Hitachimycin
Hitachimycin, also known as stubomycin, is a cyclic polypeptide produced by Streptomyces that acts as an antibiotic. It exhibits cytotoxic activity against mammalian cells, Gram-positive bacteria, yeast, and fungi, as well as hemolytic activity; this is mediated by changes at the cell membrane and subsequent lysis.[1] Owing to its cytotoxic activity against mammalian cells and tumors, it was first proposed as an antitumor antibiotic.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
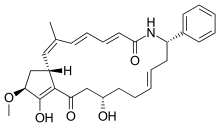
| Formula | C29H35NO5 |
| Molar mass | 477.601 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
As of 2007, it has not been used in a clinical setting.
References
- Komiyama K, Edanami K, Tanoh A, Yamamoto H, Umezawa I (1983). "Studies on the biological activity of stubomycin". J. Antibiot. 36 (3): 301–11. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.36.301. PMID 6833150.
- Umezawa I, Takeshima H, Komiyama K, Koh Y, Yamamoto H, Kawaguchi M (1981). "A new antitumor antibiotic, stubomycin". J. Antibiot. 34 (3): 259–65. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.34.259. PMID 7275806.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.