History of New Plymouth
The city of New Plymouth, New Zealand, has a history that includes a lengthy occupation and residence by Maori, the arrival of white traders and settlers in the 19th century and warfare that resulted when the demands of the two cultures clashed.
European settlement began in the early 1840s at a time when many original Maori inhabitants were absent, either because they had been taken captive by northern Maori warriors or had migrated south to avoid war.[1] The rapid growth of the colonist population, coupled with insatiable demands for land by the New Zealand Company[2] and the dubious practices it employed in purchasing it,[1][3] created friction with local Maori,[4] leading to a war in the 1860s. New Plymouth became a fortified garrison town and its residents suffered hunger and disease.[2] Farming was impeded and immigration and trade came to a halt.[2]
In the aftermath of the war, as improved road and rail links with other towns resulted in a rapid growth of population and economic stability, the town became a major exporting port for dairy produce from the Taranaki district[2] and the administrative centre for Taranaki's petro-chemical industry.
Before 1838: Early contact and inter-tribal conflict
The area where New Plymouth was founded had for centuries been the home for several Māori iwi (tribes). From about 1823 the Maori began having contact with European whalers as well as traders who arrived by schooner to buy flax.[5] In March 1828 Richard "Dicky" Barrett (1807–47) set up a trading post at Ngamotu after arriving on the trading vessel Adventure.[1]

Barrett and his companions were welcomed by Te Āti Awa tribe, who realised that the Europeans, with their muskets and cannon, could assist in their continuing wars with Waikato Maori,[1] as well as providing cloth, food and utensils. Following a bloody encounter at Ngamotu (Moturoa) in 1832, most of the 2000 Āti Awa[1] living near Ngamotu migrated south to the Kāpiti region and Marlborough, leaving about 300 to live on the newly fortified Moturoa and Mikotahi, two of the Sugar Loaf Islands west of Ngamotu. Barrett also left the area. The Waikato Maori returned in 1833, laying siege to the Āti Awa remnant until their surrender almost a year later.
1838-1840: New Zealand Company’s first land purchases
In 1838 the New Zealand Company was formed in England with the purpose of facilitating and encouraging migration from overcrowded cities to New Zealand, selling land to settlers who would work as farmers and labourers. A separate enterprise, the Plymouth Company, was established in Plymouth in February 1840, where it was run under the guidance of agent Thomas Woolcombe. (Many streets in New Plymouth bear the names of the company's directors, including Woolcombe, the Earl of Devon, Thomas Gill, Sir Anthony Buller, Lord Eliot, George Leach, Sir Charles Lemon, Edward St Aubyn, E.W.W. Pendarvis, Lord Courtenay and Hussey Vivian.) The company merged with the New Zealand Company in April 1841 after suffering financial losses through the collapse of its bank.[6]
Barrett returned to Ngamotu in November 1839 aboard the Tory, a vessel carrying out an exploratory expedition for the New Zealand Company. With him was Colonel William Wakefield, a land purchasing agent for the company. A month earlier Wakefield had claimed to have bought 80,000 km2 (20 million acres), comprising one-third of New Zealand, from certain Taranaki and other Maori in Wellington. The area extended from Aotea Harbour near Waikato to Hurunui River in north Canterbury in the South Island.[7]
Barrett, who could speak some Maori,[1] acted as the sole agent for the New Zealand Company, negotiating the purchase of Taranaki land on behalf of the company and on 15 February 1840 – the month the Treaty of Waitangi was signed – a formal Deed of Sale was signed by 75 Maori individuals, with payment made with guns, blankets and other chattels. Many witnesses later testified that Barrett had not read out the deed or adequately explained it at the time of signing. Included in the purchases was a vast area in central Taranaki extending from Mokau to Cape Egmont, and inland to the upper reaches of the Whanganui River including Mt Taranaki; a second deed, the so-called Nga Motu deed, included New Plymouth and all the coastal lands of North Taranaki, including Waitara. The company had already begun on-selling the land to prospective settlers in England with the expectation of securing its title.
