Liquid latex
Liquid latex is a compound often used for special effects makeup, body painting, mask making, and casting applications.

Composition
Liquid latex is usually made of 33% latex, 66% water, and less than 1% ammonia (to increase its shelf life and to control the pH of the solution). Liquid latex is sold in volumes ranging from 2 ounces to 1 gallon, and its consistency is similar to latex house paint. Its consistency can be augmented with the use of additives. For example, water can be added to thin the latex, and Aerosil can be added to thicken it.[1] Cosmetic liquid latex contains approximately 0.3% ammonia, while craft and mould-making liquid latex can contain more than double this amount, giving the latter a much stronger odour.
Liquid latex is naturally clear, and dries into a translucent amber colour. Manufacturers add pigments to the product to provide opaque paint choices of multiple colours. The colour of the paint in the jar may initially look chalky or pale, but as it dries, it develops into a rich colour (for example, grey becomes black). Acrylic paint can be mixed with liquid latex for custom colours, but may not be suitable for use in cosmetic applications. In these situations, liquid makeup or food coloring can be used.
As the latex dries, it becomes quite sticky and will stick to itself if accidentally folded over. Most manufacturers offer a slick spray for latex once it is dry to remove tackiness, allowing the movement of the model's limbs. Alternatively, powders can be dusted over dried liquid latex to create metallic effects. One advantage to the tackiness of liquid latex is that it can act as an adhesive for attaching items such as zippers. Unlike most other body and face paints, liquid latex is removed by peeling it off, since water does not reactivate it.
Use
Cosmetic/special effects makeup
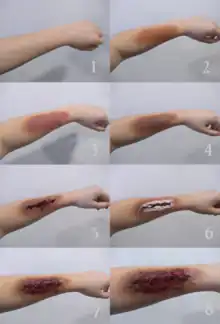
A four-ounce jar of liquid latex can typically cover an average human body. It is typically applied using a disposable sponge and takes about five to ten minutes to dry depending on how thick it is applied. As it dries, it solidifies to a rubbery consistency and in the process ends up shrinking by approximately 3%.[2]
Removing latex from skin can cause pain or pull body hairs out, similar to waxing. Even though latex is non-toxic, some people can have an allergic reaction to it. The most severe of these happen immediately and are categorized as an immediate hypersensitivity reaction.
Fumes from the ammonia in liquid latex can irritate the eyes when it is used on the face. For this reason, it is recommended that liquid latex be allowed to vent for several minutes before being applied in this way. Appropriate liquid latex safety guidelines should be followed before the cosmetic use of liquid latex.
Liquid latex used for special effects makeup projects like scars and gashes incorporate flesh-coloured latex that is applied to the skin and then built up using materials such as tissue paper and cotton.
Mold making
Liquid Latex is useful for molding due to its flexibility once dried, which allows for the casting of undercut sculpture.[3] There are several methods for making a latex mold, each with numerous variations. Below is a general outline of several methods. In any method of mold making, care must be taken to avoid air bubbles on the first layer of applied latex.
Brush method
First, the original object to be molded (master) is cleaned and dried before being paced onto a non-porous substrate. Next, liquid latex is painted onto the master, leaving the bottom uncovered, but painting out around the base on the substrate. Latex must be painted on in multiple layers, allowing the latex to dry between each one. The drying process can be expedited with the use of a fan or hair dryer. The number of layers applied typically ranges from 8 to 20, though more may be necessary depending on the size of the mold. A latex mold of a chess piece 15cm in height would normally take 8 - 10 coats. Reinforcement, such as burlap, string, or cheesecloth, may be added between layers to strengthen the latex, and prevent tearing during removal from the casting.[4]
Dip method
If your master is porous enough to draw moisture from the latex, you can simply dip the master into the liquid latex to make your mold. After dipping, bubbles may form on the surface of the master. If this happens, pop the bubbles with a brush and re-dip immediately. Allow latex to dry in between dips.
Removing the mold
Once the latex is completely dried, the latex mold is then peeled off, turning the latex mold inside-out in the process. Talcum powder or soapy water should be applied to the outside of the mold before removal, to prevent the latex from sticking to itself. After popping the latex back into its original shape, you can then use the mold to cast the item in your casting medium of choice.[5]
Safety
Due to the presence of ammonium hydroxide, liquid latex may cause skin irritation and eye irritation. The amount of ammonium varies greatly, and depends on the latex's intended use. Liquid Latex intended for mold-making may cause serious eye irritation.[6] If liquid latex gets in your eyes, rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do, and continue rinsing.
Latex is also a common allergen, and may trigger an allergic reaction in some people.
Should liquid latex start on fire, water fog, foam, dry chemical powder, and carbon dioxide are suitable extinguishing media. A water jet should not be used, as this will spread the fire.[7]
References
- Vinther, Janus (2003). Special Effects Make-up. Routledge. p. 155. ISBN 9780878301782.
- "User Instructions" (PDF). Maximum Impact. Retrieved 2019-10-17.
- Oroyan, Susanna (1999). Designing the Doll From Concept to Construction. C & T Publishing. p. 67. ISBN 9781571200600.
- "Liquid Latex — Basic Instructions" (PDF). mbfg.co.uk. Retrieved 2021-06-07.
- "Liquid Latex — Basic Instructions" (PDF). mbfg.co.uk. Retrieved 2021-06-07.
- "Safety Data Sheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2021-06-07.
- "Safety Data Sheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2021-06-07.