France–Switzerland border
The France–Switzerland border is 572 km (355 mi) long.[1][2] Its current path is mostly the product of the Congress of Vienna of 1815, with the accession of Geneva, Neuchâtel and Valais to the Swiss Confederation, but it has since been modified in detail, the last time being in 2002. Although most of the border, marked with border stones, is unguarded, several checkpoints remain staffed, most notably on busy roads.[3]
| France–Switzerland border | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) The border on the river Doubs at the Saut du Doubs waterfall between Doubs, France and Neuchâtel, Switzerland | |
| Characteristics | |
| Entities | |
| Length | 572 km (355 mi) |
Detailed path
The tripoint where the border meets the Germany–Switzerland border and France–Germany border is on the river Rhine (at 47.5898°N 7.5890°E) north of Basel. A monument has been built near it, known as the Dreiländereck.
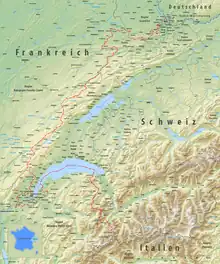

The border runs south of EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg and then towards the southwest, separating the villages of Schönenbuch (Switzerland), Neuwiller (France), Leymen (France) and Rodersdorf (Switzerland).
It then enters the Jura chain, rising above 800 metres of altitude before meeting the La Lucelle river at 460 m, between Roggenburg, Basel-Country and Kiffis (France). It follows the Lucelle as far as Lucelle municipality, running across the grounds of Lucelle Abbey. It then turns north to include the Swiss canton of Jura; it crosses the Doubs river at Brémoncourt, to include the Clos du Doubs region in Switzerland. It meets the Doubs a second time further upstream, at 481 m. From here, it follows the winding course of the river as far as the Lac des Brenets, north of Le Locle, at 756 m.
After passing the Col des Roches at 920 m, the border runs in a south-westerly direction, generally following the Jura ridge, reaching an altitude of 1,288 m (Le Meix Musy). It turns towards the south to include Pontarlier in France and again to the southwest to include Vallorbe and the Lac de Joux in Switzerland. Here it reaches an altitude of 1,377 m, before crossing the Orbe river upstream of Bois-d'Amont.

South of Les Rousses it turns to the south and then southeast, running towards Lake Geneva, rising to 1,400 m at 46.4113°N 6.0866°E, passing south of La Dôle peak. Some 3 km before reaching the lake, the border runs parallel to the shore of Lake Geneva, forming the strip of land ceded by France to Switzerland in 1815 as the canton of Geneva, so that the City of Geneva has a land bridge connecting it to the rest of Switzerland.

The border now encircles the City of Geneva. West of the city, it follows the Rhône for some 6 km, until the westernmost point of Switzerland, at 46.1324°N 5.9559°E. The border passes between Geneva and Annemasse, heading east towards Saint-Cergues; it finally finds Lake Geneva from the south, at Hermance.
The border runs along the centre of Lake Geneva, but makes landfall before reaching the mouth of the Rhône, at Saint-Gingolph, which marks the western end of the Saint-Gingolph–Saint-Maurice railway in Switzerland. A project exists to reuse a now-abandoned line to Évian-les-Bains in France and thereby reconnect the two countries by train on the south shore of Lake Geneva. From here, the border runs south and southeast into the High Alps, forming the western border of the Valais. It passes Les Cornettes de Bise (2,431 m), the Dent de Barme (2,759 m), Petit Ruan (2,846 m), the Pointe des Rosses (2,965 m), the Pointe de la Fenive (2,838 m) and Le Cheval Blanc (2,830 m), placing the Lac du Vieux Émosson in Switzerland. From Grand Perrond (2,672 m), the border descends to 1,130 m, crossing the road from Martigny to Chamonix, before ascending to Les Grandes Otanes (2,656 m), the Aiguille du Tour (3,541 m), the Aiguille d'Argentière (3,898 m), Tour Noir (3,837 m) and finally to the tripoint with the French–Italian and Swiss–Italian borders, at a point just west of Mont Dolent, 45.9227°N 7.0441°E and at 3,752 metres (12,310 ft) altitude.
Border checks

.jpg.webp)
Since Switzerland's accession to the Schengen Area in 2008, there have been no permanent passport controls along the border, although there can be customs controls.
There are two airports near the border which have both Swiss and French passport and customs controls; passengers are free to choose one. These are: EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg which is located in France, but passengers can go to Switzerland without going through French border controls; and Geneva Airport which is located in Switzerland, but passengers can go to France without going through Swiss border controls. The Geneva Airport runway was extended in 1960 after France and Switzerland swapped territories to make this possible.
Road customs control stations
From northeast to south:[4]
- Basel/St. Louis-Autobahn (E25/A35/A3)
- Boncourt/Delle-Autoroute (E27/N1019/A16)
- Col France (D461/20)
- Vallorbe (E23/N57/9)
- Bardonnex (A41/1)
- Thônex-Vallard (A411)
- St-Gingolph (D1005/21)
There are several other roads which cross the border, but without staffed customs controls.
Railway and tram lines over the border
Several railway lines cross the border, as well as three tram lines:
- Basel tram Line 3 was extended to Saint-Louis in France in 2017
- Basel tram Line 10 twice, with one station in France, in Leymen
- Geneva tram Line 17 was extended to Annemasse in France in 2019
See also
References
- "Swisstopo: National boundary". Archived from the original on 2014-10-20. Retrieved 2014-11-27.
- "Suisse". CNIG. Retrieved 2021-03-15.
- "Traité international". Swiss Federal Department of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 24 January 2013.; minor corrections resulting in the exchange of a total of 1,578 square meters of territory.
- "Dienststellenverzeichnis / Liste des offices / Elenco degli uffici / Customs offices". Pwebapps.ezv.admin.ch. Retrieved 2021-03-15.