J. Houston, writing in Maori Life in Old Taranaki (1965), observed: "Many of the true owners were absent, while others had not returned from slavery to the Waikatos in the north. Thus the 72 chiefs of Ngamotu cheerfully sold lands in which they themselves had no interest, as well as lands wherein they held only a part interest along with several others."[8] The poor understanding by Maori of the nature and extent of the sale – confusion that later led to tension and warfare over land – was not aided by Barrett's translation skills: at subsequent Land Claims Commission hearings in Wellington he was invited to demonstrate his translation ability on a lengthy, legalistic document and was said to have "turned a 1600-word document, written in English, into 115 meaningless Maori ones".[9]
The Waitangi Tribunal noted that Wakefield's purchase, and the company's subsequent sales, were patently invalid: on 14 January 1840 George Gipps, Governor of New South Wales, of which New Zealand was a dependency, had issued a proclamation that purchases of Maori land by private interests after that date would be null and void and not recognised by the Crown.[7] In November the company renounced its initial large-scale "purchases" in a deal that provided it with four acres (1.6ha) for every pound it had spent on colonisation.
1841: Selecting a site
Eleven months later, on 12 December 1840, Frederic Alonzo Carrington, the 32-year-old Chief Surveyor for the Plymouth Company, arrived in Wellington with the task of creating a 44 km2 (11,000 acre) settlement in New Zealand for people of the West Country. Wakefield had already been informed that the Plymouth Company was to take over some of the New Zealand Company land. He urged Carrington to select a site at Ngamotu.[1]
The pressure on Carrington was intense: the first settlers' ship had sailed from Plymouth on 19 November and was already en route to New Zealand. Carrington invited Barrett to join his team and about 9 January 1841, the pair arrived at Ngamotu with a party of assistant surveyors on the barque Brougham, ready to choose a site for the new town.
Carrington inspected the area around Moturoa, then set out by whaleboat to examine Waitara, rowing 5 km up the Waitara River. He returned to Wellington, determined to examine sites in the South Island before making a final decision. Barrett guided the Brougham around barren areas near Nelson, highlighting swampy areas that would be unsuited to settlement.[1] Biographer Angela Caughey claimed Barrett's choice of locations to show Carrington was part of a strategy, motivated by self-interest, to discourage the surveyor from siting New Plymouth in that area instead of Taranaki. On 26 January Carrington informed Wakefield that despite his reservations, he had opted to site his town at Ngamotu.
He wrote to Woolcombe in Plymouth: "I have selected a place where small harbours can be easily made and with trifling expense, close to an abundance of material being on the spot ... I have fixed the town between the rivers Huatoki and Henui ... two or three brooks run through the town and water is to be had in any part of it. The soil, I think, cannot be better. There is much open or fern country and an abundance of fine timber."
Carrington told Woolcombe he had wavered on the site of the town after making two forays up the Waitara River, where he discovered beautiful country. "I once had made up my mind to have the town there," he wrote, "but the almost constant surf upon the bar has caused me to prefer this place ... the New Plymouth Company has the garden of this country; all we want is labour and particularly working oxen."
New Plymouth was laid out over 550 acres (2.2 km2), with additional rural sections proposed along the coast beyond Waitara, covering a total of 68,500 acres (274 km2). By year's end his map of the town showed 2267 sections ready for selection by settlers, with streets, squares, hospitals, schools and parks surrounded by boulevards that separated the town from the suburban districts. For decades, however, Carrington would come under attack from settlers who thought the location of New Plymouth had been poorly chosen because of the lack of a natural harbour.[10]
1841: The first settlers
The first of the town's settlers arrived on the William Bryan, which anchored off the coast on 31 March 1841. In steerage were 21 married couples, 22 single adults and 70 children. George Cutfield, the head of the expedition, wrote a letter home, describing the settlement as "a fine country with a large quantity of flat land, but every part is covered with vegetation, fern, scrub and forest. The fern, on good land, is generally from four to six feet high. There are thousands of acres of this land which will require but a trifling outlay to bring into cultivation."[11]
Temporary housing sites had been provided on Mount Eliot (the present-day site of Puke Ariki museum), and frustrations mounted as settlers were forced to squat in homes built of rushes and sedges through winter, amid flourishing numbers of rats, dwindling food supplies and rising unease over the prospects of a repeat raid by Waikato Maori. The first suburban sections were not available until October, while those who had bought town sections were forced to wait until mid-November.[12]
The second ship, Amelia Thompson, arrived off the Taranaki coast on 3 September and sat off shore for five weeks because its captain feared Ngamotu's reputation as a dangerous shipping area. Its 187 passengers were helped ashore by Barrett and his men over the course of two weeks, each small boatload taking five hours to row from the vessel to the shore. The ship's precious food cargo, including flour and salted meat, was finally brought ashore for New Plymouth's starving residents on 30 September.[1] The loss of its baggage ship, the Regina, which was blown ashore on to a reef, contributed to New Plymouth's reputation as a dangerous area for shipping, discouraging other vessels from berthing.
By one account, settlers were by now "moaning vociferously about having ever left England. Living was a continual battle to shield themselves against the elements and their food supplies against termites, insects and hungry animals. Drunkenness was rife among the labourers in a dreary existence with too little to do. Flour supplies had run out again and there was no likelihood of more until the next boatload of settlers arrived. Te Ati Awa, too were hungry. The co-operative ones had planted more crops than usual, to feed the coming Pakeha, but so many more Europeans had turned up than they expected, that they also were short of food."[1]
As summer arrived, buildings began to be erected, gardens planted and wheat sown. Other ships soon arrived to provide more labour and food supplies: the Oriental (130 passengers) on 7 November 1841; the Timandra (202 passengers) on 23 February 1842; the Blenheim (138 passengers) on 19 November 1842; and the Essex (115 passengers) on 25 January 1843, by which time the town was described as a collection of raupo and pitsawn timber huts housing almost 1000 Europeans.
1842-1866: Land disputes
As settlers arrived, they occupied allotments throughout the coast to beyond Waitara. Many had bought land from the New Zealand Company before the company had purchased the land itself.[7] Tensions between Maori and settlers soon became evident: a party of settlers were driven from land north of the Waitara River in July 1842 and surveyors were obstructed by a group of 100 Maori in 1843. Yet the town continued to thrive: by 1844 it had two flour mills on the Huatoki River and by 1847 it was recorded there were 841 hectares of land in cultivation.
In May 1844 William Spain, who had been appointed Land Claims Commissioner to examine New Zealand Company land claims, began inquiries in Taranaki. The company withdrew its two large land claims of 1840, restricting its claim of "legitimately purchased" land to Nga Motu. Spain ruled in its favour, endorsing its claim to 24,000 ha extending north from the Sugar Loaf Islands, except for pas, burial places and land in cultivation (48ha), native reserves of 10 per cent of the land (2400ha), land for the Wesleyan Mission Station (40ha), and land for Barrett and his family (72ha).
On 2 July Spain wrote to Governor Robert FitzRoy advocating the imposition of a military force to persuade the Maori that everything was in their best interests, or as he put it, to demonstrate "our power to enforce obedience to the laws, and of the utter hopelessness of any attempt on their part at resistance ..." As Spain saw it, New Zealand had been colonised for philanthropic reasons, "to benefit the Natives by teaching them the usefulness of habits of industry, and the advantages attendant upon civilisation."[1]
The award, wrote J.S. Tullett in his history of the city, "was received with great hostility by the Maoris". They wrote letters of strong protest to FitzRoy, who responded with sympathy. After visiting New Plymouth in late 1844, FitzRoy formally set aside Spain's award, acknowledging that the land had been sold without the approval of the absentees. He substituted it for a 1400ha block that became known as the "Fitzroy block", which included the town site and only the immediate surrounding area. Many settlers who had taken up land outside the Fitzroy block were thus forced to move back within its boundaries, fostering widespread hostility towards FitzRoy.
According to the Waitangi Tribunal, the Fitzroy block deal was less a purchase than a "political settlement based on the reality that there were already settlers on the land, who had to be either accepted or driven out ... (the sale was) more akin to a treaty, because Maori also imposed two significant conditions. The first was that settlers still outside the Fitzroy block would be brought back into it and the second was that the settlers would expand no further." A 12-metre high boundary mark, known as the FitzRoy Pole, was later erected on the banks of the Waiwakaiho River to indicate the limit of Pākehā settlement.
Still, however, migrants continued to arrive. In 1847 FitzRoy's bellicose successor, George Grey, responded to settler resentment by pressuring Te Āti Awa leaders to sell more land. Firmly rebuffed, he then turned to individual Maori who were prepared to accept payment. By means of these secret deals Grey bought 10,800ha in five blocks: two were at Tataraimaka and Omata to the south-west of New Plymouth and thus beyond the scope of FitzRoy's accord, but three were in Te Āti Awa territory – the Mangorei or Grey block to the south of the Fitzroy block, plus Cooke's Farm and the Bell Block between New Plymouth and Waitara. The sales triggered fighting among Maori sellers and non-sellers, but the Government succeeded in its aim: by 1859 it claimed to have bought a total of 30,000ha. (The New Zealand Company had surrendered its charter in July 1850, with all its land holdings passing to the Crown).
