Efrapeptin
Efrapeptins are peptides produced by fungi in the genus Tolypocladium that have antifungal, insecticidal, and mitochondrial ATPase inhibitory activities.[1] They are produced via a biosynthetic pathway similar to but simpler than the Ciclosporin pathway, with nonribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) and/or polyketide synthase (PKS) being the key elements.[2]
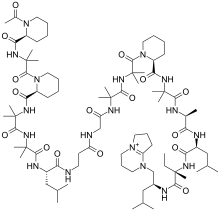
Efrapeptin F is a type of Efrapeptin.
The amino acid sequences of efrapeptins are:
- Efrapeptin F: Ac-Pip-Aib-Pip-Aib-Aib-Leu-bAla-Gly-Aib-Aib-Pip-Aib-Ala-Leu-Iva-Unk
- Efrapeptin G: Ac-Pip-Aib-Pip-Iva-Aib-Leu-bAla-Gly-Aib-Aib-Pip-Aib-Ala-Leu-Iva-Unk
- Aib: 2-methylalanine; Iva: 2-ethylalanine; Unk: does not match to a known amino acid
References
- Krasnoff, Stuart B; Gupta, Sandeep (1991). "Identification and directed biosynthesis of efrapeptins in the fungus Tolypocladium geodes gams (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes)". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 17 (10): 1953–1962. doi:10.1007/BF00992580. PMID 24258490. S2CID 6464931.
- Bushley, Kathryn E.; Raja, Rajani; Jaiswal, Pankaj; Cumbie, Jason S.; Nonogaki, Mariko; Boyd, Alexander E.; Owensby, C. Alisha; Knaus, Brian J.; Elser, Justin; Miller, Daniel; Di, Yanming; McPhail, Kerry L.; Spatafora, Joseph W.; Heitman, Joseph (20 June 2013). "The Genome of Tolypocladium inflatum: Evolution, Organization, and Expression of the Cyclosporin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster". PLOS Genetics. 9 (6): e1003496. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003496. PMC 3688495. PMID 23818858.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Efrapeptins.
- CID 3081780 from PubChem - Efrapeptin F
- Efrapeptin F at ChemSpider
- CID 44566255 from PubChem - Efrapeptin G
- Efrapeptin G at ChemSpider
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.