Homocystine
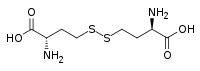
Homocystine is a chemical compound consisting of two homocysteine molecules joined by a disulfide bond.[2] Its relationship with homocysteine is analogous to the relationship between cystine and cysteine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,2′S)-4,4'-Disulfanediylbis(2-aminobutanoic acid) | |
| Other names
L-Homocystine; L-4,4′-Dithiobis(2-aminobutanoic acid) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.966 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16N2O4S2 | |
| Molar mass | 268.35 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 281–284 °C (538–543 °F; 554–557 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "L-Homocystine". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Jackson, Peter; Stanley, Keith; Luzio, J. Paul (1986). "Specific fluorescent detection of disulphide-bridged peptides on thin-layer chromatograms". Biochemical Society Transactions. 14 (4): 750–751. doi:10.1042/bst0140750.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.