HDHD1A
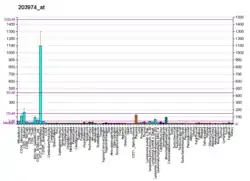
Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain-containing protein 1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDHD1A gene.[5][6][7] It encodes a pseudouridine-5'-phosphatase but can also accommodate other phopshorylated metabolites with a lower affinity.[8][9]
| PUDP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PUDP, DXF68S1E, FAM16AX, GS1, HDHD1A, HDHD1, pseudouridine 5'-phosphatase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 306480 MGI: 1914615 HomoloGene: 8093 GeneCards: PUDP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130021 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000048875 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Salido EC, Yen PH, Koprivnikar K, Yu LC, Shapiro LJ (February 1992). "The human enamel protein gene amelogenin is expressed from both the X and the Y chromosomes". American Journal of Human Genetics. 50 (2): 303–16. PMC 1682460. PMID 1734713.
- Yen PH, Ellison J, Salido EC, Mohandas T, Shapiro L (April 1992). "Isolation of a new gene from the distal short arm of the human X chromosome that escapes X-inactivation". Human Molecular Genetics. 1 (1): 47–52. doi:10.1093/hmg/1.1.47. PMID 1284467.
- "Entrez Gene: HDHD1A haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain containing 1A".
- Preumont A, Rzem R, Vertommen D, Van Schaftingen E (October 2010). "HDHD1, which is often deleted in X-linked ichthyosis, encodes a pseudouridine-5'-phosphatase". The Biochemical Journal. 431 (2): 237–44. doi:10.1042/bj20100174. PMID 20722631.
- Defenouillère Q, Verraes A, Laussel C, Friedrich A, Schacherer J, Léon S (September 2019). "The induction of HAD-like phosphatases by multiple signaling pathways confers resistance to the metabolic inhibitor 2-deoxyglucose" (PDF). Science Signaling. 12 (597): eaaw8000. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aaw8000. PMID 31481524. S2CID 201829818.
Further reading
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R, et al. (January 2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Research. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Suzuki Y, Tsunoda T, Sese J, Taira H, Mizushima-Sugano J, Hata H, et al. (May 2001). "Identification and characterization of the potential promoter regions of 1031 kinds of human genes". Genome Research. 11 (5): 677–84. doi:10.1101/gr.gr-1640r. PMC 311086. PMID 11337467.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.