Megavirus
Megavirus[1] is a viral genus containing a single identified species named Megavirus chilense (with strain Megavirus chilensis), phylogenetically related to Acanthamoeba polyphaga Mimivirus (APMV).[2] In colloquial speech, Megavirus chilensis is more commonly referred to as just “Megavirus”. Until the discovery of pandoraviruses in 2013, it had the largest capsid diameter of all known viruses, as well as the largest and most complex genome among all known viruses.[3]
| Megavirus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group I (dsDNA) |
| (unranked): | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Megavirus |
| Species: | Megavirus chilense |
| Strains | |
| |
Discovery
Megavirus was isolated from a water sample collected in April 2010 off the coast of Chile, near the marine station in Las Cruces, by Jean-Michel Claverie and Chantal Abergel from the Structural & Genomic Information laboratory (IGS, CNRS and Aix-Marseille University). Megavirus was isolated by co-cultivation with a variety of Acanthamoeba laboratory strains (A. polyphaga, A. castellanii, A. griffini) following a protocol pioneered by Timothy Rowbotham for isolating intracellular parasitic bacteria.[4] Megavirus infects amoebas.
Structure
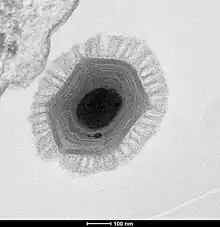
The Megavirus particle exhibits a protein capsid diameter of 440 nanometres (as seen by electron microscopy on thin sections of epoxy resin inclusions), enclosed into a solid mesh of bacterial-like capsular material 75 nm to 100 nm thick. The capsid appears hexagonal, but its icosahedral symmetry is imperfect, due to the presence of the “stargate”, at a single specific vertex of the icosahedron. The stargate is a five-pronged star structure forming the portal through which the internal core of the particle is delivered to the host's cytoplasm. This core is enclosed within two lipid membranes in the particle, also containing a large and diverse complement of viral proteins (e.g. the all transcriptional complex). Surprisingly, the Megavirus is larger than some bacteria.
Genome
The Megavirus chilensis genome is a linear, double-stranded molecule of DNA with 1,259,197 base pairs in length. It exhibits 7 aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (Table 2), the archetypes of enzymes previously thought only to be encoded by cellular organisms. While 4 of these enzymes were known to be present in Mimivirus and Mamavirus (for tyrosine, arginine, cysteine, and methionine), Megavirus exhibits three more (for tryptophan, asparagine, and isoleucine).
See also
- Mimivirus – the giant virus that revolutionized virology
- Cafeteria roenbergensis virus – the largest marine virus
- Parvovirus – smallest known single stranded DNA viruses
- Pithovirus - largest virus by capsid length (approximately 1.5 micrometre)
- Pandoraviridae - second largest virus by capsid length (approximately 1 micrometre)
- Virophage
References
- Arslan, D.; Legendre, M.; Seltzer, V.; Abergel, C.; Claverie, J.-M. (2011). "Distant Mimivirus relative with a larger genome highlights the fundamental features of Megaviridae". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 108 (42): 17486–91. Bibcode:2011PNAS..10817486A. doi:10.1073/pnas.1110889108. PMC 3198346. PMID 21987820.
- Raoult, D.; Audic, S; Robert, C; Abergel, C; Renesto, P; Ogata, H; La Scola, B; Suzan, M; Claverie, JM (2004). "The 1.2-Megabase Genome Sequence of Mimivirus". Science. 306 (5700): 1344–50. Bibcode:2004Sci...306.1344R. doi:10.1126/science.1101485. PMID 15486256. S2CID 84298461.
- D Arslan, M Legendre, V Seltzer… - Proceedings of the …, 2011 - National Acad Sciences
- Rowbotham, T J (1983). "Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from clinical specimens via amoebae, and the interaction of those and other isolates with amoebae". Journal of Clinical Pathology. 36 (9): 978–86. doi:10.1136/jcp.36.9.978. PMC 498455. PMID 6350372.
External links
- GiantVirus.org – an information resource on the genome of giant viruses.
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) picture gallery - images of mimivirus
- Van Etten, James L. (2011). "Giant Viruses". American Scientist. 99 (4): 304. doi:10.1511/2011.91.304.