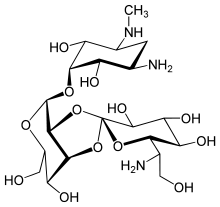
Hygromycin B
Hygromycin B is an antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus. It is an aminoglycoside that kills bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotic cells by inhibiting protein synthesis.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hygromix |
| Other names | O-6-Amino-6-deoxy-L-glycero-D-galacto-heptopyranosylidene-(1-2-3)-O-β-D-talopyranosyl(1-5)-2-deoxy-N3-methyl-D-streptamine , HYG |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.935 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H37N3O13 |
| Molar mass | 527.524 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 160 to 180 °C (320 to 356 °F) (decomp.) |
| |
| |
| | |
History
Hygromycin B was originally developed in the 1950s for use with animals and is still added into swine and chicken feed as an anthelmintic or anti-worming agent (product name: Hygromix). Hygromycin B is produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus, a bacterium isolated in 1953 from a soil sample. Resistance genes were discovered in the early 1980s.[2][3]
Mechanism of action
Hygromycin is active against both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It acts by inhibiting polypeptide synthesis. It stabilizes the tRNA-ribosomal acceptor site, thereby inhibiting translation.
Use in research
In the laboratory it is used for the selection and maintenance of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that contain the hygromycin resistance gene. The resistance gene is a kinase that inactivates hygromycin B through phosphorylation.[4] Since the discovery of hygromycin-resistance genes, hygromycin B has become a standard selection antibiotic in gene transfer experiments in many prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Based on impurity monitor method,[5] four different kinds of impurities are discovered in commercial hygromycin B from different suppliers and toxicities of different impurities to the cell lines are described in the following external links.
Use in plant research
Hygromycin resistance gene is frequently used as a selectable marker in research on plants. In rice Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system, hygromycin is used at about 30–75 mg L−1, with an average of 50 mg L−1. The use of hygromycin at 50 mg L−1 demonstrated highly toxic to non-transformed calli. Thus, it can be efficiently used to select transformants.[6]
Fungus Coniothyrium minitans was transformed with the hygromycin B resistance gene to improve the infection rates of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, a fungal parasite of many crops.[7]
References
- Pittenger RC, Wolfe RN, Hoehn MM, Marks PN, Daily WA, McGUIRE JM (December 1953). "Hygromycin. I. Preliminary studies on the production and biologic activity of a new antibiotic". Antibiotics & Chemotherapy. 3 (12): 1268–1278. PMID 24542808.
- Gritz L, Davies J (November 1983). "Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Gene. 25 (2–3): 179–188. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. PMID 6319235.
- Kaster KR, Burgett SG, Rao RN, Ingolia TD (October 1983). "Analysis of a bacterial hygromycin B resistance gene by transcriptional and translational fusions and by DNA sequencing". Nucleic Acids Research. 11 (19): 6895–6911. doi:10.1093/nar/11.19.6895. PMC 326422. PMID 6314265.
- Rao RN, Allen NE, Hobbs JN, Alborn WE, Kirst HA, Paschal JW (November 1983). "Genetic and enzymatic basis of hygromycin B resistance in Escherichia coli". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 24 (5): 689–695. doi:10.1128/aac.24.5.689. PMC 185926. PMID 6318654.
- Kauffman JS (2009). "Analytical Strategies for Monitoring Residual Impurities Best methods to monitor product-related impurities throughout the production process". BioPharm International. 23: 1–3.
- Pazuki A, Asghari J, Sohani MM, Pessarakli M, Aflaki F (2014). "Effects of Some Organic Nitrogen Sources and Antibiotics on Callus Growth of Indica Rice Cultivars" (PDF). Journal of Plant Nutrition. 38 (8): 1231–1240. doi:10.1080/01904167.2014.983118. S2CID 84495391. Retrieved November 17, 2014.
- Jones EE, Stewart A, Whipps JM (March 2003). "Use of Coniothyrium minitans transformed with the hygromycin B resistance gene to study survival and infection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum sclerotia in soil" (PDF). Mycological Research. 107 (Pt 3): 267–276. doi:10.1017/S0953756203007457. PMID 12825495.