Principality of Galilee
The principality of Galilee was one of the four major seigneuries of the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, according to 13th-century commentator John of Ibelin, grandson of Balian.[1] The direct holdings of the principality centred around Tiberias, in Galilee proper, but with all its vassals, the lordship covered all Galilee (now Israel) and southern Phoenicia (today Lebanon). The independent Lordship of Sidon was located between Galilee's holdings. The principality also had its own vassals: the Lordships of Beirut, Nazareth, and Haifa.
Principality of Galilee | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1099–1187 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
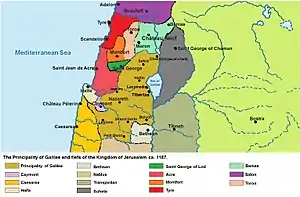 Galilee in 1187 | |||||||||
| Status | Vassal of Kingdom of Jerusalem | ||||||||
| Capital | Tiberias | ||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Old French, Italian (also Arabic and Greek) | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism, Greek Orthodoxy, Syriac Orthodoxy, Islam, Judaism | ||||||||
| Government | Feudal monarchy | ||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||
• 1099–1101 | Tancred | ||||||||
• 1174–1187 | Raymond III | ||||||||
| Historical era | High Middle Ages | ||||||||
• First Crusade | 1099 | ||||||||
• Conquered by Saladin | 1187 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The principality was established, at least in name, in 1099 when Tancred was given Tiberias, Haifa, and Bethsan by Godfrey of Bouillon. In 1101, Baldwin I limited Tancred's power by giving Haifa to Geldemar Carpenel, and Tancred was forced to give up the principality and become regent in Antioch. The principality became the fief of the families of St. Omer, Montfaucon (Falcomberques), and then Bures, and its main seat was in Tiberias; thus it was sometimes also called the Principality of Tiberias or the Tiberiad. The principality was destroyed by Saladin in 1187, although the title was used by relatives and younger sons of the kings of Cyprus (the titular kings of Jerusalem) afterwards, and some of its former holdings were briefly reclaimed by a treaty made during the Barons' Crusade.[2]
List of the princes of Galilee
Italicized names are of titular princes.
- Tancred (1099–1101)
- Hugh of Fauquembergues (1101–1106)
- Gervaise de Bazoches (1106–1108)
- Tancred, again (1109–1112)
- Joscelin I of Courtenay (1112–1119)
- William I of Bures (1120–1141)
- Elinand (1142–1148)
- William II of Bures (1148–1158)
- Gautier of Saint Omer (1159–1171), first husband of Eschiva of Bures
- Raymond III of Tripoli (1174–1187) with his wife Eschiva of Bures
- Hugh II of Saint Omer (1187–1204)
- Raoul of Saint Omer (1204–1219)
- Eschiva of Saint Omer (1219–after 1265) with her husband Odo of Montbéliard (1219–1247); 1240–1247 as ruling Princes
- Balian d'Ibelin (?–1316), Prince of Galilee and Bethlehem, son of Philip of Ibelin (died 1304) (?–1316)
- Bohemund of Lusignan (c. 1280)
- Guy of Lusignan (c. 1320–1343), son of Hugh IV of Cyprus
- Hugh of Lusignan (1343–1386), son of Guy of Lusignan
- John of Brie
- Henry of Lusignan (?–1427), son of James I of Cyprus
- Philippe of Lusignan (?–ca 1466), son of Henry of Lusignan
Lordship of Beirut
Beirut was captured in 1110 and given to Fulk of Guînes. It was one of the longest-lived seigneuries, surviving until the final collapse of the kingdom in 1291 (although only as a tiny strip on the Mediterranean coast surrounding the city). Beirut additionally held a role in European trade and even had its own sub-vassals.
Italicized names are of titular lords.
- Fulk of Guînes (1110–1117)
- Peter
- Walter I Brisebarre (1125?–1166)
- Andronicus I Comnenus (1166–?)
- Walter II Brisebarre, 1149–1156
- Guy II Brisebarre, 1156–1164
- Walter III Brisebarre, 1164–1166
- Beirut occupied by Ayyubids, 1187–1198
- John of Ibelin[3] (c. 1200–1236)
- Balian III d'Ibelin[3] (1236–1247), Lord of Beirut, Constable of Cyprus, Bailiff of Jerusalem; son of John of Ibelin, the Old Lord of Beirut
- John of Ibelin[3] (1247–1264)
- Isabella of Ibelin[3] (1264–1282) m1.(or only engaged) Hugh II of Cyprus m2. Hamo LeStrange m3. Nicolas l'Aleman m4. Guillaume Barlais
- Eschiva of Ibelin[3] (1282–1291, titular 1291–1312) m1. Humphrey of Montfort m2. Guy of Lusignan
- Rupen of Montfort (1312–1313)
- Guy of Ibelin (c. 1330)
- John of Lusignan (1384–?)
