Isothiazole
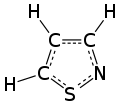
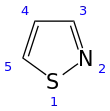
An isothiazole, or 1,2-thiazole, is a type of organic compound containing a five-membered aromatic ring that consists of three carbon atoms, one nitrogen atom, and one sulfur atom.[4] Isothiazole is a member of a class of compounds known as azoles. In contrast to the isomeric thiazole, the two heteroatoms are in adjacent positions.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Thiazole[1] | |||
| Other names
isothiazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.241.294 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3NS | |||
| Molar mass | 85.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 114 °C (237 °F; 387 K)[2] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | -0.5 (of conjugate acid)[3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
thiazole, isoxazole | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
The ring structure of isothiazole is incorporated into larger compounds with biological activity such as the pharmaceutical drugs ziprasidone and perospirone.
See also
References
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 140. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Isothiazoles, D. W. Brown and M. Sainsbury, page 513
- Zoltewicz, J. A. & Deady, L. W. Quaternization of heteroaromatic compounds. Quantitative aspects. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 22, 71-121 (1978)
- Heterocyclic Chemistry, 3rd Edition, J.A. Joule, K. Mills, and G.F. Smith, page 394
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.