Dorand AR
The Dorand AR.1 was a World War I French two-seat observation biplane aircraft used by the French Air Force, the American Expeditionary Force and, in small numbers, by Serbian Aviation.
| Dorand AR.1 and AR.2 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Dorand AR.1 | |
| Role | Reconnaissance aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Section Technique de l'Aéronautique |
| Designer | Georges Lèpere and Émile Dorand |
| First flight | 1916 |
| Introduction | 1917 |
| Primary users | French Air Force American Expeditionary Force Serbian Aviation |
Design and development
Designed by Captain Georges Lepère of the STAé to replace the obsolescent Farman F.40 pusher aircraft, Dorand AR-series were two-seater reconnaissance biplanes that were named after the STAé director, Lt. Col. Dorand. They were characterized by backward-staggered two-bay wings and angular all-moving tail surfaces. The pilot sat beneath the leading edge of the upper wing, with the observer's cockpit being under the trailing edge, and there were cut-outs in both wings to improve the latter's field of view. Rather unusually for a single-engine tractor biplane of the era, the lower wing was not directly attached to the fuselage, instead being somewhat below it, supported by struts.
Production of these aircraft began in a state-owned French Army Aircraft Establishment (or S.T.Aé.) factory at Chalais-Meudon, near Paris, after flight testing had been completed in the autumn 1916.
Operational history
.gif)
The first of the thirteen squadrons which flew Dorands on the Western Front received their aircraft in the spring 1917. Five other French squadrons used the type on the Italian Front. These aircraft were withdrawn from the combat units in early 1918.
In 1917 the American Expeditionary Force ordered the Renault-engined varieties of the Dorand, the first of 22 AR.1s being delivered in December 1917 and the first of 120 AR.2s in following February. The Americans operated these types on the Western Front for the first half 1918, until replacing them with the Salmson 2. After being retired from fighting duties, the surviving examples were used as trainers.

A small number of Dorand AR.1s were also supplied to Kingdom of Serbia, which operated these aircraft in four squadrons from April 1918 onwards. While the Dorand AR-types didn't have a particularly distinguished career in either French or American service, having a rather mediocre performance for a late-war daytime reconnaissance aircraft and suffering from having low priority for engine supplies, it is a testimony to the general soundness of the design that after the war, many AR.1s and AR.2s appeared in the French civil register, being used as 2/3-passenger transports by companies like Compagnie Aérienne Française and Réseau Aérien Transafricain. Private users found the aircraft useful for training and joy-flights as well.
Variants
There were following variants of the design:
- AR.1 A2 160
- Early production version powered by a 120 kW (160 hp) Renault 8Gd engine
- AR.1 A2 200
- Mid production version powered by a 150 kW (200 hp) Renault 8Gdy engine
- AR.1 A2 190
- Late production version powered by a 140 kW (190 hp) Renault 8Gd engine
- ARL.1 A2
- AR.1s modified with a 180 kW (240 hp) Lorraine-Dietrich engine
- AR.1 D2
- Trainers powered by Renault 12d air-cooled V-12s.[1]
- AR.2 A2
- 2nd production version powered by a 148 kW (199 hp) Renault 8Ge engine
- ARL.2 A2
- AR.2s modified with a 180 kW (240 hp) Lorraine-Dietrich engine
The AR.1 and ARL.1 had a wing span of 13.27 m (43.5 ft), and used frontal radiators, while the AR.2 and ARL.2 were slightly smaller aircraft, with a wingspan of 12.0 m (39.4 ft), the wing area being only 45 square metres, and wing mounted radiators. All these types had "A.2" added to their names in French service, indicating that they were two-seater reconnaissance aircraft.
Operators
- Operated a single example.
Specifications (AR.1)
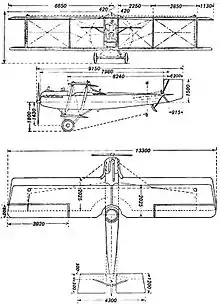
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1919 [2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 (pilot and observer)
- Length: 8.225 m (27 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 13.3 m (43 ft 8 in)
- Wing area: 50.36 m2 (542.1 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 890 kg (1,962 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,330 kg (2,932 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 170 L (37 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 1 × Renault 8Gdy V-8 water-cooled piston engine, 150 kW (200 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed wooden fixed pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 148 km/h (92 mph, 80 kn) at 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
- Endurance: 3 hours
- Service ceiling: 5,500 m (18,000 ft)
- Wing loading: 26.4 kg/m2 (5.4 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.143 kW/kg (0.087 hp/lb)
Armament
- Guns: ** 1 × fixed forward-firing 7.7 mm (.303 in) Vickers machine gun for the pilot
- 1 or 2 × 7.7 mm (.303 in) Lewis gun(s) on a movable mounting for the observer
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References
- Davilla, Dr. James J.; Soltan, Arthur M. (January 2002). French aircraft of the First World War. Flying Machines Press. pp. 37–46. ISBN 1891268090.
- Grey, C.G. (1969). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1919 (Facsimile ed.). London: David & Charles (Publishers) Limited. pp. 229a–231a. ISBN 07153-4647-4.
- Munson, Kenneth - Bombers, Patrol and Reconnaissance Aircraft 1914 - 1919 ISBN 0-7537-0918-X
- Owers, Colin - The French AR Biplanes, Windsock International Vol 6 #5 (Sept-Oct 1990) & Vol 7 #1 (Jan-Feb 1991)
External links
For the photographs of the Dorands see following pages: