Internal ribosome entry site
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at the 5' end of mRNA molecules, since 5' cap recognition is required for the assembly of the initiation complex. The location for IRES elements is often in the 5'UTR, but can also occur elsewhere in mRNAs.
History
IRES sequences were first discovered in 1988 in the poliovirus (PV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA genomes in the labs of Nahum Sonenberg[1] and Eckard Wimmer,[2] respectively. They are described as distinct regions of RNA molecules that are able to recruit the eukaryotic ribosome to the mRNA. This process is also known as cap-independent translation. It has been shown that IRES elements have a distinct secondary or even tertiary structure, but similar structural features at the levels of either primary or secondary structure that are common to all IRES segments have not been reported to date.
In recent years it has become common for molecular biologists to insert IRES sequences into their vectors to allow for expression of two genes from a single vector—for example, a transgene and a fluorescent reporter molecule. The first gene is initiated at the normal 5' cap, and the second gene is initiated at the IRES.[3]
Location
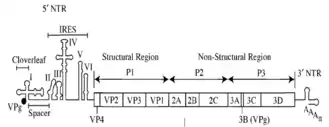
IRESs are commonly located in the 5'UTR of RNA viruses and allow translation of the RNAs in a cap-independent manner. However, mRNAs of viruses from Dicistroviridae family possess two open reading frames (ORFs), and translation of each is directed by two distinct IRESs. It has also been suggested that some mammalian cellular mRNAs also have IRESs. These cellular IRES elements are thought to be located in eukaryotic mRNAs encoding genes involved in stress survival, and other processes critical to survival. As of September 2009, there are 60 animal and 8 plant viruses reported to contain IRES elements and 115 mRNA sequences containing them as well.[4]
Activation
IRESs are often used by viruses as a means to ensure that viral translation is active when host translation is inhibited. These mechanisms of host translation inhibition are varied, and can be initiated by both virus and host, depending on the type of virus. However, in the case of most picornaviruses, such as poliovirus, this is accomplished by viral proteolytic cleavage of eIF4G so that it cannot interact with the 5'cap binding protein eIF4E. Interaction between these two eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) of the eIF4F complex is necessary for 40S ribosomal subunit recruitment to the 5' end of mRNAs, which is further thought to occur with mRNA 5'cap to 3' poly(A) tail loop formation. The virus may even use partially-cleaved eIF4G to aid in initiation of IRES-mediated translation.
Cells may also use IRESs to increase translation of certain proteins during mitosis and programmed cell death. In mitosis, the cell dephosphorylates eIF4E so that it has little affinity for the 5'cap. As a result, the 40S ribosomal subunit , and the translational machinery is diverted to IRES within the mRNA. Many proteins involved in mitosis are encoded by IRES mRNA. In programmed cell death, cleavage of eIF-4G, such as performed by viruses, decreases translation. Lack of essential proteins contributes to the death of the cell, as does translation of IRES mRNA sequences coding proteins involved in controlling cell death.[5]
Mechanism
To date, the mechanism of viral IRES function is better characterized than the mechanism of cellular IRES function,[6] which is still a matter of debate. HCV-like IRESs directly bind the 40S ribosomal subunit to position their initiator codons are located in ribosomal P-site without mRNA scanning. These IRESs still use the eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) eIF2, eIF3, eIF5, and eIF5B, but do not require the factors eIF1, eIF1A, and the eIF4F complex. In contrast, picornavirus IRESs do not bind the 40S subunit directly, but are recruited instead through the eIF4G-binding site.[7] Many viral IRES (and cellular IRES) require additional proteins to mediate their function, known as IRES trans-acting factors (ITAFs). The role of ITAFs in IRES function is still under investigation.
