Diphenylphosphite
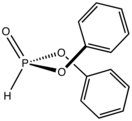
Diphenylphosphite is a diorganophosphite with the formula (C6H5O)2P(O)H. The molecule is tetrahedral. It is a colorless viscous liquid. The compounds can be prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with phenol. Many analogues can be prepared similarly. One illustrative reaction, diphenylphosphite, aldehydes, and amines react to afford aminophosphonates (Kabachnik–Fields reaction).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diphenyl phosphonate | |
| Other names
Phosphonic acid, diphenyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.911 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H11O3P | |
| Molar mass | 234.191 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.2268 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 12 °C (54 °F; 285 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Bhagat, Srikant; Chakraborti, Asit K. (2007). "An Extremely Efficient Three-Component Reaction of Aldehydes/Ketones, Amines, and Phosphites Kabachnik-Fields reaction for the Synthesis of α-Aminophosphonates Catalyzed by Magnesium Perchlorate". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (4): 1263–1270. doi:10.1021/jo062140i. PMID 17253748.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.