24-cell honeycomb
In four-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 24-cell honeycomb, or icositetrachoric honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) of 4-dimensional Euclidean space by regular 24-cells. It can be represented by Schläfli symbol {3,4,3,3}.
| 24-cell honeycomb | |
|---|---|
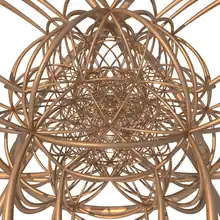 A 24-cell and first layer of its adjacent 4-faces. | |
| Type | Regular 4-honeycomb Uniform 4-honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,4,3,3} r{3,3,4,3} 2r{4,3,3,4} 2r{4,3,31,1} {31,1,1,1} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| 4-face type | {3,4,3} |
| Cell type | {3,4} |
| Face type | {3} |
| Edge figure | {3,3} |
| Vertex figure | {4,3,3} |
| Dual | {3,3,4,3} |
| Coxeter groups | , [3,4,3,3] , [4,3,3,4] , [4,3,31,1] , [31,1,1,1] |
| Properties | regular |
The dual tessellation by regular 16-cell honeycomb has Schläfli symbol {3,3,4,3}. Together with the tesseractic honeycomb (or 4-cubic honeycomb) these are the only regular tessellations of Euclidean 4-space.
Coordinates
The 24-cell honeycomb can be constructed as the Voronoi tessellation of the D4 or F4 root lattice. Each 24-cell is then centered at a D4 lattice point, i.e. one of
These points can also be described as Hurwitz quaternions with even square norm.
The vertices of the honeycomb lie at the deep holes of the D4 lattice. These are the Hurwitz quaternions with odd square norm.
It can be constructed as a birectified tesseractic honeycomb, by taking a tesseractic honeycomb and placing vertices at the centers of all the square faces. The 24-cell facets exist between these vertices as rectified 16-cells. If the coordinates of the tesseractic honeycomb are integers (i,j,k,l), the birectified tesseractic honeycomb vertices can be placed at all permutations of half-unit shifts in two of the four dimensions, thus: (i+½,j+½,k,l), (i+½,j,k+½,l), (i+½,j,k,l+½), (i,j+½,k+½,l), (i,j+½,k,l+½), (i,j,k+½,l+½).
Configuration
Each 24-cell in the 24-cell honeycomb has 24 neighboring 24-cells. With each neighbor it shares exactly one octahedral cell.
It has 24 more neighbors such that with each of these it shares a single vertex.
It has no neighbors with which it shares only an edge or only a face.
The vertex figure of the 24-cell honeycomb is a tesseract (4-dimensional cube). So there are 16 edges, 32 triangles, 24 octahedra, and 8 24-cells meeting at every vertex. The edge figure is a tetrahedron, so there are 4 triangles, 6 octahedra, and 4 24-cells surrounding every edge. Finally, the face figure is a triangle, so there are 3 octahedra and 3 24-cells meeting at every face.
Cross-sections
One way to visualize a 4-dimensional figure is to consider various 3-dimensional cross-sections. That is, the intersection of various hyperplanes with the figure in question. Applying this technique to the 24-cell honeycomb gives rise to various 3-dimensional honeycombs with varying degrees of regularity.
| Vertex-first sections | |
|---|---|
 |
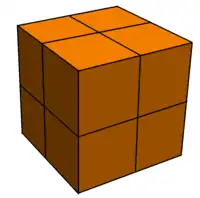 |
| Rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb | Cubic honeycomb |
| Cell-first sections | |
 |
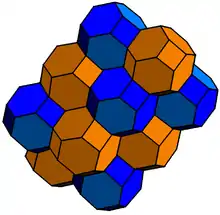 |
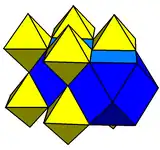
| Rectified cubic honeycomb | Bitruncated cubic honeycomb |
A vertex-first cross-section uses some hyperplane orthogonal to a line joining opposite vertices of one of the 24-cells. For instance, one could take any of the coordinate hyperplanes in the coordinate system given above (i.e. the planes determined by xi = 0). The cross-section of {3,4,3,3} by one of these hyperplanes gives a rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb. Each of the rhombic dodecahedra corresponds to a maximal cross-section of one of the 24-cells intersecting the hyperplane (the center of each such (4-dimensional) 24-cell lies in the hyperplane). Accordingly, the rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb is the Voronoi tessellation of the D3 root lattice (a face-centered cubic lattice). Shifting this hyperplane halfway to one of the vertices (e.g. xi = ½) gives rise to a regular cubic honeycomb. In this case the center of each 24-cell lies off the hyperplane. Shifting again, so the hyperplane intersects the vertex, gives another rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb but with new 24-cells (the former ones having shrunk to points). In general, for any integer n, the cross-section through xi = n is a rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb, and the cross-section through xi = n + ½ is a cubic honeycomb. As the hyperplane moves through 4-space, the cross-section morphs between the two periodically.
