Cheolli Jangseong
The Cheolli Jangseong or Great Wall of Korea may refer to either of two massive fortifications built between medieval Korea and the Chinese to the west and other tribes to the north. The first is a 7th-century network of military garrisons built by Goguryeo, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. These are now located in Northeast China. The second is an 11th-century wall built by Korea's Goryeo dynasty, now located in North Korea.
| Cheolli Jangseong | |
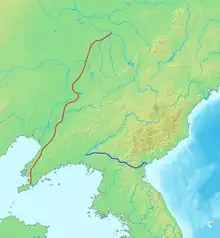 Map showing the location of the two Cheolli Jangseong. | |
| Korean name | |
|---|---|
| Hangul | 천리장성 |
| Hanja | 千里長城 |
| Revised Romanization | Cheolli Jangseong |
| McCune–Reischauer | Ch'ŏlli Changsŏng |
Name
The Korean name Cheolli Jangseong literally means the "Thousand Ri Wall", a reference to the Great Wall of China whose Chinese name is the "Ten-Thousand" or "Countless Li Wall". The second wall is also known in Korean as the Goryeo Jangseong ("Great Wall of Korea").
Goguryeo period
After Goguryeo's victory in the Goguryeo–Sui Wars, in 631 Goguryeo began the fortification of numerous military garrisons after the Tang dynasty, the successor to the Sui in China, began incursions from the northwest.[1] Its construction was supervised by Yeon Gaesomun during the reign of King Yeongnyu. The preparation and coordination was completed in 647, after which Yeon Gaesomun took control of the Goguryeo court in a coup.
The network of fortresses ran for approximately 1000 li in what is now Northeast China, from Buyeoseong (부여성, 扶餘城) (present-day Nong'an County) to the Bohai Bay.
The most important of the garrisons were as follows:
- Bisa (Hangul: 비사성, Hanja: 卑沙城, present-day Jinzhou County in Dalian)
- Geonan (Hangul: 건안성, Hanja: 建安城, present-day Gaizhou)
- Ansi (Goguryeo: 안촌홀 (安寸忽, Hangul: 안시성, Hanja: 安市城, near present-day Haicheng in Anshan Prefecture)
- Baegam (Hangul: 백암성, Hanja: 白巖城, in present-day Dengta County of Liaoyang prefecture)
- Yodong (Hangul: 요동성, Hanja: 遼東城, just to the east of present-day Liaoyang)
- Gaemo (Hangul: 개모성, Hanja: 蓋牟城, present-day Fushun, Shenyang)
- Hyeondo (Hangul: 현도성, Hanja: 玄菟城)
- Shin (Hangul: 신성 Hanja: 新城, present-day Fushun)
- Buyeo (Hangul: 부여성, Hanja: 扶餘城, present-day Nong'an County in Jilin)
Goryeo period
A second Cheolli Jangseong is the stone wall built from 1033 to 1044, during the Goryeo dynasty, in the northern Korean peninsula. It is roughly 1000 li in length, and about 24 feet in both height and width. It connected the fortresses built during the reign of Emperor Hyeonjong, passing through these cities,
- Uiju (의주, 義州)
- Wiwon (위원, 威遠)
- Heunghwa (흥화, 興化)
- Jeongju (정주, 靜州)
- Yeonghae (영해, 寧海)
- Yeongdeok (영덕, 寧德)
- Yeongsak (영삭, 寧朔)
- Jeongyung (정융, 定戎)
- Yeongwon (영원, 寧遠)
- Pyeongno (평로, 平虜)
- Sakju (삭주, 朔州)
- Maengju (맹주, 孟州)
- Unju (운주, 雲州)
- Cheongsae (청새, 淸塞)
- Ansu (안수, 安水)
- Yeongheung (영흥, 永興)
- Yodeok (요덕, 耀德)
- Jeongbyeon (정변, 靜邊)
- and ending at Hwaju (화주, 和州).
King Deokjong ordered Yuso to build the defenses in response to incursions by the Khitan of the northwest and the Jurchen of the northeast. It was completed during the reign of Emperor Jeongjong.
It ran from the mouth of the Yalu River to around Hamheung of present-day North Korea. Remnants are still extant, including in Ŭiju and Chŏngp'yŏng.
See also
References
Citations
- 《三国史记·高句丽本记八》:"荣留王十四年春二月,王动众筑长城,东北自扶余城,西南至海千余里,凡十六年毕功"
Bibliography
- https://web.archive.org/web/20051013072812/http://enc.daum.net/dic100/viewContents.do?
- https://web.archive.org/web/20051013072812/http://enc.daum.net:80/dic100/viewContents.do?
- http://kr.dic.yahoo.com/search/enc/result.html?pk=18576200&p=%C3%B5%B8%AE%C0%E5%BC%BA&field=id&type=enc Archived 2011-05-19 at the Wayback Machine