Dimethoxytrityl
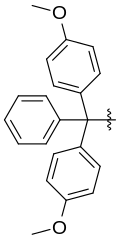
Dimethoxytrityl, often abbreviated DMT, is a protecting group widely used for protection of the 5'-hydroxy group in nucleosides, particularly in oligonucleotide synthesis.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-phenylmethyl radical | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H19O2 | |
| Molar mass | 303.4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is usually bound to a molecule, but can exist as a stable cation in solution, where it appears bright orange.[2]
References
- Krotz, Achim; Cole, Douglas; Ravikumar, Vasulinga (1999). "Dimethoxytrityl Removal in Organic Medium: Efficient Oligonucleotide Synthesis Without Chlorinated Solvents". Nucleosides and Nucleotides. 18 (6–7): 1207–1209. doi:10.1080/07328319908044664.
- "Dimethoxytrityl/DMT (Orange you glad you protected that alcohol?)". Molecule of the Day. 2006-09-05. Retrieved 2022-05-03.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.