São Paulo macrometropolis
The São Paulo Macrometropolis[1] (Portuguese: Macrometrópole Paulista),[2] also known as Expanded Metropolitan Complex[3] is a Brazilian megalopolis that emerged through the existing process of conurbation between the São Paulo's metropolitan areas located around the Greater São Paulo, with more than 30 million inhabitants, or 74 percent of São Paulo State's population,[2] and is one of the most populous urban agglomerations in the world.[4][5][6][7]

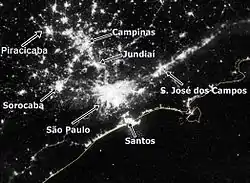
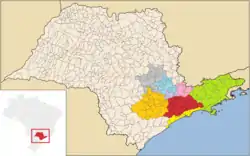
Beyond the Greater São Paulo, the megalopolis encompasses the metropolitan areas of Campinas, Santos, Sorocaba and the Paraíba Valley, and other nearby cities, which include urban agglomerations in the conurbation process, as Jundiaí and Piracicaba. The total population of these areas added to the state capital exceeds 31.5 million inhabitants, or about 75% of the population of the entire state of São Paulo.[6]
The metropolitan complex is the only urban cluster (of agglomerations) of its kind in South America and covers an area of approximately 53 thousand square kilometers, connecting 174 municipalities and retains much of the industrial and economic output of the country.[6]
Divisions
| Region[8][9] | Population | Seat city | Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metropolitan Region of São Paulo | 21,860,000 | São Paulo | 12,310,000 | ||
| 2 | Metropolitan Region of Campinas | 3,300,000 | Campinas | 1,215,000 | ||
| 3 | Metropolitan Region of Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte | 2,550,000 | São José dos Campos | 725,000 | ||
| 4 | Metropolitan Region of Sorocaba | 2,150,000 | Sorocaba | 685,000 | ||
| 5 | Metropolitan Region of Baixada Santista | 1,880,000 | Santos | 435,000 | ||
| 6 | Piracicaba Urban Agglomeration | 1,500,000 | Piracicaba | 410,000 | ||
| 7 | Jundiaí Urban Agglomeration | 825,000 | Jundiaí | 425,000 | ||
| 8 | Regional Unit of Bragança Paulista city | 480,000 | Bragança Paulista | 170,000 | ||
| São Paulo Macrometropolis | 34,500,000 | |||||
Biggest Municipalities
1,000,000+
500,000–999,999
- São Bernardo do Campo (São Paulo) (822,242)
- São José dos Campos(Vale do Paraíba) (795,992)
- Santo André (São Paulo) (712,749)
- Osasco (São Paulo) (696,382)
- Sorocaba (Sorocaba) (652,481)
200,000–499,999
- Mauá (São Paulo) (457,696)
- Santos (Baixada Santista) (434,359)
- Mogi das Cruzes (São Paulo) (429,321)
- Diadema (São Paulo) (415,180)
- Jundiaí (Jundiaí) (405,740)
- Carapicuíba (São Paulo) (394,465)
- Piracicaba (Piracicaba) (394,419)
- São Vicente (Baixada Santista) (357,989)
- Itaquaquecetuba (São Paulo) (356,774)
- Guarujá (Baixada Santista) (313,421)
- Taubaté (Vale do Paraíba) (305,174)
- Limeira (Piracicaba) (298,701)
- Praia Grande (Baixada Santista) (304,705)
- Suzano (São Paulo) (288,056)
- Taboão da Serra (São Paulo) (275,948)
- Sumaré (Campinas) (269,522)
- Barueri (São Paulo) (264,935)
- Embu das Artes (São Paulo) (264,448)
- Indaiatuba (Campinas) (235,367)
- Cotia (São Paulo) (233,696)
- Americana (Campinas) (231,621)
- Jacareí (Vale do Paraíba) (228,214)
- Itapevi (São Paulo) (226,488)
- Hortolândia (Campinas) (219,039)
- Rio Claro (Piracicaba) (201,473)
100,000–199,999
- Santa Bárbara d'Oeste (Campinas) (191,074)
- Ferraz de Vasconcelos (São Paulo)(176,000)
- Itu (Sorocaba) (170,157)
- Bragança Paulista (Jundiaí) (164,000)
- Itapetininga (Sorocaba) (160,000)
- Itapecerica da Serra (São Paulo) (159,000)
- Pindamonhangaba (Vale do Paraíba) (154,082)
- Francisco Morato (Jundiaí) (155,000)
- São Caetano do Sul (São Paulo) (151,000)
- Mogi Guaçu (Campinas) (149,296)
- Atibaia (Jundiaí) (139,683)
- Franco da Rocha (Jundiaí) (129,000)
- Cubatão (Baixada Santista) (127,000)
- Valinhos (Campinas) (122,000)
- Araras (Piracicaba) (121,282)
- Votorantim (Sorocaba) (119,000)
- Tatuí (Sorocaba) (118,000)
- Várzea Paulista (Jundiaí) (116,000)
- Salto (Sorocaba) (116,000)
- Guaratinguetá (Vale do Paraíba) (114,000)
- Itatiba (Jundiaí) (114,000)
- Poá (São Paulo) (112,481)
- Ribeirão Pires (São Paulo) (112,020)
- Santana de Parnaíba (São Paulo) (111,000)
- Jandira (São Paulo) (110,000)
- Caraguatatuba (Vale do Paraíba) (107,000)
- Itanhaém (Baixada Santista) (100,496)
- Paulínia (Campinas) (100,000)
See also
Notes and references
- Zioni, Silvana; Silva, Gerardo; Passarelli, Silvia Helena (2011), Structuring dynamics of São Paulo macrometropolis: perspectives and strategies for rail infrastructure re-functioning.ZIONI, ; , ; , .
- "Macrometrópole Paulista". Emplasa. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- "Os eixos de desenvolvimento e a estruturação urbano-industrial do estado de São Paulo, Brasil". www.ub.es. Retrieved 2010-07-04.
- Eugenio Fernandes Queiroga (May 2005). "A Megalópole do Sudeste Brasileiro: a formação de uma nova entidade urbana para além das noções de macro-metrópole e de complexo metropolitano expandido". Associação Nacional de Pós-Graduação e Pesquisa em Planejamento Urbano e Regional. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- "World Gazetteer – Welt: Ballungsräume". Archived from the original on September 30, 2007. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- Diego Zanchetta (2008-08-03). "A primeira macrometrópole do hemisfério sul". O Estado de S. Paulo. Archived from the original on June 25, 2011. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - Secretaria de Planamento de São Paulo, ed. (2007). "CAPÍTULO II DESENVOLVIMENTO REGIONAL E METROPOLITANO" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-04-04.
- "IBGE releases population estimates for municipalities in 2016". IBGE. 2016-08-30. Retrieved 2016-08-30.
- "Estimativas populacionais para os municípios e para as Unidades da Federação brasileiros em 01.07.2016". IBGE. 2016-08-30. Retrieved 2016-08-30.