Grey's determination to secure more land despite Maori opposition had been made clear from the outset: in an 1847 letter to his newly appointed Inspector of Police, the former Sub-Protector of Aborigines Donald McLean, he said that apart from reserves set aside for resident Māori and those returning from the south, "the remaining portion ... should be resumed by the Crown for use by Europeans."[7] In 1852, McLean negotiated with Karira the acquisition of Maori-owned land on the northern flank of Mt. Taranaki.[13] By 1855, the 58th Regiment had been sent to New Plymouth to reassure the settlers.[14]
On 22 February 1860 mounting tensions over the sale of a 600-acre (240 hectare) block of land at Waitara led to the declaration of martial law in Taranaki.[15] Settlers in neighbouring areas of Omata, Bell Block and Waitara began to create stockades to protect their farms.[14] Three weeks later on 17 March, Governor Thomas Gore Browne ordered a military assault on Te Āti Awa chief Wiremu Kīngi and his people at a defensive pā at Waitara.
1860-1866: Wartime crisis
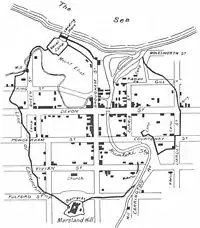
More than 3,500 troops poured into Taranaki, including the 65th, Suffolk, West Yorkshire, 40th and 57th Regiments,[14] during which New Plymouth was transformed into a fortified garrison town. Most women and children were sent to Nelson while the men joined the military forces. For more than two years all farming was carried out under military protection, with farmers returning at nightfall to the security of the many military forts. More than 200 farms were burnt or plundered while the war raged. By July 1860 the town was reported to be in a state of siege. One soldier wrote: "The natives have come close up to the town, murdering every soul who is fool enough to go half a mile outside the ramparts."[16]
Disease, a result of extreme over-crowding, was rife (121 died from disease during the war, 10 times the annual average), food was scarce and the settlers were bordering on despair. There were widespread fears the town would be attacked by Maori warriors, especially when two strong pa were built within 3 km of the town. The wave of immigrants quickly evaporated. In October 1860 a settler wrote: "Little remains of the settlement of Taranaki outside the 50 acre section to which the town is reduced."[17]
The war ended with an uneasy truce after a year, although later skirmishes, described by some historians as a second Taranaki war, later took place.[18]
References
- Angela Caughey (1998). The Interpreter: The Biography of Richard "Dicky" Barrett. David Bateman Ltd. ISBN 1-86953-346-1.
- Ron Lambert & Gail Henry (2000). Taranaki: An Illustrated History. Reed Publishing Ltd. ISBN 0-7900-0727-4.
- Michael King (2003). The Penguin History of New Zealand. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-301867-1.
- Paul Moon (2000). FitzRoy: Governor in Crisis 1843-1845. David Ling Publishing. ISBN 0-908990-70-7.
- Puke Ariki Museum essay Archived 27 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Patricia Burns (1989). Fatal Success: A History of the New Zealand Company. Heinemann Reed. ISBN 0-7900-0011-3.
- Waitangi Tribunal: The Taranaki Report – Kaupapa Tuatahi, Chapter 2
- "Maori Life in Old Taranaki" by J. Houston (1965) as cited by J.S. Tullett, "The Industrious Heart: A History of New Plymouth" (1981), page 8
- Puke Ariki museum essay. Archived 23 April 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Puke Ariki essay on Frederic Carrington". Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 17 August 2007.
- B. Wells, "The History of Taranaki", Chapter 10.
- "Puke Ariki Museum essay on Frederic Carrington". Archived from the original on 13 April 2007. Retrieved 2 May 2007.
- Taonga, New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage Te Manatu. "Karira". teara.govt.nz. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- Prickett, Nigel (1994). "PAKEHA AND MAORI FORTIFICATIONS OF THE FIRST TARANAKI WAR, 1860-61". Records of the Auckland Institute and Museum. 31: 1–87. ISSN 0067-0464.
- Cowan, James (1922). The New Zealand Wars: A History of the Maori Campaigns and the Pioneering Period, Vol. 1, chapter 18, 1845-1864.
- "The New Zealand Wars" by James Belich, Penguin, 1986, pp. 100-114. For troop numbers, see pp. 305.
- Belich, pp. 100-114.
- James Belich, in "The New Zealand Wars" (1986) dismisses as "inappropriate" the description of later conflict as a second Taranaki war (pp. 120).
Further reading
- J. S. Tullett (1981). The Industrious Heart: A History of New Plymouth. New Plymouth District Council.
- Ronald William Mclean (1994). Dicky Barrett: Trader, Whaler, Interpreter. University of Auckland.