source code
On April 27, 2007, Seoul Metropolitan Police said that seven former employees of NCSoft are suspected of selling the Lineage III source code to a major Japanese game company.[16] According to NCSoft, the potential damages may exceed US$1 billion.[17]
Worlds.com patent lawsuit
Worlds.com CEO Thom Kidrin claimed the idea of a "scalable virtual world with thousands of users" is patented by his organization[18] and targeted NCSoft for patent infringement in 2008,[19] in what he says will be the first of many lawsuits against MMO developers.[18] On April 23, 2010, the Worlds.com case settled, but the terms of the settlement were kept confidential. On July 22, 2010, Worlds.com requested the case be reopened.
Richard Garriott termination
Richard Garriott, lead developer of the failed MMORPG Tabula Rasa, sued NCSoft for US$24 million in damages concerning his termination from the company. Garriott asserted in his suit that he was forced out of the company and was made to sell his 400,000 shares in NCSoft's stock, costing him millions of dollars. In addition, he claimed that the company was guilty of fraud by forging his resignation announcement.[20] On July 30, 2010, a jury in a Texas federal court awarded him US$28 million in damages. NCSoft described Garriott as someone "who keeps finding different ways to turn the company into his personal ATM," and that "Garriott left the company voluntarily to catch his ride to the International Space Station." Citing his questionable work ethic and the failure of his video game project despite an $84.4 million investment, NCSoft pulled the plug on the game after which Garriott announced he would be leaving the company. This came after he boarded a much-publicized news on his boarding of a Russian aircraft, which cost $30 million.[21] Garriott again prevailed on appeal and NCSoft was required to pay an additional US$4 million, bringing the total damages awarded to Garriott to US$32 million.[22]
Closure of Paragon Studios and City of Heroes
On August 31, 2012, NCSoft liquidated Paragon Studios and announced the closure of City of Heroes. Over 21,000 players signed an online petition contesting the shut-down[23] and many used social media to promote their criticisms.
Games
| Year | Title | Developer | Genre | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | Lineage | NCSoft (Team L2Live) | MMORPG | |
| 2003 | Lineage II | NCSoft | MMORPG | |
| 2004 | City of Heroes | Paragon Studios | MMORPG | Shut down on November 30, 2012. |
| 2005 | Guild Wars | ArenaNet | MMORPG | |
| 2006 | Auto Assault | NetDevil | MMORPG | Shut down on August 31, 2007. |
| 2007 | Dungeon Runners | NCSoft | MMORPG | Shut down on January 1, 2010. |
| Tabula Rasa | Destination Games | MMORPG | Shut down on February 28, 2009. | |
| Exteel | NCSoft (E&G Studios) | TPS | Shut down on September 1, 2010. | |
| 2008 | Point Blank | Zepetto | FPS | Shut down on July 13, 2011. |
| 2009 | Aion | NCSoft (Team Aion) | MMORPG | |
| 2012 | Blade & Soul | NCSoft (Team Bloodlust) | MMORPG | |
| Guild Wars 2 | ArenaNet | MMORPG | ||
| 2013 | Shin Jan Ryu Mon | NCSoft Japan | Mahjong | |
| 2014 | WildStar | NCSoft (Carbine) | MMORPG | Shut down on November 30, 2018. |
| 2016 | Love Beat | CrazyDiamond | Dance/Rhythm | |
| Lineage Red Knight | NCSoft | RPG | ||
| 2017 | Final Blade | NCSoft | RPG | |
| Pro Baseball H2! | NTREEV (Baseball Team) | Sport | ||
| Master X Master | NCSoft (Studio MXM) | MOBA | Shut down on January 31, 2018. | |
| Lineage M | NCSoft | MMORPG | ||
| Aion: Legions of War | NCSoft | RPG | ||
| 2019 | Lineage II M | NCSoft (Team L2Live) | RPG | |
| 2020 | FUSER | Harmonix | Rhythm | Shut down on December 19, 2022 |
| 2021 | Pro Baseball H3! | NTREEV (Baseball Team) | Sport | |
| Trickster M | NTREEV (Trickster Team) | MMORPG | ||
| Blade & Soul 2 | NCSoft (Team Bloodlust) | MMORPG | ||
| Lineage W | NCSoft | MMORPG | ||
| 2024 | Battle Crush | NCSoft | Action, brawler | |
| TBA | Throne and Liberty | NCSoft (TL Heroes) | MMORPG | Published in the West and Japan by Amazon Games |
| Project LLL | NCSoft | MMORPG | ||
| Project G | NCSoft | Strategy RPG | ||
| AION 2 | NCSoft | MMORPG | ||
| Blade & Soul S | NCSoft | Strategy RPG | ||
| Blade & Soul Console | NC Interactive (NCWEST) | Action MMORPG | ||
| Pangya M | NTREEV (Project G Team) | Sport RPG |
In addition, NCSoft is also the developer and maintainer of a variety of web-based board games in Asian markets.
