Kurdzhips
The Kurdzhips (Russian: Курджипс), located in the Caucasus Mountains, is a river in the Apsheronsky District of Krasnodar region, Russia. It is a left tributary of the Belaya near Maykop. It is 100 kilometres (62 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 768 square kilometres (297 sq mi).[1]
| Kurdzhips | |
|---|---|
 Kurdzhips River in Guam Gorge | |
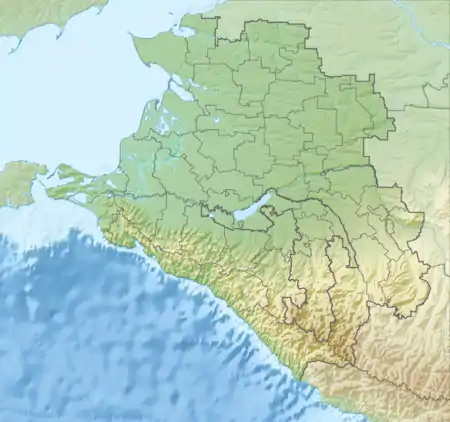  .jpg.webp) | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Belaya |
• coordinates | 44.5786°N 40.0532°E |
| Length | 100 km (62 mi) |
| Basin size | 768 km2 (297 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Belaya→ Kuban→ Sea of Azov |
The river is a venue for wilderness and extreme sports.[2][3] The river gained world attention in 2000 when Neanderthal remains were discovered in a cave on its banks.[4][5]
References
- "Река Курджипс in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- Republic of Adygea Archived 2015-06-02 at the Wayback Machine.
- International Rock Climbing Festival in Guamka, Russia.
- Igor V. Ovchinnikov, Anders Götherström, Galina P. Romanova, Vitaliy M. Kharitonov, Kerstin Lidén & William Goodwin Molecular analysis of Neanderthal DNA from the northern Caucasus. Nature 404, 490-493 (30 March 2000).
- John F. Hoffecker (2002). Desolate Landscapes: Ice-Age Settlement in Eastern Europe. Rutgers University Press.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.