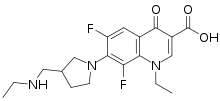
Merafloxacin
Merafloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial that inhibits the pseudoknot formation which is necessary for the frameshift in the SARS-CoV-2 genome.[1] It is a promising drug candidate for SARS-CoV-2.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23F2N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 379.408 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Bhatt PR, Scaiola A, Loughran G, Leibundgut M, Kratzel A, Meurs R, et al. (June 2021). "Structural basis of ribosomal frameshifting during translation of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome". Science. 372 (6548): 1306–1313. Bibcode:2021Sci...372.1306B. doi:10.1126/science.abf3546. PMC 8168617. PMID 34029205.
- Sun Y, Abriola L, Surovtseva YV, Lindenbach BD, Guo JU (October 2020). "Restriction of SARS-CoV-2 Replication by Targeting Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting In Vitro". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.10.21.349225. PMC 7587830. PMID 33106809.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.