References
- "Saudi Arabia's PIF ups invest in NCSoft for second largest ownership, shares rally". Archived from the original on 2022-04-24. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- "2020 earnings release". NCSoft. Archived from the original on 2021-01-21. Retrieved 2021-01-21.
- "NCSoft". NCSoft (in Korean). Archived from the original on 2018-04-09. Retrieved 2018-04-09.
- "Seven years of City of Heroes statistics". eurogamer.net. 2011-04-28. Archived from the original on 2015-07-09. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- "엔씨소프트의 역사" [History of NCsoft]. NCSoft (in Korean). Archived from the original on 2018-05-24. Retrieved 2018-05-23.
- "Games Industry Veteran Jeffrey Anderson Joins NCSOFT West as New CEO". PR Newswire. July 28, 2021. Archived from the original on July 28, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- Weber, Rachel (July 8, 2011). "NCSoft in talks to acquire Ntreev Software". Gamesindustry International. Archived from the original on July 11, 2011. Retrieved July 8, 2011.
- Caoili, Eric (February 17, 2012). "League of Legends and NCsoft's Ntreev acquisition, this week in Korean news". Game Developer. Archived from the original on May 21, 2022. Retrieved May 1, 2022.
- Caoili, Eric (July 27, 2011). "NCSoft Purchases Seoul-Based Mobile Dev Hotdog Studio". Game Developer. Archived from the original on January 21, 2022. Retrieved May 1, 2022.
- Takahashi, Dean. "Korean game togetherness: Nexon acquires 14.7 percent of NCsoft for $688M". VentureBeat. Archived from the original on 2017-07-27. Retrieved 2017-09-05.
- "About Us". us.ncsoft.com. Archived from the original on 2017-06-05. Retrieved 2017-05-30.
- NCSoft launches entertainment subsidiary Klap Archived 2022-10-05 at the Wayback Machine (The Korea Herald, August 21, 2020)
- "UNIVERSE launches with over 4 million users, here's a guide to the new fan community platform". Bandwagon. 28 January 2021. Archived from the original on 9 August 2021. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- Park, So-eun (2023-08-08). "[단독]엔씨소프트, '클렙' 지분 전량 매각…엔터 사업 손 뗀다". News 1 Korea (in Korean). Retrieved 2023-08-14.
- "Former NCSoft Employees Suspected of Stealing Lineage III Code". WIRED. 30 April 2007. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- "Chosun Ilbo article". April 26, 2007. Archived from the original on September 18, 2008.
- "Worlds.com CEO: We're 'Absolutely' Going To Sue Second Life And World Of Warcraft". Business Insider. Archived from the original on 2018-09-17. Retrieved 2019-01-17.
- "NCsoft Faces Patent Infringement Suit". WIRED. 29 December 2008. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- Voecks, K. (6 May 2009). "Richard Garriott blasts NCsoft with $24 million lawsuit". Engadget. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- Kim, Tong-hyung (July 30, 2010). "Garriott wins $28 mil. in NCsoft lawsuit". Archived from the original on September 28, 2012. Retrieved August 1, 2010.
- "Garriott wins appeal in NCsoft case". RICHARD GARRIOTT v. NCSoft CORPORATION. Archived from the original on October 26, 2012. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- "Save CoH movement invites NCsoft execs to play, petition passes 20,000 signatures". Engadget. September 27, 2012. Archived from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
External links
- NCSoft
- NCSoft West
- Business data for NCSoft: