Iodite
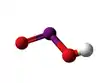
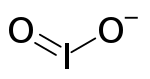
The iodite ion, or iodine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula IO−
2. Within the ion the Iodine exists in the oxidation state of +3.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodite | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
dioxidoiodate(1−) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| IO− 2 | |
| Molar mass | 58.90 g/mol |
| Conjugate acid | Iodous acid |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Chlorite Bromite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Iodite anion
Iodites (including iodous acid) are highly unstable and have been observed[1] but never isolated. They will rapidly disproportionate to molecular Iodine and Iodates.[2] However, they have been detected as intermediates in the conversion between iodide and iodate.[3][4]
Iodous acid
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodous acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
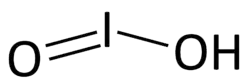
| HIO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 159.91 g/mol | ||
| Conjugate base | Iodite | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Iodous acid is acid form of the iodite ion, with the formula HIO2.
Other oxyanions
Iodine can assume oxidation states of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7. A number of neutral iodine oxides are also known.
| Iodine oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Iodide | Hypoiodite | Iodite | Iodate | periodate |
| Formula | I− | IO− | IO− 2 |
IO− 3 |
IO− 4 or IO5− 6 |
References
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Gupta, Yugul Kishore; Sharma, Devendra Nath (August 1971). "Kinetics and mechanism of the reduction of iodate to iodite by bromide in the presence of phenol". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 75 (16): 2516–2522. doi:10.1021/j100685a018.
- Gilles, Mary K.; Polak, Mark L.; Lineberger, W. C. (1992). "Photoelectron spectroscopy of the halogen oxide anions FO−, ClO−, BrO−, IO−, OClO−, and OIO−". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 96 (11): 8012. Bibcode:1992JChPh..96.8012G. doi:10.1063/1.462352.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.