- John of Lusignan (?–c. 1456)
The sub-vassals of Beirut were the Lordship of Banias and the Lordship of Toron.
Sub-vassals of Beirut
Lordship of Banias
Banias was given to the Franks by the Assassins in 1129. Baldwin gave it to Renier Brus, who also ruled the lordship of Assebebe, which was eventually merged with Banias. Renier's daughter married Humphrey II of Toron, who became lord of Banias around 1148. He sold parts of Banias and Chastel Neuf to the Knights Hospitaller in 1157. Banias was merged with Toron until it fell to Nur ad-Din Zangi in 1164, and when it was recovered it became part of the Seigneury of Joscelin III of Edessa (see below).
- Renier Brus (1128–1148)
- Humphrey II of Toron (1148–1164)
- Joscelin III of Edessa ?
Lordship of Toron
The castle of Toron was built by Hugh of St. Omer, second prince of Galilee, to help capture Tyre. After Hugh's death it was made an independent seigneury, given to Humphrey I in 1107. The lords of Toron tended to be very influential in the kingdom; Humphrey II was constable of Jerusalem. Humphrey IV was married to Isabella of Jerusalem, Amalric I's daughter (Toron passed into the royal domain during their marriage, and was then captured by Saladin, but its title was returned to Humphrey IV after their divorce). It was also one of the few to have a straight hereditary succession in male line, at least for some generations. The lords of Toron were also connected to the Lordship of Oultrejordain by the marriage of Humphrey III and the maternal inheritance of Humphrey IV. Toron was later merged with the royal domain of Tyre which went to a branch of Antioch, then their heirs from Montfort. Toron was lost in 1266.
Toron had two vassals of its own, the Lordship of Castel Neuf and the Lordship of Toron Ahmud. Chastel Neuf was built by Hugh of St. Omer around 1105 but was later given to the Hospitallers, until it fell to Nur ad-Din in 1167. Toron Ahmud remained in the Lordship of Beirut until John of Ibelin sold it to the Teutonic Knights in 1261.
For a fuller account of the lordship and the feudal family, see Toron.
Lordship of Nazareth
Nazareth was the original site of the Latin Patriarch, established by Tancred. It was created as a seigneury in Galilee in 1115. A Martin of Nazareth, who probably acted as viscount of Nazareth, is documented in 1115 and in 1130/1131.[4]
Lordship of Haifa
Haifa was partly an ecclesiastical domain ruled by the Archbishop of Nazareth, and partly created from other lands in the Principality of Galilee.
- Geldemar Carpenel (1100–1101)
- Tancred (1101–1103)
- Rorgius (1103–1107)
- Pagan (1107–1112)
- royal domain (1112–1190)
- Vivian (c. 1140s)
- Pagan (1190–?)
- Rorgius II (?–1244?)
- Helvis
- García Álvarez (c. 1250)
- John of Valenciennes (1257–1265)
- Gilles d'Estrain
- Miles ?
- Geoffrey
- Gilles II
See also
References
- W.), Edbury, P. W. (Peter (1997). John of Ibelin and the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Woodbridge, Suffolk, UK: Boydell Press. p. 113. ISBN 0585257523. OCLC 45732821.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Edbury, P. W. (Peter W. ) (1997). John of Ibelin and the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Internet Archive. Woodbridge, Suffolk, UK ; Rochester, NY, USA : Boydell Press. pp. 59–60. ISBN 9780851157030.
- "GENEALOGY.EU". Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- Murray, Alan, The Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem: A Dynastic History 1099-1125 (Unit for Prosopographical Research, Linacre College, Oxford, 2000) p. 217.
Sources
- John L. La Monte, Feudal Monarchy in the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1100-1291. The Medieval Academy of America, 1932.
- Jonathan Riley-Smith, The Feudal Nobility and the Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1174-1277. The Macmillan Press, 1973.
- Runciman, Steven (1952). A History of the Crusades, Volume II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Frankish East. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Steven Tibble, Monarchy and Lordships in the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1099-1291. Clarendon Press, 1989.