Ferruginous body
A ferruginous body is a histopathologic finding in interstitial lung disease suggestive of significant asbestos exposure (asbestosis). Asbestos exposure is associated with occupations such as shipbuilding, roofing, plumbing, and construction.
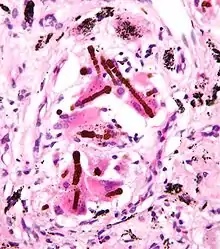
Ferruginous bodies. H&E stain.
They appear as small brown nodules in the septum of the alveolus. Ferruginous bodies are typically indicative of asbestos inhalation (when the presence of asbestos is verified they are called "asbestos bodies"). In this case they are fibers of asbestos coated with an iron-rich material derived from proteins such as ferritin and hemosiderin.[1] Ferruginous bodies are believed to be formed by macrophages that have phagocytosed and attempted to digest the fibers.
Additional images
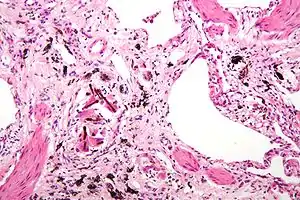 Micrograph of asbestosis with prominent ferruginous bodies. H&E stain.
Micrograph of asbestosis with prominent ferruginous bodies. H&E stain.
References
- "Formation of ferruginous bodies". Archived from the original on 2009-01-30. Retrieved 2007-09-23.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.