Molluscum contagiosum virus
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a species of DNA poxvirus that causes the human skin infection molluscum contagiosum.[1] Molluscum contagiosum affects about 200,000 people a year, about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. Diagnosis is based on the size and shape of the skin lesions and can be confirmed with a biopsy, as the virus cannot be routinely cultured.[2] Molluscum contagiosum virus is the only species in the genus Molluscipoxvirus.[3] MCV is a member of the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae of family Poxviridae.[4] Other commonly known viruses that reside in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae are variola virus (cause of smallpox) and monkeypox virus.[3]
| Molluscum contagiosum virus | |
|---|---|
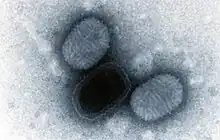 | |
| Negatively stained transmission electron micrograph of Molluscum contagiosum virus virions | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Varidnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Bamfordvirae |
| Phylum: | Nucleocytoviricota |
| Class: | Pokkesviricetes |
| Order: | Chitovirales |
| Family: | Poxviridae |
| Genus: | Molluscipoxvirus |
| Species: | Molluscum contagiosum virus |
The poxvirus family uniquely contains both non-enveloped particles (mature virions), and enveloped particles (extracellular virions).[5] The structure of the virions is consistent with that of others in the poxvirus family: they are composed of a nucleocapsid, core envelope, lateral body, and an extracellular envelope. Like other poxviruses, MCV is a DNA virus that replicates in the cytoplasm instead of the nucleus. Because of this, the virus must bring all necessary enzymes for replication with it or encode the enzymes in its genome.
Structure
The Molluscum contagiosum virus virion is described as oval-shaped and has the dimension of approximately 320 nm × 250 nm × 200 nm. The virus has two distinct infectious particles called the mature virion (MV) and the enveloped virion (EV), which differ in that the EV contains a second outer cellular membrane. Poxviridae is the only virus family that contains both enveloped and non-enveloped infectious particles. Other structures of the EV and MV virion include the nucleocapsid, core wall, and two lateral bodies.[6] Before the virion is released into the cytosol, the lateral bodies are associated with the virion core through boding interactions. However, during virion release into the cytoplasm, the virion core wall expands and forces the lateral bodies to dissociate. The lateral bodies function to transport one or more vital virion proteins needed for genome replication or expression.[7]
Genome
The genome consists of a linear double-stranded DNA molecule that is approximately 190 kilobases in length. The genome is unique in that the two ends of the double-stranded DNA sequence are inverted repeats of each other. This inverted terminal sequence is 4.7 kilobases in length, but can vary from 0.7–12 kilobases among poxviruses. There are 182 genes that are encoded by Molluscum contagiosum virus. Over 100 of these genes are conserved in other viruses from the poxvirus family, such as Variola virus and Vaccinia virus. The inverted terminal sequence of MCV differs from the sequences of others in the poxvirus family because it contains genus-specific host response evasion genes. The genome contains 64% GC bases, and thus encodes a lesser amount of the stop codons UAA, UGA, and UAG compared to other poxviruses. Further gene analysis has shown the MCV genome contains many long and overlapping open reading frames.[8]
Replication cycle
Entry into cell
Molluscum contagiosum virus, similar to all poxviruses, produces two infectious particles: mature virions (MV) and extracellular virions (EV), with the EV differing from the MV in that they possess an extra cellular membrane. To enter the cell, the membrane of MV fuses to the plasma membrane, specifically glycosaminoglycans, of the host cell and then enters via macropinocytosis. This process is initiated by the presence of phosphatidylserine molecules exposed on the MV cellular membrane.[9] Similarly, the outer membrane of EV fuses to the plasma membrane, specifically glycosaminoglycans, of the host cell and also enters via macropinocytosis. After macropinocytosis, H+ is pumped inside the internalized vacuole containing EV and this acidification breaks down the outer membrane, exposing a MV like particle. For both MV and EV, the cellular membranes then fuse with the vacuole allowing the release of the virus core into the cytosol.[9][10] The virion is then uncoated, exposing the DNA to commence replication.
Replication and transcription
Molluscum contagiosum virus, like other poxviruses, replicates entirely in the cytoplasm of the host cell. This is a property unique to poxviruses, as all other DNA viruses replicate in the nucleus. Therefore, because the host cell proteins for DNA replication are present inside the nucleus, this virus has to bring or encode for all of the proteins needed for replication.[11] Each virion sets up a region in the cytoplasm, called a 'viral factory' where DNA replication, transcription, and translation all occur sequentially.
There are three phases of DNA transcription. During the early phase, genes that encode for transcription factors, viral DNA and RNA polymerases, and proteins that stimulate host cell mitosis are transcribed by DNA dependent RNA polymerase that the virion carries with it.[10] The mRNA produced in the early phase is then translated by viral transcriptase that the virion also carries with it. Then during the intermediate phase, the proteins encoded for in the early phase are used to replicate the viral DNA. Additionally, more transcription factors are produced to help transcribe the late phase mRNA. During the late phase, the genes encoding for structural proteins and enzymes needed for future infection are transcribed and then translated. Gene expression is sequential from early to intermediate to late phase of transcription, and it is temporally regulated.[6]
Assembly and release
The virion cytoplasmic factories serve as the place where mature virions are assembled for future infection. Mature virions are released via cell lysis and aid in host to host transmission of the virus. Extracellular virions are made when the MV acquires a second membrane via the Golgi apparatus and then buds out of the cell. Extracellular virions aid in spreading the virus within the epithelial tissue.[6]
Tropism
Molluscum contagiosum virus only infects human epidermal cells. It is not spread throughout the body, which explains why the virus cannot be transmitted through coughing or sneezing.[12] People have attempted to grow the virus in cell culture to study its molecular properties, but have been largely unsuccessful due to it only infecting epidermal cells.[8]
However, there is evidence that it has the ability to adapt and survive in different types of cells in humans with severely compromised immune systems. Using qPCR analysis, it was determined that there was significant Molluscum contagiosum virus in the plasma of one patient who had a large t-cell deficiency. The patient was given CMX-001 antiviral agent as a treatment because of her severe molluscum contagiosum symptoms. Before administering the CMX-001 drug, Molluscum contagiosum virus DNA was found in 50% of her plasma samples, whereas DNA was found in 20% of samples after administering the drug. This is the first time molluscum contagiosum DNA was ever detected in the blood of a patient.[13]
Modulation of host cell processes
Several proteins produced mRNA in the intermediate phase of transcription modulate host cell processes to promote an ideal environment for the viral replication and transcription. Molecular analysis has shown that 77 MCV proteins may potentially interfere with host cell processes. However, only 7 MCV proteins have confirmed host cell functions. These proteins include MC007, MC054, MC066, MC132, MC148, MC159, and MC160.[8] The following list will give an overview of how these proteins modulate host cell processes.
- The MC007 protein sequesters retinoblastoma protein (pRb) on the mitochondria membrane, inactivating it. The pRb protein is essential in controlling cellular proliferation and the deregulation of this protein leads to tumor pathogenesis.[14]
- The MC054 long protein binds Interleukin 18 which blocks its two binding sites. Interleukin-18 a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in innate and adaptive immunity and inhibition of interleukin-18 weakens the immune system.[15]
- The MC066 protein is homologous to human glutathione peroxidase. This protein protects against cellular apoptosis caused by UV radiation and hydrogen peroxide. This shows a mechanism in which the virus can defend itself against environmental stressors.[16]
- The MC132 protein interacts with the NF-κB subunit p65 and causes p65 degradation. NF-κB is a transcription factor that is immediately activated following virus entry into cells and is important for virus detection, antiviral signaling, inflammation, and clearance of viral infection. Inhibiting and degrading this transcription factor allows the virus to further replicate without attack by the host cell.[17]
- The MC148 protein acts like a chemokine-like protein and displaces actual chemokines from their G-protein coupled receptors. Chemokines are small proteins of 70-100 amino acid residues which are involved in attracting and activating distinct leukocyte subsets. MC148 blocks this process by being an antagonist to CxC12a and CCR8 receptors.[18]
- The MC159 protein inhibits TNF-R1–induced NF-κB activation. NF-κB is a transcription factor that is activated in the cytoplasm and translocates to the cell nucleus. It plays a crucial role in regulating the immune response, the cell cycle and apoptosis.[19]
- The MC160 protein binds heat shock protein 90, keeping it from stabilizing I Kappa Kinase (IKK). IKK is a protein that phosphorylates and inactivates the inhibitor of NF-κB, allowing NF-κB to be activating. When MC160 binds heat shock protein 90, IKK is degraded and the inhibitor remains bound to NF-κB, thus making NF-κB not functional.[20]
Related disease
Molluscum contagiosum

This is a viral infection of the skin that usually presents in children ages 1–10 and immunocompromised patients.[12] The main symptom of this disease is round, hard, flesh colored, painless bumps, with sunken centers that are apparent on the surface of the skin (Figure 1). The bumps are generally less than 6 millimeters in diameter and can become red and inflamed or itchy if a person rubs them. They are generally found on the face, neck, armpits, and hands. However, the bumps may also be found on the genitals of adults if the disease was spread through sexual contact.[4][12] The virus can be spread directly from person to person through skin to skin contact or through fomites, which are inanimate objects contaminated with the virus. The most common fomites for molluscum contagiosum transmission are clothing, towels, bathing sponges, toys, and sports equipment. Additionally, the virus can spread to other skin areas of one's body through itching or rubbing the virus. It can also be spread in adults through sexual contact. The virus is not circulated throughout the body, and thus, cannot be spread by coughing or sneezing. The transmission of this virus can be prevented by washing hands, not sharing items, refraining from sexual contact and shaving, and by keeping the bumps clean and covered.[4][12]
Generally, if one has a functioning immune system no treatment is needed and the bumps and virus will go away within 6–12 months of contraction. However, treatment is suggested if the bumps are on the genital area or if the person affected is immunocompromised. In healthy (non-immunocompromised) individuals, cryotherapy, curettage, laser therapy, oral therapy, or a topical therapy is suggested to treat the lesions. Cryotherapy involves freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen, whereas curettage involves piercing the core and scraping the lesion with sterile equipment. Laser therapy involves destroying the lesion with a laser. It is a good idea to not try removing the lesions yourself, as the skin can become infected and the virus can spread to other parts of the body. A commonly prescribed oral medication used to treat the lesions is cimetidine and a topical therapy is Podophyllotoxin cream (0.5%).[12]
People with severely weakened immune systems and molluscum contagiosum may have bumps or lesions that are greater than 15 millimeters and look different from normal. Most typical therapies are ineffective in treating these people. The recommended treatment in this case are therapies that help boost the immune system.[12]
References
- Rao, K; Priya, N; Umadevi, H; Smitha, T (January 2013). "Molluscum contagiosum". Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 17 (1): 146–7. doi:10.4103/0973-029X.110726. PMC 3687174. PMID 23798852.
- "Molluscum Contagiosum | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library". www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2018b Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). February 2019. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- "Molluscum contagiosum - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2019-03-05.
- Humansandviruses (2015-03-24). "Poxviridae". humansandviruses. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- "Molluscipoxvirus ~ ViralZone page". viralzone.expasy.org. Retrieved 2019-03-11.
- Schmidt, Florian Ingo; Bleck, Christopher Karl Ernst; Reh, Lucia; Novy, Karel; Wollscheid, Bernd; Helenius, Ari; Stahlberg, Henning; Mercer, Jason (August 2013). "Vaccinia Virus Entry Is Followed by Core Activation and Proteasome-Mediated Release of the Immunomodulatory Effector VH1 from Lateral Bodies". Cell Reports. 4 (3): 464–476. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.028. ISSN 2211-1247. PMID 23891003.
- Senkevich, Tatiana G.; Koonin, Eugene V.; Bugert, Joachim J.; Darai, Gholamreza; Moss, Bernard (June 1997). "The Genome of Molluscum Contagiosum Virus: Analysis and Comparison with Other Poxviruses". Virology. 233 (1): 19–42. doi:10.1006/viro.1997.8607. ISSN 0042-6822. PMID 9201214.