A cell-first cross-section uses some hyperplane parallel to one of the octahedral cells of a 24-cell. Consider, for instance, some hyperplane orthogonal to the vector (1,1,0,0). The cross-section of {3,4,3,3} by this hyperplane is a rectified cubic honeycomb. Each cuboctahedron in this honeycomb is a maximal cross-section of a 24-cell whose center lies in the plane. Meanwhile, each octahedron is a boundary cell of a (4-dimensional) 24-cell whose center lies off the plane. Shifting this hyperplane till it lies halfway between the center of a 24-cell and the boundary, one obtains a bitruncated cubic honeycomb. The cuboctahedra have shrunk, and the octahedra have grown until they are both truncated octahedra. Shifting again, so the hyperplane intersects the boundary of the central 24-cell gives a rectified cubic honeycomb again, the cuboctahedra and octahedra having swapped positions. As the hyperplane sweeps through 4-space, the cross-section morphs between these two honeycombs periodically.
Kissing number
If a 3-sphere is inscribed in each hypercell of this tessellation, the resulting arrangement is the densest known[note 1] regular sphere packing in four dimensions, with the kissing number 24. The packing density of this arrangement is
Each inscribed 3-sphere kisses 24 others at the centers of the octahedral facets of its 24-cell, since each such octahedral cell is shared with an adjacent 24-cell. In a unit-edge-length tessellation, the diameter of the spheres (the distance between the centers of kissing spheres) is √2.
Just outside this surrounding shell of 24 kissing 3-spheres is another less dense shell of 24 3-spheres which do not kiss each other or the central 3-sphere; they are inscribed in 24-cells with which the central 24-cell shares only a single vertex (rather than an octahedral cell). The center-to-center distance between one of these spheres and any of its shell neighbors or the central sphere is 2.
Alternatively, the same sphere packing arrangement with kissing number 24 can be carried out with smaller 3-spheres of edge-length-diameter, by locating them at the centers and the vertices of the 24-cells. (This is equivalent to locating them at the vertices of a 16-cell honeycomb of unit-edge-length.) In this case the central 3-sphere kisses 24 others at the centers of the cubical facets of the three tesseracts inscribed in the 24-cell. (This is the unique body-centered cubic packing of edge-length spheres of the tesseractic honeycomb.)
Just outside this shell of kissing 3-spheres of diameter 1 is another less dense shell of 24 non-kissing 3-spheres of diameter 1; they are centered in the adjacent 24-cells with which the central 24-cell shares an octahedral facet. The center-to-center distance between one of these spheres and any of its shell neighbors or the central sphere is √2.
Symmetry constructions
There are five different Wythoff constructions of this tessellation as a uniform polytope. They are geometrically identical to the regular form, but the symmetry differences can be represented by colored 24-cell facets. In all cases, eight 24-cells meet at each vertex, but the vertex figures have different symmetry generators.
| Coxeter group | Schläfli symbols | Coxeter diagram | Facets (24-cells) |
Vertex figure (8-cell) |
Vertex figure symmetry order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = [3,4,3,3] | {3,4,3,3} | 8: |
384 | |||
| r{3,3,4,3} | 6: 2: |
96 | ||||
| = [4,3,3,4] | 2r{4,3,3,4} | 4,4: |
64 | |||
| = [4,3,31,1] | 2r{4,3,31,1} | 2,2: 4: |
32 | |||
| = [31,1,1,1] | {31,1,1,1} | 2,2,2,2: |
16 | |||
See also
Other uniform honeycombs in 4-space:
Notes
- The sphere packing problem and the kissing number problem are remarkably difficult and optimal solutions are only known in 1, 2, 3, 8, and 24 dimensions (plus dimension 4 for the kissing number problem).
References
- Coxeter, H.S.M. Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8 p. 296, Table II: Regular honeycombs
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- George Olshevsky, Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs, Manuscript (2006) (Complete list of 11 convex uniform tilings, 28 convex uniform honeycombs, and 143 convex uniform tetracombs) - Model 88
- Klitzing, Richard. "4D Euclidean tesselations". o4o3x3o4o, o3x3o *b3o4o, o3x3o *b3o4o, o3x3o4o3o, o3o3o4o3x - icot - O88
| Space | Family | / / | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | Uniform tiling | {3[3]} | δ3 | hδ3 | qδ3 | Hexagonal |
| E3 | Uniform convex honeycomb | {3[4]} | δ4 | hδ4 | qδ4 | |
| E4 | Uniform 4-honeycomb | {3[5]} | δ5 | hδ5 | qδ5 | 24-cell honeycomb |
| E5 | Uniform 5-honeycomb | {3[6]} | δ6 | hδ6 | qδ6 | |
| E6 | Uniform 6-honeycomb | {3[7]} | δ7 | hδ7 | qδ7 | 222 |
| E7 | Uniform 7-honeycomb | {3[8]} | δ8 | hδ8 | qδ8 | 133 • 331 |
| E8 | Uniform 8-honeycomb | {3[9]} | δ9 | hδ9 | qδ9 | 152 • 251 • 521 |
| E9 | Uniform 9-honeycomb | {3[10]} | δ10 | hδ10 | qδ10 | |
| E10 | Uniform 10-honeycomb | {3[11]} | δ11 | hδ11 | qδ11 | |
| En-1 | Uniform (n-1)-honeycomb | {3[n]} | δn | hδn | qδn | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 |