Grayling Army Airfield
Grayling Army Airfield (ICAO: KGOV, FAA LID: GOV) is a public/military use airport located one nautical mile (1.85 km) northwest of the central business district of Grayling, in Crawford County, Michigan, United States. It is owned by United States Army.[1] The airfield is located 7 miles (11 km) northeast of the main cantonment area of Camp Grayling. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a general aviation facility.[2]
Grayling AAF | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public / military | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | United States Army | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Grayling, Michigan | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 1,158 ft / 353 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 44°40′49″N 084°43′44″W | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
 GOV Location of airport in Michigan  GOV GOV (the United States) | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2019) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
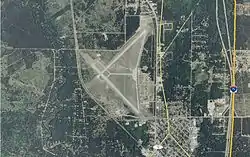
Grayling AAF covers an area of 923 acres (374 ha) at an elevation of 1,158 feet (353 m) above mean sea level. For the 12-month period ending December 31, 2008, the airport had 4,691 aircraft operations, an average of 10 per day: 63% general aviation and 37% military.[1]
Although most U.S. airports use the same three-letter location identifier for the FAA and IATA, this airport is assigned GOV by the FAA but has no designation from the IATA[3] (which assigned GOV to Gove Airport in Australia[4]).
History
Camp Grayling itself has existed since 1913, and the airport was first built in 1977.[5][6]
In 2022, the State of Michigan authorized $1 million to go towards expansions to the airport. Up to 250 square miles of public land could be repurposed for the base in general. The plans were opposed by conservation groups, citing potential environmental and economic impacts.[7][8]
The airport received an additional $100 million in 2023 for modernization efforts, including a goal to address the inequities that female service members face as well as efforts to increase recruitment of women in the area.[6][7]
Military Use
The airport is part of Camp Grayling, the largest National Guard training facility in the United States.[9]
In 2020, the Michigan National Guard officially unveiled the National All-Domain Warfighting Center to train in a variety of operations, including sea, land, air, space, and cyber. The airport is the base for aircraft that use 147,000 acres of multi-use ranges and maneuver courses to accommodate a variety of air-to-air and air-to-ground training exercises. The airport is also a training hub for national guard units from surrounding states.[10][11]
Facilities and aircraft
The airfield consists of two 5000x150-foot runways with 1,200-foot (370 m) overrun and 50-foot (15 m) wide connecting taxiways.
- Runway 5/23: 5,000 x 150 ft (1,524 x 46 m), surface: concrete
- Runway 14/32: 5,005 x 150 ft (1526 x 46 m), surface: asphalt
Runway 5/23 and taxiways A/D/E are closed during the winter months, since there is no snow removal on these surfaces.
The airport is staffed from dawn until dusk. The 29,000-square-foot (2,700 m2) parking area can accommodate fixed-wing aircraft with parking for 100 helicopters, 50 with cement pads with a total of 70 tie downs. The control tower was recently upgraded to a STVS (Small Tower Voice Switch) system with positions in three different locations. There is an 800-square-foot (74 m2) operations building which includes an operations center, flight planning room, safety office, commander's office, and a weather room. Additionally, the airfield contains a 6,400-square-foot (590 m2) maintenance hangar, crash rescue barn and NAVAIDS which include TVOR, NDB, VASI and REIL.
The airport is accessible by road from M-93 and BL I-75, and is close to M-72 and I-75.
The airport has a fixed-base operator that sells fuel and offers various facilities and amenities.[12]
For the 12-month period ending December 29, 2019, the airport had 11,000 airport operations, an average of 30 per day. This includes 56% military and 44% general aviation. For the same time period, there were 9 aircraft based on the field, all single-engine airplanes.[13][14]
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for GOV PDF. Federal Aviation Administration. effective 17 December 2009.
- "List of NPIAS Airports" (PDF). FAA.gov. Federal Aviation Administration. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 25 November 2016.
- KGOV - Grayling, Michigan - Grayling Army Airfield. Great Circle Mapper. Accessed 25 January 2010.
- GOV / YPGV - Gove, Australia. Great Circle Mapper. Accessed 25 January 2010.
- "Camp Grayling". Military History of the Upper Great Lakes. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Armory at Camp Grayling Airfield Undergoes Millions in Renovations". 9 & 10 News. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Camp Grayling facilities to receive upgrade". Up North Live. 13 September 2022. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Conservation groups voice opposition to proposed Camp Grayling expansion". WCMU Public Radio. 9 December 2022. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Camp Grayling". Michigan National Guard. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Michigan National Guard goes all-in on all-domain training". US Army. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "2/147th Bravo Co. Renegades take over Camp Grayling Airfield to Conduct Annual Training". Kentucky National Guard. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "Crawford County Air Terminal". FlightAware. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "AirNav: KGOV — Grayling Army Airfield". AirNav.com. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- "GOV — Grayling Army Airfield". SkyVector Aeronautical Charts. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
External links
- Grayling Army Airfield page at Michigan National Guard website
- Aerial photo as of 30 April 1999 from USGS The National Map
- "Grayling Army Airfield (GOV)" (PDF). (52.4 KiB) page at Michigan Airport Directory
- FAA Terminal Procedures for GOV, effective October 5, 2023
- Resources for this airport:
- FAA airport information for GOV
- AirNav airport information for KGOV
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart, Terminal Procedures