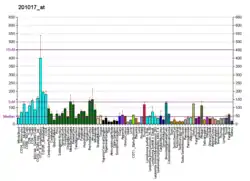
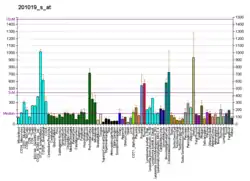
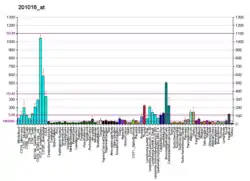
EIF1AX
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-chromosomal (eIF1A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF1AX gene.[5][6][7] This gene encodes an essential eukaryotic translation initiation factor. The protein is a component of the 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC), which mediates the recruitment of the small 40S ribosomal subunit to the 5' cap of messenger RNAs.[7]
| EIF1AX | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | EIF1AX, EIF1A, EIF1AP1, EIF4C, eIF-1A, eIF-4C, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A X-linked | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300186 MGI: 95298 HomoloGene: 20364 GeneCards: EIF1AX | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
eIF1A is a small protein (17 kDa in budding yeast) and a component of the 43S preinitiation complexes (PIC). eIF1A binds near the ribosomal A-site, in a manner similar to the functionally related bacterial counterpart IF1.[8]
Clinical significance
Mutations in this gene have been recurrently seen associated to cases of uveal melanoma with disomy 3.[9] eIF1A is mutated in thyroid cancers.[10]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173674 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000057561 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Dever TE, Wei CL, Benkowski LA, Browning K, Merrick WC, Hershey JW (Feb 1994). "Determination of the amino acid sequence of rabbit, human, and wheat germ protein synthesis factor eIF-4C by cloning and chemical sequencing". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (5): 3212–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)41850-3. PMID 8106356.
- Lahn BT, Page DC (Oct 1997). "Functional coherence of the human Y chromosome". Science. 278 (5338): 675–80. Bibcode:1997Sci...278..675L. doi:10.1126/science.278.5338.675. PMID 9381176.
- "Entrez Gene: EIF1AX eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked".
- Fraser, Christopher S. (2015). "Quantitative studies of mRNA recruitment to the eukaryotic ribosome". Biochimie. 114: 58–71. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2015.02.017. PMC 4458453. PMID 25742741.
- Martin M, Maßhöfer L, Temming P, Rahmann S, Metz C, Bornfeld N, van de Nes J, Klein-Hitpass L, Hinnebusch AG, Horsthemke B, Lohmann DR, Zeschnigk M (Aug 2013). "Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic mutations in EIF1AX and SF3B1 in uveal melanoma with disomy 3". Nature Genetics. 45 (8): 933–6. doi:10.1038/ng.2674. PMC 4307600. PMID 23793026.
- Xu, Yichen; Ruggero, Davide (2020-03-09). "The Role of Translation Control in Tumorigenesis and Its Therapeutic Implications". Annual Review of Cancer Biology. 4 (1): 437–457. doi:10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030419-033420. ISSN 2472-3428.
- Mingot JM, Kostka S, Kraft R, Hartmann E, Görlich D (Jul 2001). "Importin 13: a novel mediator of nuclear import and export". The EMBO Journal. 20 (14): 3685–94. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.14.3685. PMC 125545. PMID 11447110.
Further reading
- Battiste JL, Pestova TV, Hellen CU, Wagner G (Jan 2000). "The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function". Molecular Cell. 5 (1): 109–19. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80407-4. PMID 10678173.
- Choi SK, Olsen DS, Roll-Mecak A, Martung A, Remo KL, Burley SK, Hinnebusch AG, Dever TE (Oct 2000). "Physical and functional interaction between the eukaryotic orthologs of prokaryotic translation initiation factors IF1 and IF2". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (19): 7183–91. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.19.7183-7191.2000. PMC 86272. PMID 10982835.
- Mingot JM, Kostka S, Kraft R, Hartmann E, Görlich D (Jul 2001). "Importin 13: a novel mediator of nuclear import and export". The EMBO Journal. 20 (14): 3685–94. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.14.3685. PMC 125545. PMID 11447110.
- Sørensen HP, Hedegaard J, Sperling-Petersen HU, Mortensen KK (May 2001). "Remarkable conservation of translation initiation factors: IF1/eIF1A and IF2/eIF5B are universally distributed phylogenetic markers". IUBMB Life. 51 (5): 321–7. doi:10.1080/152165401317190842. PMID 11699879. S2CID 45654480.
- Bohnsack MT, Regener K, Schwappach B, Saffrich R, Paraskeva E, Hartmann E, Görlich D (Nov 2002). "Exp5 exports eEF1A via tRNA from nuclei and synergizes with other transport pathways to confine translation to the cytoplasm". The EMBO Journal. 21 (22): 6205–15. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf613. PMC 137205. PMID 12426392.
- Olsen DS, Savner EM, Mathew A, Zhang F, Krishnamoorthy T, Phan L, Hinnebusch AG (Jan 2003). "Domains of eIF1A that mediate binding to eIF2, eIF3 and eIF5B and promote ternary complex recruitment in vivo". The EMBO Journal. 22 (2): 193–204. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg030. PMC 140105. PMID 12514125.
- Marintchev A, Kolupaeva VG, Pestova TV, Wagner G (Feb 2003). "Mapping the binding interface between human eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B: a new interaction between old partners". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (4): 1535–40. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.1535M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0437845100. PMC 149867. PMID 12569173.
- Agate RJ, Choe M, Arnold AP (Feb 2004). "Sex differences in structure and expression of the sex chromosome genes CHD1Z and CHD1W in zebra finches". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 21 (2): 384–96. doi:10.1093/molbev/msh027. PMID 14660691.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Kim S, Kim GJ, Miyoshi H, Moon SH, Ahn SE, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Cha KY, Chung HM (Aug 2007). "Efficiency of the elongation factor-1alpha promoter in mammalian embryonic stem cells using lentiviral gene delivery systems". Stem Cells and Development. 16 (4): 537–45. doi:10.1089/scd.2006.0088. PMID 17784828.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.