Testing
Testing a particular RNA sequence for IRES activity relies on a bicistronic reporter construct. When an IRES segment is located between two reporter open reading frames in a eukaryotic mRNA molecule (a bicistronic mRNA), it can drive translation of the downstream protein coding region independently of the 5'-cap structure bound to the 5' end of the mRNA molecule. In such a setup, both proteins are produced in the cell. The first reporter protein located in the first cistron is synthesized by the cap-dependent initiation, while translation initiation of the second protein is directed by the IRES element located in the intercistronic spacer between the two reporter protein coding regions. However, there are several caveats to be aware of when interpreting data produced using bicistronic reporter constructs.[8] For example, there are several known cases of mis-reported IRES elements that were later recognized as promoter-containing regions. More recently, splice acceptor sites within several presumed IRES segments have been shown to be responsible for apparent IRES function in bicistronic reporter assays.[9]
Applications
IRES sequences are often used in molecular biology to co-express several genes under the control of the same promoter, thereby mimicking a polycistronic mRNA. One can put several genes on one plasmid and just need one promotor and terminator. Within the past decades, IRES sequences have been used to develop hundreds of genetically modified rodent animal models. [10] The advantage of this technique is that molecular handling is improved. The problem about IRES is that the expression for each subsequent gene is decreased.[11]
Another viral element to establish polycistronic mRNA in eukaryotes are 2A-peptides. Here, the potential decrease in gene expression and the degree of incomplete separation of proteins is context dependent.[12]
Types
See also
References
- Pelletier J, Sonenberg N (July 1988). "Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA". Nature. 334 (6180): 320–325. Bibcode:1988Natur.334..320P. doi:10.1038/334320a0. PMID 2839775. S2CID 4327857.
- Jang SK, Kräusslich HG, Nicklin MJ, Duke GM, Palmenberg AC, Wimmer E (August 1988). "A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation". Journal of Virology. 62 (8): 2636–2643. doi:10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. PMC 253694. PMID 2839690.
- Renaud-Gabardos, E; Hantelys, F; Morfoisse, F; Chaufour, X; Garmy-Susini, B; Prats, AC (20 February 2015). "Internal ribosome entry site-based vectors for combined gene therapy". World Journal of Experimental Medicine. 5 (1): 11–20. doi:10.5493/wjem.v5.i1.11. PMC 4308528. PMID 25699230.
- Mokrejs M, Vopálenský V, Kolenaty O, Masek T, Feketová Z, Sekyrová P, Skaloudová B, Kríz V, Pospísek M (January 2006). "IRESite: the database of experimentally verified IRES structures (www.iresite.org)". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D125–30. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj081. PMC 1347444. PMID 16381829.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science. pp. 447–448. ISBN 978-0-8153-4072-0.
- López-Lastra M, Rivas A, Barría MI (2005). "Protein synthesis in eukaryotes: the growing biological relevance of cap-independent translation initiation". Biological Research. 38 (2–3): 121–146. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.463.2059. doi:10.4067/s0716-97602005000200003. PMID 16238092.
- Hellen CU, Sarnow P (July 2001). "Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules". Genes & Development. 15 (13): 1593–1612. doi:10.1101/gad.891101. PMID 11445534.
- Kozak M (2005). "A second look at cellular mRNA sequences said to function as internal ribosome entry sites". Nucleic Acids Research. 33 (20): 6593–6602. doi:10.1093/nar/gki958. PMC 1298923. PMID 16314320.
- Baranick BT, Lemp NA, Nagashima J, Hiraoka K, Kasahara N, Logg CR (March 2008). "Splicing mediates the activity of four putative cellular internal ribosome entry sites". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (12): 4733–4738. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.4733B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710650105. PMC 2290820. PMID 18326627.
- Shaimardanova, AA; Chulpanova, DS (2019). "Production and Application of Multicistronic Constructs for Various Human Disease Therapies". Pharmaceutics. 11 (11): 580–590. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics11110580. PMC 6920891. PMID 31698727.
- Michnick, Donna; Wasley, Louise C.; Davies, Monique V.; Kaufman, Randal J. (1991-08-25). "Improved vectors for stable expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells by use of the untranslated leader sequence from EMC virus". Nucleic Acids Research. 19 (16): 4485–4490. doi:10.1093/nar/19.16.4485. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC 328638. PMID 1653417.
- Xia, Qingyou; Ping Zhao; Wang, Riyuan; Wang, Feng; Wang, Yuancheng (2015-11-05). "2A self-cleaving peptide-based multi-gene expression system in the silkworm Bombyx mori". Scientific Reports. 5: 16273. Bibcode:2015NatSR...516273W. doi:10.1038/srep16273. PMC 4633692. PMID 26537835.