- Schmidt, Florian Ingo; Bleck, Christopher Karl Ernst; Helenius, Ari; Mercer, Jason (2011-08-31). "Vaccinia extracellular virions enter cells by macropinocytosis and acid-activated membrane rupture: Cell entry of vaccinia extracellular virions". The EMBO Journal. 30 (17): 3647–3661. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.245. PMC 3181475. PMID 21792173.
- Burrell, Christopher J.; Howard, Colin R.; Murphy, Frederick A. (January 2017). Fenner and White's Medical Virology. Academic Press. pp. 229–236. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-375156-0.00016-3. ISBN 9780123751560.
- Moss, B. (2013-09-01). "Poxvirus DNA Replication". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 5 (9): a010199. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a010199. ISSN 1943-0264. PMC 3753712. PMID 23838441.
- "Molluscum Contagiosum | Poxvirus | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 2019-01-03. Retrieved 2019-03-10.
- Cohen, Jeffrey I.; Davila, Wilmer; Ali, Mir A.; Turk, Siu-Ping; Cowen, Edward W.; Freeman, Alexandra F.; Wang, Kening (2012-01-19). "Detection of Molluscum Contagiosum Virus (MCV) DNA in the Plasma of an Immunocompromised Patient and Possible Reduction of MCV DNA With CMX-001". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 205 (5): 794–797. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir853. ISSN 1537-6613. PMC 3274371. PMID 22262788.
- Mohr, S.; Grandemange, S.; Massimi, P.; Darai, G.; Banks, L.; Martinou, J.-C.; Zeier, M.; Muranyi, W. (2008-08-13). "Targeting the Retinoblastoma Protein by MC007L, Gene Product of the Molluscum Contagiosum Virus: Detection of a Novel Virus-Cell Interaction by a Member of the Poxviruses". Journal of Virology. 82 (21): 10625–10633. doi:10.1128/jvi.01187-08. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 2573180. PMID 18701596.
- Xiang, Y.; Moss, B. (2003-02-15). "Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Interleukin-18 (IL-18) Binding Protein Is Secreted as a Full-Length Form That Binds Cell Surface Glycosaminoglycans through the C-Terminal Tail and a Furin-Cleaved Form with Only the IL-18 Binding Domain". Journal of Virology. 77 (4): 2623–2630. doi:10.1128/jvi.77.4.2623-2630.2003. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 141116. PMID 12552001.
- Shisler, J. L. (1998-01-02). "Ultraviolet-Induced Cell Death Blocked by a Selenoprotein from a Human Dermatotropic Poxvirus". Science. 279 (5347): 102–105. Bibcode:1998Sci...279..102S. doi:10.1126/science.279.5347.102. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9417017.
- Brady, Gareth; Haas, Darya A.; Farrell, Paul J.; Pichlmair, Andreas; Bowie, Andrew G. (2015-06-03). "Poxvirus Protein MC132 from Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Inhibits NF-κB Activation by Targeting p65 for Degradation". Journal of Virology. 89 (16): 8406–8415. doi:10.1128/jvi.00799-15. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 4524246. PMID 26041281.
- Jin, Qingwen; Altenburg, Jeffrey D.; Hossain, Mohammad M.; Alkhatib, Ghalib (September 2011). "Role for the conserved N-terminal cysteines in the anti-chemokine activities by the chemokine-like protein MC148R1 encoded by Molluscum contagiosum virus". Virology. 417 (2): 449–456. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2011.07.001. ISSN 0042-6822. PMC 3760151. PMID 21802105.
- Randall, C. M. H.; Jokela, J. A.; Shisler, J. L. (2012-02-01). "The MC159 Protein from the Molluscum Contagiosum Poxvirus Inhibits NF- B Activation by Interacting with the I B Kinase Complex". The Journal of Immunology. 188 (5): 2371–2379. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100136. ISSN 0022-1767. PMC 3288875. PMID 22301546.
- Nichols, D. B.; Shisler, J. L. (2009-01-21). "Poxvirus MC160 Protein Utilizes Multiple Mechanisms To Inhibit NF- B Activation Mediated via Components of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 Signal Transduction Pathway". Journal of Virology. 83 (7): 3162–3174. doi:10.1128/jvi.02009-08. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 2655573. PMID 19158250.